Abstract
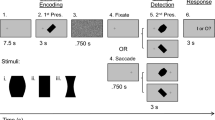
Allocentric and egocentric are two types of spatial coding. Previous studies reported the dorsal attention network’s involvement in both types. To eliminate possible paradigm-specific confounds in the results, this study employed fine-grained cue-to-target paradigm to dissociate allocentric (aSC) and egocentric (eSC) spatial coding. Twenty-two participants completed a custom visuospatial task, and changes in the concentration of oxygenated hemoglobin (O2-Hb) were recorded using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator-regularized principal component (LASSO-RPC) algorithm was used to identify cortical sites that predicted the aSC and eSC conditions’ reaction times. Significant changes in O2-Hb concentration in the right inferior parietal lobule (IPL) and post-central gyrus regions were common in both aSC and eSC. Results of inter-channel correlations further substantiate cortical activities in both conditions were predominantly over the right parieto-frontal areas. Together with right superior frontal gyrus areas be the reaction time neural correlates, the results suggest top-down attention and response-mapping processes are common to both spatial coding types. Changes unique to aSC were in clusters over the right intraparietal sulcus, right temporo-parietal junction, and left IPL. With the left pre-central gyrus region, be the reaction time neural correlate, aSC is likely to involve more orienting attention, updating of spatial information, and object-based response selection and inhibition than eSC. Future studies will use other visuospatial task designs for testing the robustness of the findings on spatial coding processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amso D, Scerif G (2015) The attentive brain: insights from developmental cognitive neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(10):606–619. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn4025
Au BK (2014) Aging effect on egocentric and allocentric frames of reference in visual attention: an event-related potential (ERP) study. (PhD dissertation). The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong
Barrett DJ, Bradshaw MF, Rose D, Everatt J, Simpson PJ (2001) Reflexive shifts of covert attention operate in an egocentric coordinate frame. Perception 30(9):1083–1091
Burgess N (2006) Spatial memory: how egocentric and allocentric combine. Trends Cogn Sci 10(12):551–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2006.10.005
Burgess N (2008) Spatial cognition and the brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1124(1):77–97. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1440.002
Castiello U (2005) The neuroscience of grasping. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(9):726–736. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1744
Chang PH, Lee S-H, Koo K-M, Lee S-H, Jin S-H, Yeo SS et al (2014) The cortical activation pattern by a rehabilitation robotic hand: a functional NIRS study. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00049
Chen Q, Weidner R, Weiss PH, Marshall JC, Fink GR (2012) Neural interaction between spatial domain and spatial reference frame in parietal-occipital junction. J Cogn Neurosci 24(11):2223–2236. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00260
Chun MM, Golomb JD, Turk-Browne NB (2011) A taxonomy of external and internal attention. Annu Rev Psychol 62:73–101. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.093008.100427
Colombo D, Serino S, Tuena C, Pedroli E, Dakanalis A, Cipresso P, Riva G (2017) Egocentric and allocentric spatial reference frames in aging: a systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 80:605–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.07.012
Committeri G, Galati G, Paradis AL, Pizzamiglio L, Berthoz A, LeBihan D (2004) Reference frames for spatial cognition: different brain areas are involved in viewer-, object-, and landmark-centered judgments about object location. J Cogn Neurosci 16(9):1517–1535. https://doi.org/10.1162/0898929042568550
Cooper ACG, Humphreys GW (2000) Coding space within but not between objects: evidence from Balint’s syndrome. Neuropsychologia 38(6):723–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0028-3932(99)00150-5
Cope M, Delpy DT (1988) System for long-term measurement of cerebral blood and tissue oxygenation on newborn infants by near infra-red transillumination. Med Biol Eng Comput 26(3):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02447083
Corbetta M, Kincade JM, Shulman GL (2002) Neural systems for visual orienting and their relationships to spatial working memory. J Cognitive Neurosci 14(3):508–523. https://doi.org/10.1162/089892902317362029
Corbetta M, Kincade MJ, Lewis C, Snyder AZ, Sapir A (2005) Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect. Nat Neurosci 8(11):1603–1610. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1574
Corbetta M, Patel G, Shulman GL (2008) The reorienting system of the human brain: from environment to theory of mind. Neuron 58(3):306–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.017
Corbetta M, Shulman GL (2002) Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(3):201–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn755
Culham JC, Valyear KF (2006) Human parietal cortex in action. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16(2):205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2006.03.005
Derbie AY, Chau B, Chan C (2020) Modulation of allocentric spatial coding in inferior parietal lobule and frontal eye-fields are associated to changes in white-matter integrity: a combined DTI-fMRI study. Paper presented at the 48th of the Annual Meeting of the Neuropsychological Society, Denver, CO., USA
Desimone R, Duncan J (1995) Neural mechanisms of selective visual attention. Annu Rev Neurosci 18(1):193–222. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.001205
Eickhoff SB, Stephan KE, Mohlberg H, Grefkes C, Fink GR, Amunts K, Zilles K (2005) A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. Neuroimage 25(4):1325–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.12.034
Ekstrom AD, Arnold AE, Iaria G (2014) A critical review of the allocentric spatial representation and its neural underpinnings: toward a network-based perspective. Front Hum Neurosci 8:803. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00803
Epstein RA (2008) Parahippocampal and retrosplenial contributions to human spatial navigation. Trends Cogn Sci 12(10):388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2008.07.004
Filimon F (2015) Are all spatial reference frames egocentric? Reinterpreting evidence for allocentric, object-centered, or world-centered reference frames. Front Hum Neurosci 9:648. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00648
Fink GR, Marshall JC, Weiss PH, Stephan T, Grefkes C, Shah NJ et al (2003) Performing allocentric visuospatial judgments with induced distortion of the egocentric reference frame: an fMRI study with clinical implications. Neuroimage 20(3):1505–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.07.006
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(27):9673–9678. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504136102
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2009) glmnet: Lasso and elastic-net regularized generalized linear models. R package version, 1(4)
Gagnon L, Perdue K, Greve DN, Goldenholz D, Kaskhedikar G, Boas DA (2011) Improved recovery of the hemodynamic response in diffuse optical imaging using short optode separations and state-space modeling. Neuroimage 56(3):1362–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.001
Galati G, Committeri G, Sanes JN, Pizzamiglio L (2001) Spatial coding of visual and somatic sensory information in body-centred coordinates. Eur J Neurosci 14(4):737–746. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01674.x
Galati G, Lobel E, Vallar G, Berthoz A, Pizzamiglio L, Le Bihan D (2000) The neural basis of egocentric and allocentric coding of space in humans: a functional magnetic resonance study. Exp Brain Res 133(2):156–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000375
Galati G, Pelle G, Berthoz A, Committeri G (2010) Multiple reference frames used by the human brain for spatial perception and memory. Exp Brain Res 206(2):109–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2168-8
Geng JJ, Vossel S (2013) Re-evaluating the role of TPJ in attentional control: contextual updating? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37(10 Pt 2):2608–2620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.08.010
Gomez A, Cerles M, Rousset S, Remy C, Baciu M (2014) Differential hippocampal and retrosplenial involvement in egocentric-updating, rotation, and allocentric processing during online spatial encoding: an fMRI study. Front Hum Neurosci 8:150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2014.00150
Harris M, Wiener J, Wolbers T (2012) Aging specifically impairs switching to an allocentric navigational strategy. Front Aging Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2012.00029
Hong W-J, Tao J, Wong AWK, Yang S-L, Leung M-T, Lee TMC et al (2018) Psychometric properties of the Chinese (Putonghua) version of the Oxford Cognitive Screen (OCS-P) in Subacute Poststroke patients without neglect. Biomed Res Int 2018:6827854. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6827854
Hopfinger JB, Buonocore MH, Mangun GR (2000) The neural mechanisms of top-down attentional control. Nat Neurosci 3(3):284–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/72999
Iaria G, Chen JK, Guariglia C, Ptito A, Petrides M (2007) Retrosplenial and hippocampal brain regions in human navigation: complementary functional contributions to the formation and use of cognitive maps. Eur J Neurosci 25(3):890–899. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05371.x
James TW, Humphrey GK, Gati JS, Menon RS, Goodale MA (2002) Differential effects of viewpoint on object-driven activation in dorsal and ventral streams. Neuron 35(4):793–801
Jang KE, Tak S, Jung J, Jang J, Jeong Y, Ye JC (2009) Wavelet minimum description length detrending for near-infrared spectroscopy. J Biomed Opt 14(3):034004. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3127204
Japee S, Holiday K, Satyshur MD, Mukai I, Ungerleider LG (2015) A role of right middle frontal gyrus in reorienting of attention: a case study. Front Syst Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2015.00023
Kocsis L, Herman P, Eke A (2006) The modified Beer-Lambert law revisited. Phys Med Biol 51(5):N91. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/5/N02
Kozhevnikov M, Motes MA, Rasch B, Blajenkova O (2006) Perspective-taking vs. mental rotation transformations and how they predict spatial navigation performance. Appl Cogn Psychol 20(3):397–417
Krall S, Rottschy C, Oberwelland E, Bzdok D, Fox P, Eickhoff S et al (2015) The role of the right temporoparietal junction in attention and social interaction as revealed by ALE meta-analysis. Brain Struct Funct 220(2):587–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0803-z
Kravitz DJ, Saleem KS, Baker CI, Mishkin M (2011) A new neural framework for visuospatial processing. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(4):217–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3008
Kravitz DJ, Saleem KS, Baker CI, Ungerleider LG, Mishkin M (2013) The ventral visual pathway: an expanded neural framework for the processing of object quality. Trends Cogn Sci 17(1):26–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2012.10.011
Li C-SR, Huang C, Constable RT, Sinha R (2006) Imaging response inhibition in a stop-signal task: neural correlates independent of signal monitoring and post-response processing. J Neurosci 26(1):186–192
Lithfous S, Dufour A, Blanc F, Després O (2014) Allocentric but not egocentric orientation is impaired during normal aging: An ERP study. Neuropsychology 28(5):761
Liu N, Li H, Su W, Chen Q (2017) Common and specific neural correlates underlying the spatial congruency effect induced by the egocentric and allocentric reference frame. Hum Brain Mapp 38(4):2112–2127. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23508
Moffat SD, Resnick SM (2002) Effects of age on virtual environment place navigation and allocentric cognitive mapping. Behav Neurosci 116(5):851–859. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7044.116.5.851
Murphy K, Garavan H (2004) An empirical investigation into the number of subjects required for an event-related fMRI study. NeuroImage 22(2):879–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.02.005
MurtaghF (1985) Multidimensional clustering algorithms. In: Compstat Lectures. Physika Verlag, Vienna
Nachev P, Kennard C, Husain M (2008) Functional role of the supplementary and pre-supplementary motor areas. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:856. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2478
Neggers SF, Van der Lubbe RH, Ramsey NF, Postma A (2006) Interactions between ego- and allocentric neuronal representations of space. Neuroimage 31(1):320–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.12.028
Noudoost B, Chang MH, Steinmetz NA, Moore T (2010) Top-down control of visual attention. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20(2):183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2010.02.003
Pelt SV, Toni I, Diedrichsen J, Medendorp WP (2010) Repetition suppression dissociates spatial frames of reference in human saccade generation. J Neurophysiol 104(3):1239–1248. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00393.2010
Posner MI (1980) Orienting of attention. Q J Exp Psychol 32(1):3–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/00335558008248231
Ptak R (2012) The frontoparietal attention network of the human brain: action, saliency, and a priority map of the environment. Neuroscientist 18(5):502–515. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858411409051
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.R-project.org/
Re R, Muthalib M, Contini D, Zucchelli L, Torricelli A, Spinelli L et al (2013) Cerebral cortex activation mapping upon electrical muscle stimulation by 32-channel time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy. In: Oxygen transport to tissue XXXV. Springer, New York, pp 441–447
Ruotolo F, van Der Ham IJ, Iachini T, Postma A (2011) The relationship between allocentric and egocentric frames of reference and categorical and coordinate spatial information processing. Q J Exp Psychol 64(6):1138–1156
Ryali S, Chen T, Supekar K, Menon V (2012) Estimation of functional connectivity in fMRI data using stability selection-based sparse partial correlation with elastic net penalty. Neuroimage 59(4):3852–3861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.11.054
Saj A, Cojan Y, Musel B, Honore J, Borel L, Vuilleumier P (2014) Functional neuro-anatomy of egocentric versus allocentric space representation. Neurophysiol Clin 44(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2013.10.135
Sato T, Nambu I, Takeda K, Aihara T, Yamashita O, Isogaya Y et al (2016) Reduction of global interference of scalp-hemodynamics in functional near-infrared spectroscopy using short distance probes. NeuroImage 141:120–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.06.054
Scarapicchia V, Brown C, Mayo C, Gawryluk JR (2017) Functional magnetic resonance imaging and functional near-infrared spectroscopy: insights from combined recording studies. Front Hum Neurosci 11:419–419. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00419
Schafer RJ, Moore T (2011) Selective attention from voluntary control of neurons in prefrontal cortex. Science 332(6037):1568–1571. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1199892
Singh AK, Okamoto M, Dan H, Jurcak V, Dan I (2005) Spatial registration of multichannel multi-subject fNIRS data to MNI space without MRI. Neuroimage 27(4):842–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.05.019
Szczepanski SM, Pinsk MA, Douglas MM, Kastner S, Saalmann YB (2013) Functional and structural architecture of the human dorsal frontoparietal attention network. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(39):15806–15811. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313903110
Thibault RT, Lifshitz M, Raz A (2016) Body position alters human resting-state: insights from multi-postural magnetoencephalography. Brain Imaging Behav 10(3):772–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9447-8
Thompson KG, Biscoe KL, Sato TR (2005) Neuronal basis of covert spatial attention in the frontal eye field. J Neurosci 25(41):9479–9487. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0741-05.2005
Toronov V, Webb A, Choi JH, Wolf M, Michalos A, Gratton E, Hueber D (2001) Investigation of human brain hemodynamics by simultaneous near-infrared spectroscopy and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Med Phys 28(4):521–527. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1354627
Tremblay P, Small SL (2011) From language comprehension to action understanding and back again. Cereb Cortex 21(5):1166–1177
Vallar G, Lobel E, Galati G, Berthoz A, Pizzamiglio L, Le Bihan D (1999) A fronto-parietal system for computing the egocentric spatial frame of reference in humans. Exp Brain Res 124(3):281–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050624
Vossel S, Geng JJ, Fink GR (2014) Dorsal and ventral attention systems: distinct neural circuits but collaborative roles. Neuroscientist 20(2):150–159. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858413494269
Wallentin M, Roepstorff A, Burgess N (2008) Frontal eye fields involved in shifting frame of reference within working memory for scenes. Neuropsychologia 46(2):399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.08.014
Worsley KJ, Friston KJ (1995) Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited—again. Neuroimage 2(3):173–181
Ye JC, Tak S, Jang KE, Jung J, Jang J (2009) NIRS-SPM: statistical parametric mapping for near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage 44(2):428–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.08.036
Zaehle T, Jordan K, Wustenberg T, Baudewig J, Dechent P, Mast FW (2007) The neural basis of the egocentric and allocentric spatial frame of reference. Brain Res 1137(1):92–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.12.044
Zhang H, Ekstrom A (2013) Human neural systems underlying rigid and flexible forms of allocentric spatial representation. Hum Brain Mapp 34(5):1070–1087. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21494
Acknowledgement
The General Research Fund of Research Grant Council of Hong Kong (151044) partially supported this study. The authors thank the University Research Facility in Behavioral and Systems Neuroscience at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University for its support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Micah M. Murray.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derbie, A.Y., Chau, B., Lam, B. et al. Cortical Hemodynamic Response Associated with Spatial Coding: A Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study. Brain Topogr 34, 207–220 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-021-00821-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-021-00821-9