Abstract
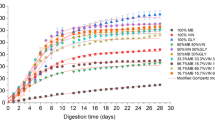
Anaerobic co-digestion of sludge from recycled pulp and paper industry (RPPS) with vinasse effluent from alcohol distilleries (VW) was performed under mesophilic conditions (37 °C) at laboratory scale, using one-liter continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTRs). The physicochemical parameters were monitored during the process. The average pH and alkalinity were 7.7 and 1000 mg CaCO3 Kg−1, respectively, indicating that the process is working well without the risk of acidification. The methane yield and biodegradability of this mixture were determined. The methane yield was about 112 (NmL CH4 g−1 VS added) and biodegradability reached 73%. Nevertheless, in monodigestion of RPPS, the methane yield was 94 (NmL CH4 g−1 VS added) and biodegradability 65%. The anaerobic co-digestion of (RPPS) with (VW) at a proportion of (70:30) improved methane production by 16% and biodegradability by 11%. Bioenergy recovery from industrial (RPPS) is promoted by co-digestion with (VW), and the removal efficiency of 73% indicates the performance of the process adopted. A kinetic study was performed using five models Richards, modified Gompertz, Logistic, Cone, and first order. The results show that Richards' was the most appropriate model for adjusting methane production from (RPPS) and (VW) co-digestion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Availability of data and material (data transparency)
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Anaerobic digestion
- CSTR:
-
Continuous stirred tank reactor
- RPPS:
-
Recycled Pulp and Paper Sludge
- VW:
-
Vinasse wastewater
- RPPI:
-
Recycled Pulp and Paper Industry
- EPD:
-
Ethanol Production Distilleries
- COD:
-
Chemical Oxygen Demand (g.L−1)
- TS:
-
Total Solids (%)
- VS:
-
Volatile Solids (%)
- FS:
-
Fixed Solids (%)
- OLR:
-
Organic Loading Rate (gVS.L−1. d−1)
References
Amahrouch A, (2012), Le biogas, Centre for the Development of Renewable Energy (CDER), Morocco, pp 13
Bakraoui M, Karouach F, Belhadj S, Joute Y, Ouhammou B, Aggour M, Essamri A, El Bari H, (2018), Modified Gompertz Kinetic Study of Methane Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Recycled Paper Mill Sludge, the 26th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, 14–17 May 2018, Copenhagen, Denmark, Poster presentation 2CV.7.20.
Bakraoui M, Karouach F, Ouhammou B, Aggour M, Essamri A, El Bari H, (2019) Kinetics study of the methane production from recycled pulp and paper sludge by CSTR technology. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag, Springer, ISSN 1438–4957.
Bakraoui M, Karouach F, Ouhammou B, Lahboubi N, El Gnaoui Y, Aggour M, El Bari H (2020) Kinetics study of methane production from anaerobic digestion of sludge and wastewater recycled pulp and paper by different models simulation. Int J Smart Grid Clean Energy 9(1):170–179
Balaguer MD, Vicent MT, Paris JM (1992) Anaerobic fluidized bed reactor with sepiolite as support for anaerobic treatment of vinasses. Biotechnol. Lett. 14:433–438. (Balaguer et al. 1992)
Belhadj S, Karouach F, ElBari H, Joute Y (2013) The biogas production from mesophilic anaerobic digestion of vinasse. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol (IOSR-JESTFT) 5:72–77
Belhadj S, Joute Y, El Bari H, Serrano A, Gil A, Siles JA, Chica AF, Martín MA (2014) Evaluation of the anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and tomato waste at mesophilic temperature. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:3862–3874
Camacho P, et Prévot C (2008) Méthanisation des boues. In: Moletta, R., La méthanisation (chap. 9, p. 205–233). Paris, Éditions Tec & Doc.
El Gnaoui Y, Sounni F, Bakraoui M, Karouach F, Benlemlih M, Barz M, El Bari H (2020) Anaerobic co-digestion assessment of olive mill wastewater and food waste: effect of mixture ratio on methane production and process stability. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103–874
Elouazzani DC (2005) Physico-chemical characterization and valorization in building and public works of ashes from the incineration of paper sludge, November 2005, Laboratory for Environmental Analysis of Industrial Processes and Systems.
Fu S-F, Xu X-H, Dai M, Yuan X-Z, Guo R-B (2017) Hydrogen and methane production from vinasse using two-stage anaerobic digestion. Process Saf Environ Prot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.01.024
González LML et al. (2017), Anaerobic co-digestion of sugarcane press mud with vinasse on methane yield, Universidad de Sancti Spíritus ‘‘José Martí Pérez”, pp 145
Hernandez SC (2005) Strategy for intelligent integrated control of wastewater treatment processes through anaerobic digestion, Doctoral thesis from the National Polytechnique Institut of Grenoble, p: 14, July 2005.
Jiménez AM, Borja R, Martin A (2002) Aerobic-anaerobic biodegradation of beet molasses alcoholic fermentation wastewater. Process Biochem 38:1275–1284
Jiménez AM, Borja R, Martin A (2004) A comparative kinetic evaluation of the anaerobic digestion of untreated molasses and molasses previously fermented with Penicillium decumbensin batch reactors. Biochem Eng J 18:121–132
Joute Y, El Bari H, Belhadj S, Karouach F, Gradi Y, Stelte W, Bjerre A (2016) Semi-continuous Anaerobic Co-digestion of cow manure and banana waste: Effects of mixture ratio. Appl Ecol Environ Res (AEE) 14(2):337–349
Kafle KK, Kim SH (2012) Kinetic study of the anaerobic digestion of swine manure at mesophilic temperature: a lab scale batch operation. J Biosyst Eng 37:233e244. https://doi.org/10.5307/JBE.2012.37.4.233
Karouach F, Gomhaned R, Bakraoui M, Gnaoui YE, Kerrou O, Lahboubi N, El Bari H (2020) Study of ultrasonic pre-treatment effect on the methanogenic potential of University Canteen Waste. In: Proceedings of 2019 7th international renewable and sustainable energy conference, IRSEC 2019.
Karouach F, Bakraoui M, El Gnaoui Y, Lahboubi N, El Bari H (2020) Effect of combined mechanical-ultrasonic pretreatment on mesophilic anaerobic digestion of household organic waste fraction in Morocco. Energy Rep 6:310–314
Lin Y et al. (2017) Anaerobic digestion of pulp and paper mill sludge pretreated by microbial consortium OEM1 with simultaneous degradation of lignocellulose and chlorophenols " South China Agricultural University, pp 108
Lopez JA, Martin Santos MA, Perez AFC, Martin AM (2009) Anaerobic digestion of glycerol derived from biodiesel. Biores Technol 2009:5609–5615
Martín MA, Siles JA, Chica AF, Martín A (2010) Biomethanization of orange peel. Biores Technol 101:8993–8999
Meng L, Jin K, Yi R, Chen M, Peng J, Pan Y (2020) Enhancement of bioenergy recovery from agricultural wastes through recycling of cellulosic alcoholic fermentation vinasse for anaerobic codigestion. Bioresour Technol 311:123511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123511
Moletta M (2005) Characterization of the airborne microbial diversity of biogas, Thesis of the Montpellier University II; P.17; December 2005.
Moletta R (2008) La méthanisation. p. 3. Handbook, édition LAVOISIER.
Mouline S (2012) Industrial waste, The guides CGEM; P.7–8; Mai 2012.
Mota VT, Araújo TA, Amaral MCS (2015) Comparison of Aerobic and Anaerobic Biodegradation of Sugarcane Vinasse. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176:1402–1412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1653-8
Pavlostathis SG, et Giraldo-Gomez E (1991) Kinetics of anaerobic treatment. Water Sci Technol 24(18):35–59
Robles-González a V, Galíndez-Mayera J, Rinderknecht-Seijas b N, Poggi-Varaldoc HM (2012) Treatment of mezcal vinasses: a review. J Biotechnol 157:524–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.09.006
Serrano A, Siles JÁ, Chica AF, Martín ÁM, Karouach F, Mesfioui A, El Bari H (2013) Mesophilic anaerobic co digestion of sewage sludge and orange peel waste, Enviromental Technology. Taylor & Francis, Abingdon
Siles JA, García-García I, Martín A, Martín MA (2011) ‘Integrated ozonation and biomethanization treatments of vinasse derived from ethanol manufacturing.’ J Hazard Mater 188:247–253
Switzenbaum MS, Giraldo-Gomez E, Hickey RF (1990) Monitoring of the anaerobic methane fermentation process. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:722–730
Thu LP (2013) Wet oxidation of effluents from sugarcane alcohol distilleries in the presence of RU and PT catalysts supported on TIO2 and ZRO2, Thesis from the University of Lyon, pp. 13–14
Vieira S, Hoffmann R (1977) Comparison of the logistic and the Gompertz growth functions considering additive and multiplicative error terms. J. R. Stat. Soc. 26:143e148. https://doi.org/10.2307/2347021
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the Research Institute in Solar Energy and New Energies (IRESEN) "www.iresen.org" for funding this research through Project “InnoThermo-InnoBiomass Digester 14.”
Funding
This study was funded by the Research Institute in Solar Energy and New Energies (IRESEN) "www.iresen.org’’ through Project “InnoThermo-InnoBiomass Digester 14.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, analysis, and modeling were performed by [Fadoua Karouach], [Mohammed Bakraoui], [Ayoub Zguani1], and [Aziz Hammadi]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [Fadoua Karouach] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The review and editing were performed by Hassan El Bari. Supervision was performed by Hassan El Bari.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no financial interests. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. Authors are responsible for correctness of the statements provided in the manuscript. See also Authorship Principles. The Editor-in-Chief reserves the right to reject submissions that do not meet the guidelines described in this section.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Zhenyao Shen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karouach, F., Bakraoui, M., Zguani, A. et al. Co-digestion of industrial recycled pulp and paper sludge with vinasse wastewater: experimental and theoretical study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 3651–3664 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03111-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03111-2