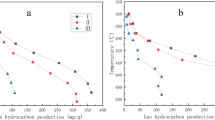
Late Triassic-early Jurassic silica rocks are widely developed in Northeast China. To evaluate the silica rock hydrocarbon generating capacity, we have simulated the hydrocarbon evolution process by thermal simulation experiments and analyzed the hydrocarbon generation characteristics. The experiments were carried out at six temperature points 250, 270, 290, 310, 330, and 350°C, and the content of the gaseous and liquid products was measured. The experiments results showed that the organic-rich siliceous rocks are characterized by a relatively high hydrocarbon-generating capacity. The gaseous products are generated at different temperatures, while natural gas is mainly generated when the peak period of oil generation is completed. Natural gas includes hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon gases. Hydrocarbon gases include methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, and other heavy hydrocarbon gases. Non-hydrocarbon gases include hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is the main component of the gas products, followed by hydrogen, methane, nitrogen, and other gases, but the total content of other gases is extremely low. Carbon dioxide generated during all stages of the oil generation process accounts for the vast majority, but in geological conditions, it will eventually be consumed by hydration. Nitrogen is mainly produced in the early stage. The content of hydrogen and hydrocarbon gases increases with increase in temperature, but hydrogen is usually depleted in the actual reservoir due to its strong chemical activity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Feng, H. Bao, J. Jia, Y. Wang, and X. Deng, “Lithofacies palaeogeography as a guide to petroleum exploration,” J. Palaeogeography, 2(2),109-126 (2013).
J. Ma, T. Zhang, and L. Xue, “Characteristics of the T3-J1 radiolarian chert and potential for hydrocarbon in Eastern Heilongjiang province,” Geol. Res., 17(4) 312-313 (2008).
F. Lu, J. Liu, Y. Li, and Z. Liu, “Types and characteristics of chert reservoirs in oversea petroliferous basins,” Pet. Explor. Dev., 38(5), 628-635 (2011).
X. Yao, Y. Zhou, S. Li et al., “Research status and advances in chert and Permian chert event,” Adv. Earth Sci., 28(11), 1189-1200 (2013).
G. Gao and G. Liu, “Simulation study of evolution characteristics of hydrocarbon generatedfrom blended organic matters in the Lacustrine source rock,” Bull. Mineral., Petrol. Geochem., 29(3), 233-237 (2010).
Y. Meng, W. Shen, X. Zhou, S. Li, D. Wang, W. Zhang, G. Qu, and C. Cui, “Characteristics of the Lower Cretaceous source rocks and shale gas exploration potential of eastern basin group, NE China,” Oil Gas Geol., 37(6), 893-902 (2016).
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (UNPYSCT-2016122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 6, pp. 86 – 90, November – December, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, G., Liu, N., Liu, Y. et al. Simulation Study of Hydrocarbon Generation Characteristics in Siliceous Rock. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 56, 985–993 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-021-01215-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-021-01215-0