Abstract
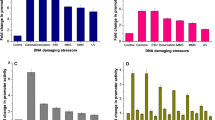
Deinococcus indicus is a novel bacteria isolated from West Bengal, India known for its UV radiation and heavy metal tolerance. Since, this organism is reported from a region known for heavy metal contamination and earlier investigations demonstrated its radiation resistance, our study focused on the multiple stress responsive and DNA repair mechanisms. Though, most of the members of the genus Deinococcus are Gram positive cocci, D. indicus postures Gram negative rod shaped cells. Hence, the objectives were framed precisely to understand DNA repair pathway and stress responsive genes expression with a broader perspective. Based on available whole genome sequence of D. indicus, quantitative real time PCR (qPCR) was done to determine the expression pattern of multiple stress responsive genes upon various environmental extremities. Among them, UV responsive genes like UvrD and UvsE showed elevated expression when subjected to UV-C radiation at different time intervals. Similarly, when supplemented with arsenic and chromium, ArsR and ArsB exhibited considerably higher level of expression. While all the genes were subsequently analyzed in-silico, depicted that most of them were with N-glycosylation site, GPI anchor sites, N-terminal trans-membrane helix region besides putative signal peptides. Overall, this study opined the functional information on stress tolerance genes that aid to understand the DNA damage recovery mechanism towards elucidation of DNA repair pathways.
Graphic abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidadi, H., Sany, S. B. T., Oftadeh, B. Z. G., Mohamad, T., Shamszade, H., & Fakhari, M. (2019). Health risk assessments of arsenic and toxic heavy metal exposure in drinking water in northeast Iran. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, 24(1), 59.
Bentchikou, E., Servant, P., Coste, G., & Sommer, S. (2010). A major role of the RecFOR pathway in DNA double-strand-break repair through ESDSA in Deinococcusradiodurans. PLoS Genetics, 6(1), e1000774.
Bernstein, K. A., Gangloff, S., & Rothstein, R. (2010). The RecQ DNA helicases in DNA repair. Annual Review of Genetics, 44, 393–417.
Bowman, S. M., Piwowar, A., Vierula, J., & Free, S. J. (2006). Mutational analysis of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor pathway demonstrates that GPI-anchored proteins are required for cell wall biogenesis and normal hyphal growth in Neurosporacrassa. Eukaryotic Cell, 5(3), 587–600.
Chauhan, D., Srivastava, P. A., Yennamalli, R. M., & Priyadarshini, R. (2017). Draft genome sequence of Deinococcus indicus DR1, a novel strain isolated from a freshwater wetland. Genome Announcements, 5(31), e00754-17.
Chen, A., Contreras, L. M., & Keitz, B. K. (2017). Imposed environmental stresses facilitate cell-free nanoparticle formation by Deinococcusradiodurans. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 83(18), e00798-e817.
Craney, A., & Romesberg, F. E. (2017). Stable Signal Peptides and the Response to Secretion Stress in Staphylococcus aureus. MBio, 8(6), e01507-e1517.
Das, D., Tripsianes, K., Jaspers, N. G., Hoeijmakers, J. H., Kaptein, R., Boelens, R., & Folkers, G. E. (2008). The HhH domain of the human DNA repair protein XPF forms stable homodimers. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 70(4), 1551–1563.
Dugo, M. A., Han, F., & Tchounwou, P. B. (2012). Persistent polar depletion of stratospheric ozone and emergent mechanisms of ultraviolet radiation-mediated health dysregulation. Reviews on Environmental Health, 27(2–3), 103–116.
Earl, A. M., Rankin, S. K., Kim, K. P., Lamendola, O. N., & Battista, J. R. (2002). Genetic evidence that the uvsE gene product of Deinococcus radiodurans R1 is a UV damage endonuclease. Journal of Bacteriology, 184(4), 1003–1009.
Gamboa-Loira, B., Cebrian, M. E., Franco-Marina, F., & Lopez-Carrillo, L. (2017). Arsenic metabolism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Environmental research, 156, 551–558.
Gršković, B., Zrnec, D., Popović, M., Petek, M. J., Primorac, D., & Mršić, G. (2013). Effect of ultraviolet C radiation on biological samples. Croatian Medical Journal, 54(3), 263–271.
Iost, I., Bizebard, T., & Dreyfus, M. (2013). Functions of DEAD-box proteins in bacteria: current knowledge and pending questions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 1829(8), 866–877.
Iost, I., & Dreyfus, M. (2006). DEAD-box RNA helicases in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Research, 34(15), 4189–4197.
Kang, J., & Blaser, M. J. (2006). UvrD helicase suppresses recombination and DNA damage-induced deletions. Journal of Bacteriology, 188(15), 5450–5459.
Keller, K. L., Overbeck-Carrick, T. L., & Beck, D. J. (2001). Survival and induction of SOS in Escherichia coli treated with cisplatin, UV-irradiation, or mitomycin C are dependent on the function of the RecBC and RecFOR pathways of homologous recombination. Mutation Research/DNA Repair, 486(1), 21–29.
Kim, T. H., Seo, J. W., Hong, Y. S., & Song, K. H. (2017). Case–control study of chronic low-level exposure of inorganic arsenic species and non-melanoma skin cancer. The Journal of Dermatology, 44(12), 1374–1379.
Kulkarni, R. R., Shaiwale, N. S., Deobagkar, D. N., & Deobagkar, D. D. (2015). Synthesis and extracellular accumulation of silver nanoparticles by employing radiation-resistant Deinococcusradiodurans, their characterization, and determination of bioactivity. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 10, 963.
Manning, A. J., & Kuehn, M. J. (2013). Functional advantages conferred by extracellular prokaryotic membrane vesicles. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 23(1–2), 131–141.
Martin, K. L., & Smith, T. K. (2006). The glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) biosynthetic pathway of bloodstream-form Trypanosomabrucei is dependent on the de novo synthesis of inositol. Molecular Microbiology, 61(1), 89–105.
Mogk, A., Huber, D., & Bukau, B. (2011). Integrating protein homeostasis strategies in prokaryotes. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 3(4), a004366.
Mohania, D., Chandel, S., Kumar, P., Verma, V., Digvijay, K., Tripathi, D., et al. (2017). Ultraviolet radiations: Skin defense-damage mechanism. Ultraviolet Light in Human Health, Diseases and Environment (pp. 71–87). Cham: Springer.
Nielsen, K. K., & Boye, M. (2005). Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analysis of expression stability of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae housekeeping genes during in vitro growth under iron-depleted conditions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(6), 2949–2954.
Paulino-Lima, I. G., Fujishima, K., Navarrete, J. U., Galante, D., Rodrigues, F., Azua-Bustos, A., & Rothschild, L. J. (2016). Extremely high UV-C radiation resistant microorganisms from desert environments with different manganese concentrations. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 163, 327–336.
Rehman, K., Fatima, F., Waheed, I., & Akash, M. S. H. (2018). Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 119(1), 157–184.
Roy, S. (2017). Impact of UV radiation on genome stability and human health. Ultraviolet Light in Human Health, Diseases and Environment (pp. 207–219). Cham: Springer.
Sher, S., & Rehman, A. (2019). Use of heavy metals resistant bacteria—a strategy for arsenic bioremediation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103(15), 6007–6021.
Smedley, P. L., Nicolli, H. B., Macdonald, D. M. J., Barros, A. J., & Tullio, J. O. (2002). Hydrogeochemistry of arsenic and other inorganic constituents in groundwaters from La Pampa. Argentina. Applied Geochemistry, 17(3), 259–284.
Suresh, K., Reddy, G. S. N., Sengupta, S., & Shivaji, S. (2004). Deinococcusindicus sp. nov., an arsenic-resistant bacterium from an aquifer in West Bengal, India. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54(2), 457–461.
Suvarapu, L. N., & Baek, S. O. (2017). Determination of heavy metals in the ambient atmosphere: A review. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 33(1), 79–96.
Walsh, N. P., Alba, B. M., Bose, B., Gross, C. A., & Sauer, R. T. (2003). OMP peptide signals initiate the envelope-stress response by activating DegS protease via relief of inhibition mediated by its PDZ domain. Cell, 113(1), 61–71.
Wang, W., & Chan, J. Y. (2006). Nrf1 is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane by an N-terminal transmembrane domain Inhibition of nuclear translocation and transacting function. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281(28), 19676–19687.
Wilson, T., & Carson, J. (2001). Rapid, high-throughput extraction of bacterial genomic DNA from selective-enrichment culture media. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 32(5), 326–330.
Yatera, K., Morimoto, Y., Ueno, S., Noguchi, S., Kawaguchi, T., Tanaka, F., et al. (2018). Cancer risks of hexavalent chromium in the respiratory tract. Journal of UOEH, 40(2), 157–172.
Yuan, W., Yang, N., & Li, X. (2016). Advances in understanding how heavy metal pollution triggers gastric cancer. BioMed Research International, 2016, 1–10.
Acknowledgement
The author Anand Raj. D would like to acknowledge Bharathiar University for his Fellowship vide URF: C2/2023/2019. The authors are grateful to University Grant Commission (UGC, Govt of India) for the support provided to establish infrastructure in the Department of Biotechnology grant vide UGC/SAP/No.F.3-20/2013, through Special Assistance Program (SAP) and Department of Science and technology (DST) towards Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure in Universities and Higher Educational Institutions vide (FIST) and DST-PURSE phase-II vide BU/DST-PURSE/2017/28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.R.D. and P.S.R. conceived and designed the research; A.R.D. and B.V. carried out experiments and drafting the article; P.S.R. critically evaluated the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanapal, A.R., Venkidasamy, B. & Solai Ramatchandirane, P. Molecular characterization of stress tolerance genes associated with D. indicus strain under extreme environment conditions. Environ Geochem Health 43, 4905–4917 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00788-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00788-9