Abstract
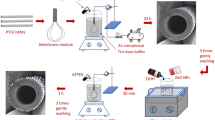
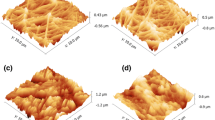
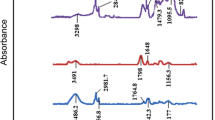
Surface engineering with polydopamine coatings has been considered a promising surface functionalisation tool. However, it is difficult to control the self-polymerisation for polydopamine formation, which usually causes severe interparticle aggregation. In this study, polydopamine self-polymerisation was controlled by adjusting its reducing environment using a reductant (NaBH4) to fabricate mixed cellulose ester (MCE)/polydopamine membranes. An oxidising environment using NaIO4 was additionally tested as the control. The results showed that a thin polydopamine coating with small polydopamine particles was formed on the skeleton frameworks of the MCE membrane with NaBH4, and the self-polymerisation rate was suppressed. The polydopamine coating formed in the reducing environment facilitated excellent water transport performance with a water permeance of approximately 400 L · m−2 · h−1 · bar−1 as well as efficient organic foulant removal with a bovine serum albumin rejection of approximately 90%. In addition, the polydopamine coating with NaBH4 exhibited both excellent chemical stability and anti-microbial activity, demonstrating the contribution of the reducing environment to the performance of the MCE/polydopamine membranes. It shows significant potential for use in water purification.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee A, Elam J W, Darling S B. Membrane materials for water purification: design, development, and application. Environmental Science. Water Research & Technology, 2016, 2(1): 17–42
Fane A G, Wang R, Hu M X. Synthetic membranes for water purification: status and future. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(11): 3368–3386
Yu H, Qiu X, Moreno N, Ma Z, Calo V M, Nunes S P, Peinemann K V. Self-assembled asymmetric block copolymer membranes: bridging the gap from ultra to nanofiltration. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(47): 13937–13941
Sorribas S, Gorgojo P, Téllez C, Coronas J, Livingston A G. High flux thin film nanocomposite membranes based on metal-organic frameworks for organic solvent nanofiltration. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(40): 15201–15208
Lau W J, Ismail A F. Polymeric nanofiltration membranes for textile dye wastewater treatment: preparation, performance evaluation, transport modelling, and fouling control—a review. Desalination, 2009, 245(1): 321–348
Xu J, Feng X, Hou J, Wang X, Shan B T, Yu L M, Gao C J. Preparation and characterization of a novel polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane using a copolymer with capsaicin-mimic moieties for improved anti-fouling properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 446: 171–180
Xu J, Feng X S, Chen P P, Gao C J. Development of an antibacterial copper (II)-chelated polyacrylonitrile ultrafiltration membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 431–414: 62–69
Li M, Xu J, Chang C Y, Feng C, Zhang L, Tang Y, Gao C. Bioinspired fabrication of composite nano-filtration membrane based on the formation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine/PEI layer followed by cross-linking. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 459: 62–71
Wang K, Dong Y, Yan Y, Zhang S, Li J. Mussel-inspired chemistry for preparation of super-hydrophobic surfaces on porous substrates. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(46): 29149–29158
Postma A, Yan Y, Wang Y, Zelikin A N, Tjipto E, Caruso F. Self-polymerization of dopamine as a versatile and robust technique to prepare polymer capsules. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(14): 3042–3044
Ryou M H, Lee Y M, Park J K, Choi J W. Mussel-inspired polydopamine-treated polyethylene separators for high-power Li-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(27): 3066–3070
Peng H P, Liang R P, Zhang L, Qiu J D. Facile preparation of novel core-shell enzyme-Au-polydopamine-Fe3O4 magnetic bio-nanoparticles for glucosesensor. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 2013, 42: 293–299
Cao Y, Zhang X, Tao L, Li K, Xue Z, Feng L, Wei Y. Mussel-inspired chemistry and Michael addition reaction for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(10): 4438–4442
Liu M, Zeng G, Wang K, Wan Q, Tao L, Zhang X, Wei Y. Recent developments in polydopamine: an emerging soft matter for surface modification and biomedical applications. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(38): 16819–16840
Lee H, Dellatore S M, Miller W M, Messersmith P B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science, 2007, 318(5849): 426–430
Shi G M, Chung T S. Thin film composite membranes on ceramic for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 448: 34–43
Jiang J H, Zhu L P, Li X L, Xu Y Y, Zhu B K. Surface modification of PE porous membranes based on the strong adhesion of polydopamine and covalent immobilization of heparin. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 364(1–2): 194–202
Yang Z, Wu Y, Guo H, Ma X H, Lin C E, Zhou Y, Cao B, Zhu B K, Shi K, Tang C Y. A novel thin-film nano-templated composite membrane with in situ silver nanoparticles loading: separation performance enhancement and implications. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 544: 351–358
Zhu J, Uliana A, Wang J, Yuan S, Li J, Tian M, Simoens K, Volodin A, Lin J, Bernaerts K, Zhang Y, Van der Bruggen B. Elevated salt transport of antimicrobial loose nanofiltration membranes enabled by copper nanoparticles via fast bioinspired deposition. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2016, 4(34): 13211–13222
Zhu J, Wang J, Uliana A, Tian M, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Volodin A, Simoens K, Yuan S, Li J, Lin J, Bernaerts K, Van der Bruggen B. Mussel-inspired architecture of high-flux loose nanofiltration membrane functionalized with antibacterial reduced graphene oxide-copper nanocomposites. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(34): 28990–29001
Shen H, Wang N, Ma K, Wang L, Chen G, Ji S. Tuning inter-layer spacing of graphene oxide laminates with solvent green to enhance its nanofiltration performance. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 527: 43–50
Shao L, Wang Z X, Zhang Y L, Jiang Z X, Liu Y Y. A facile strategy to enhance PVDF ultrafiltration membrane performance via self-polymerized polydopamine followed by hydrolysis of ammonium fluotitanate. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 461: 10–21
Yang H C, Pi J K, Liao K J, Huang H, Wu Q Y, Huang X J, Xu Z K. Silica-decorated polypropylene microfiltration membranes with a mussel-inspired intermediate layer for oil-in-water emulsion separation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(15): 12566–12572
Zeng R, Luo Z, Zhou D, Cao F, Wang Y. A novel PEG coating immobilized onto capillary through polydopamine coating for separation of proteins in CE. Electrophoresis, 2010, 31(19): 3334–3341
Zeng T, Zhang X L, Niu H Y, Ma Y R, Li W H, Cai Y Q. In situ growth of gold nanoparticles onto polydopamine-encapsulated magnetic microspheres for catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 134–135: 26–33
Lee H, Rho J, Messersmith P B. Facile conjugation of biomolecules onto surfaces via mussel adhesive protein inspired coatings. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(4): 431–434
Hou C, Qi Z, Zhu H. Preparation of core-shell magnetic polydopamine/alginate biocomposite for Candida rugosa lipase immobilization. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2015, 128: 544–551
Yang K, Lee J S, Kim J, Lee Y B, Shin H, Um S H, Kim J B, Park K I, Lee H, Cho S W. Polydopamine-mediated surface modification of scaffold materials for human neural stem cell engineering. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(29): 6952–6964
Zhou R, Ren P F, Yang H C, Xu Z K. Fabrication of antifouling membrane surface by poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate)/polydopamine co-deposition. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 466: 18–25
Shevate R, Kumar M, Karunakaran M, Hedhili M N, Peinemann K V. Polydopamine/cysteine surface modified isoporous membranes with selfcleaning properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 529: 185–194
Ingole P G, Choi W, Kim K H, Park C H, Choi W K, Lee H K. Synthesis, characterization and surface modification of PES hollow fiber membrane support with polydopamine and thin film composite for energy generation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 243: 137–146
Arena J T, Manickam S S, Reimund K K, Freeman B D, McCutcheon J R. Solute and water transport in forward osmosis using polydopamine modified thin film composite membranes. Desalination, 2014, 343: 8–16
Li F, Meng J, Ye J, Yang B, Tian Q, Deng C. Surface modification of PES ultrafiltration membrane by polydopamine coating and poly (ethyleneglycol) grafting: morphology, stability, and anti-fouling. Desalination, 2014, 344: 422–430
Tripathi B P, Dubey N C, Subair R, Choudhury S, Stamm M. Enhanced hydrophilic and antifouling polyacrylonitrile membrane with polydopamine modified silica nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(6): 4448–4457
Chen Y, He C. High salt permeation nanofiltration membranes based on NMG assisted polydopamine coating for dye/salt fractionation. Desalination, 2017, 413: 29–39
Xu L N, Xu J, Shan B T, Wang X L, Gao C J. Novel thin-film composite membranes via manipulating the synergistic interaction of dopamine and m-phenylenediamine for highly efficient forward osmosis desalination. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2017, 5(17): 7920–7932
Jiang J H, Zhu L P, Zhang H T, Zhu B K, Xu Y Y. Improved hydrodynamic permeability and antifouling properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes using polydopamine nanoparticles as additives. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 457: 73–81
Cheng C, Li S, Zhao W, Wei Q, Nie S, Sun S, Zhao C. The hydrodynamic permeability and surface property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes with mussel-inspired polydopamine coatings. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 417–418: 228–236
Guo H, Yao Z, Wang J, Yang Z, Ma X, Tang C Y. Polydopamine coating on a thin film composite forward osmosis membrane for enhanced mass transport and antifouling performance. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 551: 234–242
Ryu J, Ku S H, Lee H, Park C B. Mussel-inspired polydopamine coating as a universal route to hydroxyapatite crystallization. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(13): 2132–2139
Liu X, Cao J, Li H, Li J, Jin Q, Ren K, Ji J. Mussel-inspired polydopamine: a biocompatible and ultrastable coating for nano-particles in vivo. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(10): 9384–9395
Ryu J H, Messersmith P B, Lee H. Polydopamine surface chemistry: a decade of discovery. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(9): 7523–7540
Fei B, Qian B, Yang Z, Wang R, Liu W C, Mak C L, Xin J H. Coating carbon nanotubes by spontaneous oxidative polymerization of dopamine. Carbon, 2008, 46(13): 1795–1797
Han G, Zhang S, Li X, Widjojo N, Chung T S. Thin film composite forward osmosis membranes based on polydopamine modified polysulfone substrates with enhancements in both water flux and salt rejection. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 80: 219–231
Yang H C, Liao K J, Huang H, Wu Q Y, Wan L S, Xu Z K. Mussel-inspired modification of a polymer membrane for ultra-high water permeability and oil-in-water emulsion separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2014, 2(26): 10225–10230
Yang X, Du Y, Zhang X, He A, Xu Z K. Nanofiltration membrane with a mussel-inspired interlayer for improved permeation performance. Langmuir, 2017, 33(9): 2318–2324
Wei H, Ren J, Han B, Xu L, Han L, Jia L. Stability of polydopamine and poly(DOPA) melanin-like films on the surface of polymer membranes under strongly acidic and alkaline conditions. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2013, 110: 22–28
Jiang J, Zhu L, Zhu L, Zhang H, Zhu B, Xu Y. Zhu, Xu B Y. Antifouling and antimicrobial polymer membranes based on bioinspired polydopamine and strong hydrogen-bonded poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone). ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(24): 12895–12904
Bernsmann F, Ball V, Addiego F, Ponche A, Michel M, Gracio J J, Toniazzo V, Ruch D. Dopamine-melanin film deposition depends on the used oxidant and buffer solution. Langmuir, 2011, 27(6): 2819–2825
Xu J, Tang Y Y, Wang Y H, Shan B T, Yu L M, Gao C J. Effect of coagulation bath conditions on the morphology and performance of PSf membrane blended with a capsaicin-mimic copolymer. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 455: 121–130
Xu J, Feng S, Gao C J. Surface modification of thin-film-composite poly-amide membranes for improved reverse osmosis performance. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 370(1–2): 116–123
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21878279), Fundamental Research funds for the Central Universities (No. 201841012), Natural science fund of Shandong Province Project (No. ZR2018MB032). There was no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Lu, J., Wang, Y. et al. Reductant-assisted polydopamine-modified membranes for efficient water purification. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15, 109–117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1987-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1987-9