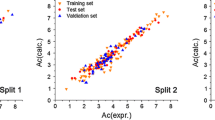
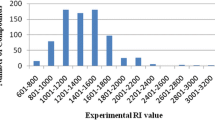
Abstract
Two homologous series of alkoxyphenylcarbamic acids esters with biological activities were subjected to the QSRR (Quantitative Structure–Retention Relationships) study. Retention factors of studied derivatives were measured in four different HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) systems. Experimental data in combination with in silico calculated molecular descriptors were used for development complex QSRR model for prediction of retention factor and partially for elucidation of separation mechanisms. The best results in QSRR modelling were given by artificial neural networks in the terms of developing one single robust model with high accuracy of logk prediction (\({Q}_{\mathrm{F}3}^{2}\) = 0.998) for all studied chromatographic systems. Chemometrical techniques were also used to elucidate the separation mechanisms occurring in the HPLC systems. We found similarities between particular systems and we identified systems which were the most suitable for separation of positional isomers of studied compounds. We observed that solvent significantly influenced the chromatographic separation of positional isomers depending on the used column, whereas combination of acetonitrile and C18-phenyl column caused suppression of π − π interactions, so retention was wholly determined by the hydrophobic interactions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AcN:
-
Acetonitrile
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural networks
- CL:
-
Chain length
- DPCA:
-
2-Dimethylamino ethyl esters of alkoxyphenylcarbamic acid
- Etype:
-
Type of ester
- HE:
-
Hydration energy
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- MeOH:
-
Methanol
- MLR:
-
Multiple linear regression
- MS:
-
Molecular surface
- MV:
-
Molecular volume
- MW:
-
Molecular weight
- NUC:
-
Nucleodur-Sphinx C18-Phenyl column
- PC:
-
Principal component
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- Plr:
-
Polarizability
- PPCA:
-
2-Pyrrolidine-1-yl-ethyl esters of alkoxyphenylcarbamic acid
- Ptype:
-
Type of position
- QSAR:
-
Quantitative structure–activity relationship
- QSRR:
-
Quantitative structure–retention relationship
- Ref:
-
Refractivity
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- RP:
-
Reversed phase
- SASA:
-
Solvent accessible surface area
- YMC:
-
YMC-Triart C18 column
References
Arase S, Kimura S, Ikegami T (2018) Method optimization of hydrophilic interaction chromatography separation of nucleotides using design of experiment approaches I: comparison of several zwitterionic columns. J Pharm Biomed Anal 158:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.05.014
Bak A, Kozik V, Malík I, Jampílek J, Smolinski A (2018) Probability-driven 3D pharmacophore mapping of antimycobacterial potential of hybrid molecules combining phenylcarbamoyloxy and N-arylpiperazine fragments. SAR QSAR Environ Res 29(10):801–821. https://doi.org/10.1080/1062936X.2018.1517278
Bodzioch K, Durand A, Kaliszan R, Bączek T, Vander Heyden Y (2010) Advanced QSRR modeling of peptides behavior in RPLC. Talanta 81:1711–1718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.03.028
Consonni V, Ballabio D, Todeschini R (2010) Evaluation of model predictive ability by external validation techniques. J Chemom 24(3–4):194–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.1290
Daghir-Wojtkowiak E, Studzińska S, Buszewski B, Kaliszan R, Markuszewski MJ (2014) Quantitative structure-retention relationships of ionic liquid cations in characterization of stationary phases for HPLC. Anal Methods 4:1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AY41805G
Ďurčeková T, Mocák J, Lehotay J, Čižmárik J, Boronová K (2010) Chemometrical study of the anaesthetical activity of alkoxyphenylcarbamic acid esters. Pharmazie 65(3):169–174. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2010.9691
Ďurčeková T, Boronová K, Mocák J, Lehotay J, Čižmárik J (2012) QSRR models for potential local anaesthetic drugs using high performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 59:209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2011.09.035
Fouad MA, Tolba EH, El-Shal MA, El Kerdawy AM (2018) QSRR modeling for the chromatographic retention behavior of some β-lactam antibiotics using forward and firefly variable selection algorithms coupled with multiple linear regression. J Chromatogr A 1549:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.03.042
Golubović J, Protić A, Otašević B, Zečević M (2016) Quantitative structure-retention relationships applied to development of liquid chromatography gradient-elution method for the separation of sartans. Talanta 150:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.035
Gyűrösiová L, Sedlárová E, Čižmárik J (2002) Study of local anaesthetics, part 156: Some physicochemical and lipophilic properties of pyrrolidinoethyl esters of o-, m-, p-alkoxy-substituted phenylcarbamic acid. Chem Pap 56(5):340–344
Héberger K (2007) Quantitative structure-(chromatographic) retention relationships. J Chromatogr A 1158(1–2):273–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.03.108
HyperChem(TM) Professional 8.06, Hypercube, Inc., 1115 NW 4th Street, Gainesville, Florida 32601, USA
IBM Corp (2013) Released 2013. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0. IBM Corp, Armonk
Jevrić LR, Karadžić MŽ, Mandić AI, Podunavac-Kuzmanović SO, Kovačević SZ, Nikolić AR, Oklješa AM, Sakač MN, Penov Gaši KM, Stojanović SZ (2017) Lipophilicity estimation and characterization of selected steroid derivatives of biomedical importance applying RP HPLC. J Pharm Biomed Anal 134:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2016.11.015
JMP® Version 11. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, 1989–2007
Karadžić MŽ, Lončar DM, Benedeković G, Kovačević I, Popsavin V, Kovačević SZ, Jevrić LR, Podunavac-Kuzmanović SO (2017) A comparative study of chromatographic behavior and lipohilicity of selected natural styryl lactones, their derivatives and analogues. Eur J Pharm Sci 105:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.05.006
Kouskoura MG, Kachrimanis KG, Markopoulou CK (2014) Modeling the drugs’ passive transfer in the body based on their chromatographic behavior. J Pharm Biomed Anal 100:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.07.031
Malík I, Csöllei J, Solovič I, Pospíšilová Š, Michnová H, Jampílek J, Čížek A, Kapustíková I, Čurillová J, Pecháčová M, Stolaříková J, Pecher D, Oravec M (2018) Dibasic derivatives of phenylcarbamic acid against mycobacterial strains: old drugs and new tricks? Molecules 23(10):2493. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102493
Park SH, De Pra M, Haddad PR, Grosse S, Pohl CA, Steiner F (2020) Localised quantitative structure-retention relationship modeling for rapid method development in reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1609:460508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460508
Plenis A, Olędzka I, Bączek T (2013) Classification of LC columns based on the QSRR method and selectivity toward moclobemide and its metabolites. J Pharm Biomed Anal 78–79:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2013.02.020
Pospíšilová Š, Malík I, Bezoušková K, Kauerová T, Kollár P, Csöllei J, Oravec M, Čížek A, Jampílek J (2020) Dibasic derivatives of phenylcarbamic acid as prospective antibacterial agents interacting with cytoplasmic membrane. Antibiotics 9(2):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020064
StatSoft Inc. (2009) Statistica Neural Networks v80 (software). StatSoft Inc., Tulsa
Stankovičová M, Miháliková V, Mezovský Ľ, Lašáková A, Medlenová V, Malík I (2015) Phenylcarbamic acid derivatives with integrated n-phenylpiperazine moiety in the structure kinetics of alkaline hydrolysis study. Acta Fac Pharm Univ Comen 57(2):38–42. https://doi.org/10.1515/afpuc-2015-0032
Stanzel L, Maruniak M, Malík I, Havranová Sichrovská Ľ, Kapustíková I, Sedlárová E, Csöllei J (2015) Synthesis and antioxidant activity of phenylcarbamic acid derivatives acting on the cardiovascular system. Ceska Slov Farm 64(6):291–293 (PMID:26837882)
Studzińska S, Buszewski B (2015) Different approaches to quantitative structure-retention relationships in the prediction of oligonucleotide retention. J Sep Sci 38(12):2076–2084. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201401395
Studzińska S, Molíková M, Kosobucki P, Jandera P, Buszewski B (2011) Study of the interactions of ionic liquids in IC by QSRR. Chromatographia 73(Suppl 1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-011-1960-3
Studzińska S, Bocian S, Siecińska L, Buszewski B (2017) Application of phenyl-based stationary phases for the study of retention and separation of oligonucleotides. J Chromatogr B 1060:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.05.033
Taraji M, Haddad PR, Amos RIJ, Talebi M, Szucz R, Dolan JW, Pohl CA (2017) Prediction of retention in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography using solute molecular descriptors based on chemical structures. J Chromatogr A 1486:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.025
Trifunović Ristovski J, Janković N, Borčić V, Jain S, Bugarčić Z, Mikov M (2018) Evaluation of antimicrobial activity and retention behavior of newly synthesized vanilidene derivatives of Meldrum’s acids using QSRR approach. J Pharm Biomed Anal 155:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.03.038
VCCLAB (2005) Virtual Computational Chemistry Laboratory, http://www.vcclab.org. Accessed 25 May 2019
Wahajuddin SSP, Raju KSR, Nafis A, Jain GK (2012) Simultaneous determination of nine model compounds in permeability samples using RP-HPLC: Application to prove the cassette administration principle in single pass intestinal perfusion study in rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal 67–68:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2012.03.048
Waisser K, Čižmárik J (2012) Derivatives of phenylcarbamic acid as potential antituberculotics. Ceska Slov Far 61(1–2):17–20 (PMID: 22536648)
Wöll S, Schiller S, Bachran C, Swee LK, Scherließ R (2018) Pentaglycine lipid derivatives rp-HPLC analytics for biorthogonal anchor molecules in targeted, multiple-composite liposomal drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm 547(1–2):602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.05.052
Yang M, Fazio S, Munch D, Drumm P (2005) Impact of methanol and acetonitrile on separations based on π–π interactions with a reversed-phase phenyl column. J Chromatogr A 1097(1–2):124–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.08.028
Yang X, Peng H, Han N, Zhang Z, Bai X, Zhao T, Zhao J, Liu J (2020) Quantitative structure-chromatographic retention relationship of synthesized peptides (HGRFG, NPNPT) and their derivatives. Anal Biochem 597:113653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113653
Zapadka M, Kaczmarek M, Kupcewicz B, Dekowski P, Walkowiak A, Kokotkiewicz A, Łuczkiewicz M, Buciński A (2019) An application of QSRR approach and multiple linear regression method for lipophilicity assessment of flavonoids. J Pharm Biomed Anal 164:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.11.024
Zhang X, Lin J, Wang C, Song D, Hu C (2017) Identification of impurities in macrolides by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric detection and prediction of retention times of impurities by constructing quantitative structure-retention relationship (QSRR). J Pharm Biomed Anal 145:262–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.06.069
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by VEGA 1/0048/19 and VEGA 1/0919/17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranušová, P., Nemeček, P., Lehotay, J. et al. QSRR modelling aimed on the HPLC retention prediction of dimethylamino- and pyrrolidino-substitued esters of alkoxyphenylcarbamic acid. Chem. Pap. 75, 2525–2535 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01470-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01470-1