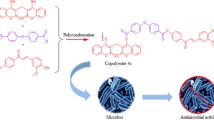
Abstract
Objective
The present report describes the enzymatic acylation of umbelliferone with different vinyl esters as acyl donors biocatalyzed by the commercial lipase Novozym® 435, and the investigation for their antibacterial activity against ATCC and clinical strains isolated from hospital infection sites.
Results
The umbelliferone esters (1–5) were synthesized through the acylation reaction of 7-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one with different long chain vinyl esters catalyzed by the lipase Novozym 435. The reaction conditions were: 10% Novozym 435; tetrahydrofuran:acetone (3:1) for the reactions with acetate, propionate and butyrate vinyl esters 50–90% conversion, and (9:1) for decanoate and laurate vinyl esters 10–15% conversion; acyl donor/umbelliferone molar ratio of 10:1 and 60 °C. All the umbelliferone esters were characterized NMR and (HRMS). The antibacterial activity of the products were tested using the broth microdilution method in order to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The results displayed by 7-laurate and 7-decanoate-umbelliferone esters showed the highest antibacterial potential, with 1 mM inhibitory activity for ATCC 33591, a methicillin and oxacillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain. They were also able to inhibit gram-negative bacterial strains, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MIC 0.5 mM) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (MIC 1 mM). In addition, 7-laurate- and 7-decanoate-umbelliferone esters were able to inhibit all clinical strains (MIC 1 mM; except 7-laurate-umbelliferone in which MIC 0.5 mM against 55a).
Conclusions
This is the first study performing the biocatalysis of umbelliferone followed by the purification of the products and the antibacterial evaluation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Majedy YK, Kadhum AAH, Al-Amiery AA, Mohamad AB (2017) Coumarins: the antimicrobial agents. Syst Rev Pharm 8:62–70. https://doi.org/10.5530/srp.2017.1.11
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2016) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, CLSI supplement M100S, 26th edn. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
De Araújo ME, Franco YE, Messias MC, Longato GB, Pamphile JA, Carvalho PO (2017) Biocatalytic synthesis of flavonoid esters by lipases and their biological benefits. Planta Med 83:7–22. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-118883
Kumar V, Mathur D, Srivastava S, Malhotra S, Rana N, Singh SK, Singh BK, Prasad AK, Varma AJ, Len C, Kuhad RC, Saxena RK, Parmar VS (2016) Biocatalytic synthesis of novel partial esters of a bioactive dihydroxy4-methylcoumarin by Rhizopus oryzae lipase (ROL). Molecules 21:1499–1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111499
Leal I, dos Santos K, Júnior I, Antunes O, Porzel A, Wessjohann L, Kuster R (2010) Ceanothane and lupane type triterpenes from – An Anti-staphylococcal evaluation. Planta Med 76(01):47–52
Lee JH, Kim YG, Cho HS, Ryu SY, Cho MH, Lee AJ (2014) Coumarins reduce biofilm formation and the virulence of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Phytomedicine 21:1037–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2014.04.008
Liu D, Cai S, Luan F, Wang Q (2015) Synthesis of long chain fatty acids acylated coumarin glycoside esters with lipase as catalyst. Chem Res Chin Univ 31:534–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-015-5048-8
Mecenas AS, Malafaia CRA, Sangenito LS, Simas DLR, Machado TB, Amaral ACF, Santos ALS, Freire DMG, Leal ICR (2018) Rutin derivatives obtained by transesterification reactions catalyzed by Novozym 435: antioxidant properties and absence of toxicity in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 13:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203159
Nicolosi G, Piattelli ME, Sanfilippo C (1992) Acetylation of phenols in organic solvent catalyzed by a lipase from Chromobacterium viscosum. Tetrahedron 48:2477–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88766-4
Novaes FJM, Junior II, Sutili FK, Marriott PJ, Bizzo HR, Neto FRA, Souza ROMA, Rezende CM (2018) Lipase-catalysed esters synthesis of cafestol and kahweol. Food Chem 259:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.111
Ortiz C, Ferreira ML, Barbosa O, Dos Santos JCS, Rodrigues RC, Murcia AB, Briand LE, Lafuente RF (2019) Novozym 435: the “perfect” lipase immobilized biocatalyst? Catal Sci Technol 9:2380–2420. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CY00415G
Paroul N, Biasi A, Rovani AC, Prigol C, Dallago R, Treichel H, Cansian RL, Oliveira JV, Oliveira D (2010) Enzymatic production of linalool esters in organic and solvent-free. Syst Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-009-0384-z
Sánchez DA, Tonetto GM, Ferreira ML (2016) An insight on acyl migration in solvent-free ethanolysis of model triglycerides using Novozym 435. J Biotechnol 220:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.01.001
Ziaullah KS, Bhullar SN, Warnakulasuriya HP, Rupasinghe V (2013) Biocatalytic synthesis, structural elucidation, antioxidant capacity and tyrosinase inhibition activity of long chain fatty acid acylated derivatives of phloridzin and isoquercitrin. Bioorg Med Chem 21:684–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2012.11.034
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CAPES-grices (PROCAD- Grant Number 88881.068489/2014-01), CNPq (Produtividade em Pesquisa/PQ2014, Process 312045/2014-0 and Universal 2016-1, Process 430752/2016-4) and FAPERJ (Jovem Cientista do Nosso Estado/JCNE, Process E-26/202.728/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soares, V., Marini, M.B., de Paula, L.A. et al. Umbelliferone esters with antibacterial activity produced by lipase-mediated biocatalytic pathway. Biotechnol Lett 43, 469–477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03014-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03014-9