Abstract
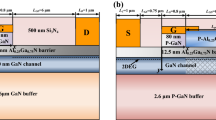
This research article reports the operational characteristics of gate field plate double heterojunction (DH) high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) using SiN (SiO2) passivation techniques. The proposed HEMT exhibits 496 (292) V breakdown voltage (VBR) for LG (gate-length) = 0.25 μm, LGD (drain-gate distance) = 3.2 μm and 1 μm field plate length HEMT. The n + GaN source/drain regions with SiN (SiO2) passivation AlGaN/GaN/AlGaN HEMT delivered 1.4 (1.3) A/mm peak drain current density (Ids), 540 (550) mS/mm gm (transconductance), fT/fMAX of 54/198 (62/252) GHz, and the sub-threshold drain leakage current of 4 × 10−13 (1 × 10−11) A/mm. The high Johnson figure of merit (JFoM = fT × VBR) of 28.76 (19.27) THz.V and excellent VBR × fMAX product of 90.27 (73.29) THz.V demonstrates the great potential of the optimized gate field plate DH-HEMTs structure for U and V band high power microwave electronics.
Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ikeda N, Niiyama Y, Kambayashi H, Sato Y, Nomura T, Kato S, Yoshida S (2010) GaN power transistors on Si substrates for switching applications. Proc IEEE 98:1151–1161
Moon JS, Wu S, Milosavljevic I, Conway A, Hashomoto P, Hu M, Antcliffe M, Micovicv M (2005) Gate-recessed AlGaN-GaN HEMTs for high-performance millimeter-wave applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 26:348–350
Palacios T, Charkraborty A, Rajan S, Poblenz C, Keller S, DenBaars SP, Speck JS, Mishra UK (2005) High-power AlGaN/GaN HEMTs for Ka-band applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 26:781–783
Chu KK, Chao PC, Pizzella MT, Actis R, Meharry DE, Nichols KB, Vaudo RP, Xu X, Flynn JS, Dion J, Brandes GR (2004) 9.4 W/mm power density AlGaN-GaN HEMTs on free-standing GaN substrates. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 25:596–598
Vetury R, Zhang N, Keller S, Mishra U (2001) The impact of surface states on the DC and RF characteristics of AlGaN/GaN HFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 48:560–566
Huang H, Liang YC, Samudra GS, Chang T-F, Huang C-F (2014) Effects of gate field plates on the surface state related current collapse in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs. IEEE Trans Power Electronics 29:2164–2173
Brown DF, Shinohara K, Corrion AL, Chu R, Williams A, Wong JC, Alvarado-Rodriguez I, Grabar R, Johnson M, Butler CM, Santos D, Burnham SD, Robinson JF, Zehnder D, Kim SJ, Oh TC, Micovic M (2013) High-speed, enhancement-mode GaN power switch with regrown n+ GaN ohmic contacts and staircase field plates. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34:1118–1120
Wu Y-F, Moore M, Saxler A, Wisleder T, Parikh P (2006) 40-W/mm double field-plated GaN HEMTs. in Proc IEEE Device Res Conf:151–152
Wakejima A, Ota K, Matsunaga K, Kuzuhara M (2003) A GaAs-based field-modulating plate HFET with improved WCDMA peak-output-power characteristics. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 50:1983–1987
Pei Y, Chen Z, Brown D, Keller S, Denbaars SP, Mishra UK (2009) Deep-submicrometer AlGaN/GaN HEMTs with slant field plates. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 30:328–330
Coffie R (2014) Slant field plate model for field-effect transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 61:2867–2872
Hao Y, Yang L, Ma X, Ma J, Cao M, Pan C, Wang C, Zhang J (2011) High-performance microwave gate-recessed AlGaN/AlN/GaN MOS-HEMT with 73% power-added efficiency. IEEE Electron Device Lett 32:626–628
Saito W, Nitta T, Kakiuchi Y, Saito Y, Tsuda K, Omura I, Yamaguchi M (2007) Suppression of dynamic ON-resistance increase and gate charge measurements in high-voltage GaN-HEMTs with optimized field-plate structure. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 54:1825–1830
Nidhi T, Palacios A, Chakraborty SK, Mishra UK (2006) Study of impact of access resistance on high-frequency performance of GaN HEMTs by measurements at low temperature. IEEE Electron Device Lett 27:877–880
Tasker PJ, Hughes B (1989) Importance of source and drain resistance to the maximum ft of millimeter-wave MODFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 10:291–293
Bolognesi CR, Kwan AC, DiSanto DW (2002) Transistor delay analysis and effective channel velocity extraction in GaN HFETs. IEDM Tech Dig 4:685–688
Hanawa H, Horio K (2014) Increase in breakdown voltage of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs with a high-k dielectric layer. Phys Status Solidi A 211:784–787
Liu C, Chor EF, Tan LS (2007) Enhanced device performance of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs using HfO2 high-k dielectric for surface passivation and gate oxide. Semicond Sci Technol 22:522–527
Micovic M, Hashimoto P, Hu M, Milosavljevic I, Duvall J, Willadsen PJ, Wong W-S, Conway AM, Kurdoghlian A, Deelman PW, Moon J-S, Schmitz A, Delaney MJ (2004) GaN double heterojunction field effect transistor for microwave and millimeterwave power applications. IEDM Tech Dig 4:807–810
ATLAS User’s Manual, Device simulation software, (2009) SILVACO Int., Santa Clara, CA,
Chini A, Buttari D, Coffie R, Shen L, Heikman S, Chakraborty A, Keller S, Mishra UK (2004) Power and linearity characteristics of field-plated recessed-gate AlGaN–GaN HEMTs. IEEE Electron Device Lett 25:229–231
Moon JS, Wong D, Hu M, Hashimoto P, Antcliffe M, McGuire C, Micovic M, Willadson P (2008) 55% PAE and high power Ka-band GaN HEMTs with linearized Transconductance via n+ GaN source contact ledge. IEEE Electron Device Lett 29:834–837
Marti D, Tirelli S, Alt AR, Roberts J, Bolognesi CR (2012) 150-GHz cutoff frequencies and 2-W/mm output power at 40 GHz in a millimeter-wave AlGaN/GaN HEMT technology on silicon. IEEE Electron Device Lett 33:1372–1374
Song D, Liu J, Cheng Z, Tang WCW, Lau KM, Chen KJ (2007) Normally off AlGaN/GaN low-density drain HEMT (LDD-HEMT) with enhanced breakdown voltage and reduced current collapse. IEEE Electron Device Lett 28:189–191
Wong J, Shinohara K, Corrion AL, Brown DF, Carlos Z, Williams A, Tang Y, Robinson JF, Khalaf I, Fung H, Schmitz A, Thomas O, Kim S, Chen S, Burnham S, Margomenos A, Micovic M (2017) Novel asymmetric slant field plate Technology for High-Speed low-Dynamic Ron E/D-mode GaN HEMTs. IEEE Electron Device Lett 38:95–98
Xie G, Xu E, Lee J, Hashemi N, Zhang B, Fu FY, Ng WT (2012) Breakdown-voltage-enhancement technique for RF-based AlGaN/GaN HEMTs with a source-connected air-bridge field plate. IEEE Electron Device Lett 33:670–672
Fletcher A, Nirmal D, Ajayan J, Arivazhagan L (2019) Analysis of AlGaN/GaN HEMT using discrete field plate technique for high power and high frequency applications. Int J Electron Commun 99:325–330
Augustine Fletcher AS, Nirmal D, Arivazhagan L, Ajayan J, Varghese A (2019) Enhancement of Johnson figure of merit in III-V HEMT combined with discrete field plate and AlGaN blocking layer. Int J RF Microw Comput Aided Eng 30:e22040
Chandera S, Guptaa S, Ajayb MG (2018) Enhancement of breakdown voltage in algan/gan hemt using passivation technique for microwave application. Superlattices and Microstructures 120:217–222
Subramani NK, Julien C, Ahmad A, Jean C, Raphael S, Raymond Q (2017) Identification of GaN buffer traps in microwave power AlGaN/GaN HEMTs through low frequency S parameters measurements and TCAD-based physical device simulations. J Elect Dev Soc 5:12–18
Adachi S (2008) Properties of semiconductor alloys: group-IV, III-V and II-VI semiconductors. Wiley, Chichester
Giovanni C, Dongping X, Schreurs DM, Multibias A (2006) Equivalent-circuit extraction for GaN HEMTs. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech 54:3616–3622
Kawada Y, Hanawa H, Horio K (2017) Effects of acceptors in a Fe-doped buffer layer on breakdown characteristics of AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors with a high-k passivation layer. Jpn J Appl Phys 108003:1–3
Satoh Y, Hanawa H, Horio K (2016) Effects of buffer leakage current on breakdown voltage in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs with a high-k passivation layer, 2016 11th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), London, 341-344,
Kabemura T, Ueda S, Kawada Y, Horio K (2018) Enhancement of breakdown voltage in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs: field plate plus high- k passivation layer and high acceptor density in buffer layer, in. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 65:3848–3854
Karmalkar S, Mishra UK (2001) Enhancement of breakdown voltage in AlGaN/GaN high electron mobility transistors using a field plate. in IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 48:1515–1521
Brown DF (2013) High-speed, enhancement-mode GaN power switch with regrown n+ GaN Ohmic contacts and staircase field plates. IEEE Electron Device Letters 4:1118–1120
Saito W, Suwa T, Uchihara T, Naka T, Kobayashi T (2015) Breakdown behaviour of high-voltage GaN-HEMTs. Microelect Real 55:1682–1686
Meneghesso G, Meneghini M, Zanoni E (2014) Breakdown mechanisms in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs: an overview. Japan J App Phy 53:1–9
Binola K, Shobha R, Prajoon P, Mohankumar N, Nirmal D (2015) The influence of high-k passivation layer on breakdown voltage of schottky AlGaN/GaN HEMTs. J Microelectron 46:1387–1391
Toshiki K, Shingo U, Yuki K, Kazushige H (2018) Enhancement of breakdown voltage in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs: field plate plus high-k passivation layer and high acceptor density in buffer layer. IEEE Trans Elect Dev 65:9–14
Fletcher ASA, Nirmal D, Ajayan J, Arivazhagan L (2020) An intensive study on assorted substrates suitable for high JFOM AlGaN/GaN HEMT. Silicon. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00549-4
Soni A, Ajay, Shrivastava M (2020) Novel drain-connected field plate GaN HEMT designs for improved VBD−RON tradeoff and RF PA performance. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 67(4):1718–1725. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2020.2976636
Prasannanjaneyulu B, Karmalkar S (2020) Relative effectiveness of high-k passivation and gate-connected field plate techniques in enhancing GaN HEMT breakdown. Microelectron Reliab 110:113698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2020.113698
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the works in this paper have done together by P. Murugapandiyan, D. Nirmal, J. Ajayan, Arathy Varghese and N. Ramkumar.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest reported in this paper.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable as the manuscript does not contain any data from individual.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murugapandiyan, P., Nirmal, D., Ajayan, J. et al. Investigation of Influence of SiN and SiO2 Passivation in Gate Field Plate Double Heterojunction Al0.3Ga0.7N/GaN/Al0.04Ga0.96N High Electron Mobility Transistors. Silicon 14, 1421–1429 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00899-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00899-z