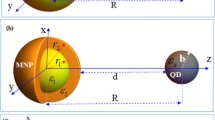
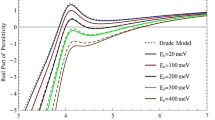
Abstract
In this paper, the optical properties of two small silver metallic nanoparticles (sAgNPs) coupled to a quantum dot (QD) are studied. The interaction between sAgNP and QD is investigated theoretically using the compact density matrix method. In this paper, due to the small size of the AgNP, the dielectric function does not follow the classical models and quantum-size effects must be considered. The excitation of surface plasmons in sAgNP is observed using the finite element method. The main result of the current study shows that when AgNPs are small, the absorption spectrum profile of the QD is strongly affected due to the plasmon–exciton–plasmon interaction. The absorption spectrum profile of the QD shows an electromagnetically induced transparency with two peaks and a minimum in the transition frequency. Then, the near-field enhancement of the sAgNP, the field experienced by the QD, the exciton transition energy shift, and the Förster-enhanced broadening of the excitonic transition are also examined.
Graphic Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.]
References
P. Harrison, A. Valavanis, Quantum wells, wires and dots: theoretical and computational physics of semiconductor nanostructures (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2016)
W. Kirk, Nanostructures and mesoscopic systems (Academic Press, Singapore, 2012)
T. Tsakalakos, I.A. Ovid’ko, A.K. Vasudevan, Nanostructures: synthesis, functional properties and application, vol. 128 (Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 2012)
E. Cao, W. Lin, M. Sun, W. Liang, Y. Song, Nanophotonics 7(1), 145 (2018)
V.V. Savchuk, R.V. Gamernyk, I.S. Virt, S.Z. Malynych, A.O. Pinchuk, AIP Adv. 9(4), 045021 (2019)
A.R. Warrier, R. Gandhimathi, Methods Appl Fluoresc 6(3), 035009 (2018)
R.M. Pereira, J. Borges, G.V. Smirnov, F. Vaz, M.I. Vasilevskiy, ACS Photonics 6(1), 204 (2018)
N. Zamani, A. Keshavarz, H. Nadgaran, Superlattices Microstruct. 77, 82 (2015)
S.A. Maier, Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications (Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 2007)
M.R. Singh, D.G. Schindel, A. Hatef, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(18), 181106 (2011)
R.D. Artuso, G.W. Bryant, Nano lett. 8(7), 2106 (2008)
N. Zamani, A. Keshavarz, H. Nadgaran, Physica B: Condensed Matter 490, 57 (2016)
N. Zamani, A. Keshavarz, H. Nadgaran, Eur. Phys. J. D 74(6), 1 (2020)
A. Hatef, S.M. Sadeghi, M.R. Singh, Nanotechnology 23(6), 065701 (2012)
J.B. Li, S. Liang, S. Xiao, M.D. He, N.C. Kim, L.Q. Chen, G.H. Wu, Y.X. Peng, X.Y. Luo, Z.P. Guo, Optics Express 24(3), 2360 (2016)
N. Zamani, A. Hatef, H. Nadgaran, A. Keshavarz, J. Nanophotonics 11(3), 036011 (2017)
H. Baida, P. Billaud, S. Marhaba, D. Christofilos, E. Cottancin, A. Crut, J. Lerme, P. Maioli, M. Pellarin, M. Broyer et al., Nano Lett. 9(10), 3463 (2009)
V. Chegel, O. Rachkov, A. Lopatynskyi, S. Ishihara, I. Yanchuk, Y. Nemoto, J.P. Hill, K. Ariga, J. Phys. Chem. C 116(4), 2683 (2012)
J. Borges, R. Pereira, M. Rodrigues, T. Kubart, S. Kumar, K. Leifer, A. Cavaleiro, T. Polcar, M. Vasilevskiy, F. Vaz, J. Phys. Chem. C 120(30), 16931 (2016)
L. Genzel, T. Martin, U. Kreibig, Z. Phys. B Condensed Matter 21(4), 339 (1975)
X. Jiang, K. Guo, G. Liu, T. Yang, Y. Yang, Superlattices Microstruct. 105, 56 (2017)
J.A. Scholl, A.L. Koh, J.A. Dionne, Nature 483(7390), 421 (2012)
C. Kumarasinghe, M. Premaratne, G.P. Agrawal, Optics Exp. 22(10), 11966 (2014)
C.F. Bohren, D.R. Huffman, Absorption and scattering of light by small particles (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008)
U. Kreibig, L. Genzel, Surface Sci. 156, 678 (1985)
W. Kraus, G.C. Schatz, J. Chem. Phys. 79(12), 6130 (1983)
M.C. Ko, N.C. Kim, C.J. Jang, G.J. Kim, Z.H. Hao, J.B. Li, Q.Q. Wang, arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.06636 (2017)
A. Hatef, N. Zamani, W. Johnston, J. Phys.: Condensed Matter 29(15), 155305 (2017)
R.D. Artuso, G.W. Bryant, Phys. Rev. B 82(19), 195419 (2010)
L.W. Wang, A. Zunger, J. Phys. Chem. B 102(34), 6449 (1998)
A. Hatef, S.M. Sadeghi, É. Boulais, M. Meunier, Nanotechnology 24(1), 015502 (2012)
P.B. Johnson, R.W. Christy, Phys. Rev. B 6(12), 4370 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed equally to the interpretation of the results and the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamani, N., Nadgaran, H. & Hatef, A. The effect of quantum correction for the dielectric function on the optical properties of a plasmon–exciton–plasmon hybrid system. Eur. Phys. J. D 75, 33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00053-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00053-3