Abstract
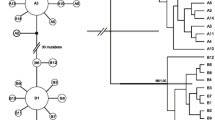
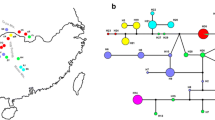
Hippuris vulgaris is a widespread aquatic plant in the Northern Hemisphere. Phylogenetic analysis on a low-copy nuclear gene (PHYB) indicated that this species originated from a hybridization between two unknown ancestral parents. Two distinct lineages (I and II) were detected using chloroplast intergenic regions, and their divergence time was 1.51 Ma. Lineage I was composed of the populations from North China, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP), and Europe while lineage II included the populations from North China, Europe and Japan. Based on the results of the Bayesian binary MCMC (BBM) analysis, QTP was likely the original center of these two lineages. The possible dispersal route for lineage I was inferred to be directly from QTP to North China and Europe, respectively, while lineage II likely dispersed first to Japan and from there moved separately to North China and Europe. In this study, we illustrate two important evolutionary events of H. vulgaris: hybridization and long-distance dispersals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken SG, Dallwitz MJ, Consaul LL, McJannet CL, Boles RL, Argus GW, Gillett JM, Scott PJ, Elven R, LeBlanc MC, Gillespie LJ, Brysting AK, Solstad H, Harris JG (2007) Flora of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago: descriptions, illustrations, identification, and information retrieval. NRC Research Press, National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa
Ali SS, Yu Y, Pfosser M, Wetschnig W (2012) Inferences of biogeographical histories within subfamily Hyacinthoideae using S-DIVA and Bayesian binary MCMC analysis implemented in RASP (Reconstruct Ancestral State in Phylogenies). Ann Bot (Oxford) 109:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr274
Alix K, Gérard PR, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (2017) Polyploidy and interspecific hybridization: partners for adaptation, speciation and evolution in plants. Ann Bot (Oxford) 120:183–194
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Röhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Molec Biol Evol 16:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036
Barker MS, Arrigo N, Baniaga AE, Li Z, Levin DA (2016) On the relative abundance of autopolyploids and allopolyploids. New Phytol 210:391–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13698
Becquey S, Gersonde R (2002) Past hydrographic and climatic changes in the Subantarctic Zone of the South Atlantic—The Pleistocene record from ODP Site 1090. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 182:221–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00497-7
Chen JM, Du ZY, Sun SS, Gituru RW, Wang QF (2013) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography reveals repeated range expansion in a widespread aquatic herb Hippuris vulgaris in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and adjacent areas. PLoS ONE 8:e60948. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060948
Dessborn L, Brochet AL, Elmberg J, Legagneux P, Gauthier-Clerc M, Guillemain M (2011) Geographical and temporal patterns in the diet of pintail Anas acuta, wigeon Anas penelope, mallard Anas platyrhynchos and teal Anas crecca in the Western Palearctic. Eur J Wildlife Res 57:1119–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-011-0577-z
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Molec Biol Evol 29:1969–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss075
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molec Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lacourse T, Mathewes RW, Fedje DW (2003) Paleoecology of late–glacial terrestrial deposits with in situ conifers from the submerged continental shelf of western Canada. Quatern Res 60:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-5894(03)00083-8
Lu Q, Zhu J, Yu D, Xu X (2016) Genetic and geographical structure of boreal plants in their southern range: phylogeography of Hippuris vulgaris in China. BMC Evol Biol 16:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-016-0603-6
McNeal JR, Bennett JR, Wolfe AD, Mathews S (2013) Phylogeny and origins of holoparasitism in Orobanchaceae. Amer J Bot 100:971–983. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1200448
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v1.4. Available at: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer.
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
Rozas J, Sanchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg359
Shaw J, Lickey EB, Schilling EE, Small RL (2007) Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: the tortoise and the hare III. Amer J Bot 94:275–288. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.94.3.275
Shi YF (2002) Characteristics of late Quaternary monsoonal glaciation on the Tibetan Plateau and in East Asia. Quatern Int 97:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1040-6182(02)00053-8
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Warner BG, Clague JJ, Mathewes RW (1984) Geology and paleoecology of a mid-Wisconsin peat from the Queen Charlotte Islands, British Columbia, Canada. Quatern Res 21:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/0033-5894(84)90073-5
Yamane K, Yano K, Kawahara T (2006) Pattern and rate of indel evolution inferred from whole chloroplast intergenic regions in sugarcane, maize and rice. DNA Res 13:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsl012
Zhang DF, Li FQ, Ben JM (2000) Eco–environmental effects of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau uplift during the Quaternary in China. Environm Geol 39:1352–1358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540000174
Zheng BX, Xu QQ, Shen YP (2002) The relationship between climate change and Quaternary glacial cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: review and speculation. Quatern Int 97:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1040-6182(02)00054-X
Zheng Z, Yuan BY, Petit-Maire N (1998) Paleoenvironments in China during the last glacial maximum and the Holocene optimum. Episodes 21:152–158
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Wolfram Lobin from Botanic Gardens University of Bonn, Marja Koistinen (Senior Museum Technician) from Botanical Museum of Finnish Museum of Natural History—LUOMUS, prof. Hans Henrik Bruun from University of Copenhagen, and Pin Guo for providing the materials from foreign countries. We thank our colleagues Tianfeng Lv, Yuqian Hunag, Fei Hao, Chunlin Fu, Fengqing Tian, Shengnan Wang, and Mingfang Du for assistance with the field collections and experiments.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XKD performed part of the analysis, made the Figures, uploaded the sequences into NCBI, and made a major contribution to writing the manuscript. XL analyzed part of the results and contributed to writing the manuscript. XYS was responsible for the most of the experiments. XL conceived the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling editor: Ying-Xiong Qiu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1. GenBank accession numbers of the trnT-psbD sequences.
Online Resource 2. GenBank accession numbers of the atpI-H sequences.
Online Resource 3. GenBank accession numbers of the PHYB sequences.
Online Resource 4. Phylogenic tree of Hippuris vulgaris based on the nuclear DNA region, PHYB, employing 241 sequences.
Online Resource 5. The alignment of the chloroplast sequences (trnT-psbD and atpI-H).
Online Resource 6. The alignment of the 241 PHYB sequences.
Online Resource 7. The alignment of the PHYB, from 50 individuals in 49 populations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, X., Li, X., Song, X. et al. The evolutionary history and phylogeographic pattern of Hippuris vulgaris: hybridization and long-distance dispersal from China. Plant Syst Evol 307, 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01739-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01739-8