Abstract
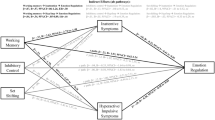
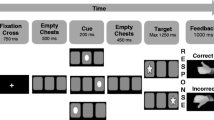
Emotional Lability (EL) is a source of impairment in multiple mental disorders of children, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It has been proposed that the overlap between EL and ADHD symptoms is the result of common neuropsychological deficits. The aim of the present study was to test this hypothesis by using a multi-method approach. In a mixed sample of 61 children (49 community sample and 12 children with an ADHD diagnosis) aged between 8 and 12 years, we examined the relationship between parental reports of ADHD and EL, real-time children’s emotional expressions in an experimental context, children’s performance on neuropsychological tasks and parental ratings of neuropsychological functioning. Parental EL ratings were significantly predicted by task-based reaction time variability and by questionnaire measures of Self-Direction & Organization and Arousal Regulation. Parental EL ratings were also significantly related to both ADHD symptom dimensions. After controlling for shared neuropsychological factors, ADHD symptoms no longer predicted parental EL ratings. Neuropsychological task performance was not significantly related to real time emotional expressions. However, positive emotional expressions were significantly predicted by higher parental ratings of Cognition and negative emotional expressions by parental ratings of low Effort engagement – accounting for some of the correlation with ADHD symptoms. The current results highlight the plausible role of cognitive energetic processes in explaining the EL and ADHD symptom association.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amsel, A. (1958). The role of frustrative nonreward in noncontinuous reward situations. Psychological Bulletin, 55(2), 102–119.
Amsel, A. (1962). Frustrative nonreward in partial reinforcement and discrimination learning: Some recent history and a theoretical extension. Psychological Review, 69(4), 306–328.
Amsel, A. (1992). Frustration theory: Many years later. Psychological Bulletin, 112(3), 396–399.
Anastopoulos, A. D., Smith, T. F., Garrett, M. E., Morrissey-Kane, E., Schatz, N. K., Sommer, J. L., Kollins, S. H., & Ashley-Koch, A. (2011). Self-regulation of emotion, functional impairment, and comorbidity among children with AD/HD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 15(7), 583–592. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054710370567.
Banaschewski, T., Jennen-Steinmetz, C., Brandeis, D., Buitelaar, J. K., Kuntsi, J., Poustka, L., ... Asherson, P. (2012). Neuropsychological correlates of emotional lability in children with ADHD. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 2012(6), 1469–7610.
Barkley, R. A. (1997). Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: Constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychological Bulletin, 121(1), 65–94.
Barkley, R. A. (2010). Why emotional impulsiveness should be a central feature of ADHD. The ADHD Report, 18(4), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1521/adhd.2010.18.4.1.
Barkley, R. A., & Fischer, M. (2010). The unique contribution of emotional impulsiveness to impairment in major life activities in hyperactive children as adults. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(5), 503–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2010.01.019.
Barrett, L. F., Quigley, K. S., Bliss-Moreau, E., & Aronson, K. R. (2004). Interoceptive sensitivity and self-reports of emotional experience. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87(5), 684–697. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.87.5.684.
Beauchaine, T. P. (2015). Future directions in emotion Dysregulation and youth psychopathology. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 44(5), 875–896. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2015.1038827.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society: series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
Bitsakou, P., Psychogiou, L., Thompson, M., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S. (2009). Delay aversion in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: An empirical investigation of the broader phenotype. Neuropsychologia, 47(2), 446–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.09.015.
Blair, C. (2002). School readiness: Integrating cognition and emotion in a neurobiological conceptualization of children's functioning at school entry. American Psychologist, 57(2), 111–127.
Bolea-Alamañac, B., Nutt, D. J., Adamou, M., Asherson, P., Bazire, S., Coghill, D., ... & Sayal, K. (2014). Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Update on recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 28(3), 179–203.
Bunford, N., Evans, S. W., & Langberg, J. M. (2014). Emotion Dysregulation is associated with social impairment among young adolescents with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 22, 66–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054714527793.
Bush, G., Luu, P., & Posner, M. I. (2000). Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(6), 215–222.
Childress, A. C., & Sallee, F. R. (2015, August 13). Emotional lability in patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Impact of pharmacotherapy. CNS Drugs, 29, 683–693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-015-0264-9.
Coghill, D., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. (2012). Annual research review: Categories versus dimensions in the classification and conceptualisation of child and adolescent mental disorders–implications of recent empirical study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(5), 469–489.
Coghill, D. R., Seth, S., & Matthews, K. (2013). A comprehensive assessment of memory, delay aversion, timing, inhibition, decision making and variability in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: advancing beyond the three-pathway models. Psychol Med, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291713002547.
Dovis, S., Van der Oord, S., Wiers, R. W., & Prins, P. J. M. (2012). Can motivation normalize working memory and task persistence in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? The effects of money and computer-gaming. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(5), 669–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-011-9601-8.
Ebner-Priemer, U. W., & Trull, T. J. (2009). Ambulatory assessment an innovative and promising approach for clinical psychology. European Psychologist, 14(2), 109–119. https://doi.org/10.1027/1016-9040.14.2.109.
Elmaghrabi, S., Nahmias, M. J., Adamo, N., Di Martino, A., Somandepalli, K., Patel, V., et al. (2020). Is increased response time variability related to deficient emotional self-regulation in children with ADHD? Journal of Attention Disorders, 24(7), 1045–1056.
Fortunato, C. K., Gatzke-Kopp, L. M., & Ram, N. (2013). Associations between respiratory sinus arrhythmia reactivity and internalizing and externalizing symptoms are emotion specific. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 13(2), 238–251. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-012-0136-4.
Gisbert, L., Richarte, V., Corrales, M., Ibáñez, P., Bosch, R., Bellina, M., Fadeuilhe, C., Casas, M., & Ramos-Quiroga, J. A. (2019). The relationship between neuropsychological deficits and emotional Lability in adults with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 23(12), 1514–1525.
Graziano, P. A., & Garcia, A. (2016). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and children's emotion dysregulation: A meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 46, 106–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2016.04.011.
Groves, N. B., Kofler, M. J., Wells, E. L., Day, T. N., & Chan, E. S. (2020). An examination of relations among working memory, ADHD symptoms, and emotion regulation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 1–13.
Haslam, N., Williams, B., Prior, M., Haslam, R., Graetz, B., & Sawyer, M. (2006). The latent structure of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A taxometric analysis. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 40(8), 639–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1614.2006.01863.x.
Hoeksma, J. B., Oosterlaan, J., & Schipper, E. M. (2004). Emotion regulation and the dynamics of feelings: A conceptual and methodological framework. Child Development, 75(2), 354–360.
Jensen, D. A., Høvik, M. F., Monsen, N. J. N., Eggen, T. H., Eichele, H., Adolfsdottir, S., Plessen, K. J., & Sørensen, L. (2018). Keeping emotions in mind: The influence of working memory capacity on parent-reported symptoms of emotional lability in a sample of children with and without ADHD. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1846.
Kaufman, J., Birmaher, B., Brent, D., Rao, U. M. A., Flynn, C., Moreci, P., ... & Ryan, N. (1997). Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): Initial reliability and validity data. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(7), 980–988.
Kring, A. M., & Sloan, D. M. (2007). The facial expression coding system (FACES): Development, validation, and utility. Psychological Assessment, 19(2), 210–224.
Kuntsi, J., Oosterlaan, J., & Stevenson, J. (2001a). Psychological mechanisms in hyperactivity: I response inhibition deficit, working memory impairment, delay aversion, or something else? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42(2), 199–210.
Kuntsi, J., Stevenson, J., Oosterlaan, J., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. (2001b). Test-retest reliability of a new delay aversion task and executive function measures. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 19(3), 339–348.
Kuntsi, J., Wood, A. C., Van Der Meere, J., & Asherson, P. (2009). Why cognitive performance in ADHD may not reveal true potential: findings from a large population-based sample. J Int Neuropsychol Soc, 15(4), 570–579. https://doi.org/10.1017/S135561770909081X.
Lilienfeld, S. O. (2014). The research domain criteria (RDoC): An analysis of methodological and conceptual challenges. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 62, 129–139.
Liu, L., Chen, W., Sun, L., Cheng, J., Su, Y., Rudaizky, D., Li, H. M., Yang, L., Qian, Q. J., & Wang, Y.-F. (2017). The characteristics and age effects of emotional Lability in ADHD children with and without oppositional defiant disorder. Journal of Attention Disorders, 2042–2053. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054717745594.
Liu, L., Chen, W., Vitoratou, S., Sun, L., Yu, X., Hagger-Johnson, G., Wu, Z., Yang, L., Qian, Q., & Wang, Y. (2019). Is Emotional Lability Distinct From “Angry/Irritable Mood,” “Negative Affect,” or Other Subdimensions of Oppositional Defiant Disorder in Children With ADHD? Journal of Attention Disorders, 23(8), 859–868. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054715624228.
Luman, M., Oosterlaan, J., & Sergeant, J. A. (2005). The impact of reinforcement contingencies on AD/HD: A review and theoretical appraisal. Clinical Psychology Review, 25(2), 183–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2004.11.001.
Luman, M., van Noesel, S. J., Papanikolau, A., Van Oostenbruggen-Scheffer, J., Veugelers, D., Sergeant, J. A., & Oosterlaan, J. (2009). Inhibition, reinforcement sensitivity and temporal information processing in ADHD and ADHD+ODD: Evidence of a separate entity? J Abnorm Child Psychol, 37(8), 1123–1135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-009-9334-0.
Machado, L., & Cantilino, A. (2017). A systematic review of the neural correlates of positive emotions. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria, 39(2), 172–179. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2016-1988.
Marco, R., Miranda, A., Schlotz, W., Melia, A., Mulligan, A., Muller, U., ... Sonuga-Barke, E. J. (2009). Delay and reward choice in ADHD: an experimental test of the role of delay aversion. Neuropsychology, 23(3), 367–380. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014914.
Martin, R. E., & Ochsner, K. N. (2016). The neuroscience of emotion regulation development: Implications for education. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 10, 142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.06.006.
Martinussen, R., & Tannock, R. (2006). Working memory impairments in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with and without comorbid language learning disorders. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 28(7), 1073–1094.
Merwood, A., Chen, W., Rijsdijk, F., Skirrow, C., Larsson, H., Thapar, A., Kuntsi, J., & Asherson, P. (2014). Genetic associations between the symptoms of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder and emotional lability in child and adolescent twins. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 53(2), 209–220.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2013.11.006.
Metin, B., Roeyers, H., Wiersema, J. R., van der Meere, J., & Sonuga-Barke, E. (2012). A meta-analytic study of event rate effects on go/no-go performance in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 72(12), 990–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.08.023.
Nichols, S. L., & Waschbusch, D. A. (2004). A review of the validity of laboratory cognitive tasks used to assess symptoms of ADHD. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 34(4), 297–315.
Nigg, J. T. (2006). What causes ADHD? Understanding what Goes wrong and why. New York: The Guilford Press.
Nutt, D. J., Fone, K., Asherson, P., Bramble, D., Hill, P., Matthews, K., ... & Weiss, M. (2007). Evidence-based guidelines for management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adolescents in transition to adult services and in adults: Recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 21(1), 10–41.
Ochsner, K. N., Silvers, J. A., & Buhle, J. T. (2012). Functional imaging studies of emotion regulation: A synthetic review and evolving model of the cognitive control of emotion. In A. Kingstone & M. B. Miller (Eds.), Year in Cognitive Neuroscience (Vol. 1251, pp. E1-E24).
Oosterlaan, J., Baeyens, D., Scheres, A., Antrop, I., Roeyers, H., & Sergeant, J. (2008). VvGK6–16: Vragenlijst voor gedragsproblemen bij kinderen 6 tot en met 16 jaar. Amsterdam: Pearson.
Orobio de Castro, B., Slot, N. W., Bosch, J. D., Koops, W., & Veerman, J. W. (2003). Negative feelings exacerbate hostile attributions of intent in highly aggressive boys. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 32(1), 56–65. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3201_06.
Rhodes, S. M., Park, J., Seth, S., & Coghill, D. R. (2012). A comprehensive investigation of memory impairment in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder. J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 53(2), 128–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02436.x.
Rosen, P. J., Walerius, D. M., Fogleman, N. D., & Factor, P. I. (2015). The association of emotional lability and emotional and behavioral difficulties among children with and without ADHD. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord, 7(4), 281–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-015-0175-0.
Russell, J., & Barrett, L. (1999). Core affect, prototypical emotional episodes, and other things called emotion: Dissecting the elephant. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76(5), 805–819.
Scheres, A., Oosterlaan, J., & Sergeant, J. A. (2001). Response execution and inhibition in children with AD/HD and other disruptive disorders: The role of behavioural activation. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 42(3), 347–357.
Seidman, L. J. (2006). Neuropsychological functioning in people with ADHD across the lifespan. Clinical Psychology Review, 26(4), 466–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2006.01.004.
Sergeant, J. (2000). The cognitive-energetic model: An empirical approach to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(1), 7–12.
Sergeant, J. (2005). Modeling attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A critical appraisal of the cognitive-energetic model. Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1248–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bps.2004.09.010.
Shanahan, M. A., Pennington, B. F., Yerys, B. E., Scott, A., Boada, R., Willcutt, E. G., ... DeFries, J. C. (2006). Processing speed deficits in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and reading disability. J Abnorm Child Psychol, 34(5), 585-602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-006-9037-8.
Shaw, P., Stringaris, A., Nigg, J., & Leibenluft, E. (2014). Emotion dysregulation in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 171(3), 276–293. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13070966.
Shrout, P. E., & Fleiss, J. L. (1979). Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychological Bulletin, 86(2), 420–428.
Sjöwall, D., Roth, L., Lindqvist, S., & Thorell, L. B. (2013). Multiple deficits in ADHD: Executive dysfunction, delay aversion, reaction time variability, and emotional deficits. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54(6), 619–627.
Skirrow, C., & Asherson, P. (2013). Emotional lability, comorbidity and impairment in adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 147(1–3), 80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2012.10.011.
Skirrow, C., McLoughlin, G., Kuntsi, J., & Asherson, P. (2009). Behavioral, neurocognitive and treatment overlap between attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and mood instability. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 9(4), 489–503. https://doi.org/10.1586/ern.09.2.
Smith, A., Taylor, E., Rogers, J. W., Newman, S., & Rubia, K. (2002). Evidence for a pure time perception deficit in children with ADHD. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43(4), 529–542.
Sobanski, E., Banaschewski, T., Asherson, P., Buitelaar, J., Chen, W., Franke, B., Holtmann, M., Krumm, B., Sergeant, J., Sonuga-Barke, E., Stringaris, A., Taylor, E., Anney, R., Ebstein, R. P., Gill, M., Miranda, A., Mulas, F., Oades, R. D., Roeyers, H., Rothenberger, A., Steinhausen, H. C., & Faraone, S. V. (2010). Emotional lability in children and adolescents with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Clinical correlates and familial prevalence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51(8), 915–923. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02217.x.
Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., Taylor, E., Sembi, S., & Smith, J. (1992). Hyperactivity and delay aversion—I. The effect of delay on choice. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 33(2), 387–398.
Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., Bitsakou, P., & Thompson, M. (2010). Beyond the dual pathway model: Evidence for the dissociation of timing, inhibitory, and delay-related impairments in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(4), 345–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2009.12.018.
Stringaris, A., & Goodman, R. (2009). Three dimensions of oppositionality in youth. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(3), 216–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01989.x.
Surman, C. B. H., Biederman, J., Spencer, T., Miller, C. A., Petty, C. R., & Faraone, S. V. (2015). Neuropsychological deficits are not predictive of deficient emotional self-regulation in adults with ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 19(12), 1046–1053. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054713476548.
Toplak, M. E., & Tannock, R. (2005). Tapping and anticipation performance in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 100(3), 659–675. https://doi.org/10.2466/pms.100.3.659-675.
Toplak, M. E., Dockstader, C., & Tannock, R. (2006). Temporal information processing in ADHD: findings to date and new methods. J Neurosci Methods, 151(1), 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2005.09.018.
Toplak, M. E., West, R. F., & Stanovich, K. E. (2012). Practitioner review: Do performance-based measures and ratings of executive function assess the same construct? J Child Psychol Psychiatry, 54(2), 131–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12001.
van der Meere, J. (2005). State regulation and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. In Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (pp. 413–433). Totowa: Humana Press.
van der Oord, S., & Tripp, G. (2020). How to improve behavioral parent and teacher training for children with ADHD: Integrating empirical research on learning and motivation into treatment. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 23, 577–604.
Van Liefferinge, D., Sonuga-Barke, E., Van Broeck, N., Van Der Oord, S., Lemiere, J., & Danckaerts, M. (2017). A rating measure of ADHD-related neuropsychological impairment in children and adolescents: Data from the cognition and motivation in everyday life (CAMEL) scale from population and clinical samples. Child Neuropsychol, 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049.2016.1170798.
Van Liefferinge, D., Sonuga-Barke, E., Danckaerts, M., Van Broeck, N., & Van Der Oord, S. (2018). Measuring child and adolescent emotional lability: How do questionnaire-based ratings relate to experienced and observed emotion in everyday life and experimental settings? International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research, 27(3), e1720.
Verbruggen, F., Logan, G. D., & Stevens, M. A. (2008). STOP-IT: Windows executable software for the stop-signal paradigm. Behavior Research Methods, 40(2), 479–483.
Verbruggen, F., Chambers, C. D., & Logan, G. D. (2013). Fictitious inhibitory differences: How skewness and slowing distort the estimation of stopping latencies. Psychological Science, 24(3), 352–362.
von Leupoldt, A., Rohde, J., Beregova, A., Thordsen-Sorensen, I., zur Nieden, J., & Dahme, B. (2007). Films for eliciting emotional states in children. Behavior Research Methods, 39(3), 606–609.
Walcott, C. M., & Landau, S. (2004). The relation between disinhibition and emotion regulation in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33(4), 772–782. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp3304_12.
Willcutt, E. G. (2012). The prevalence of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analytic review. Neurotherapeutics, 9(3), 490–499.
Willcutt, E. G., Doyle, A. E., Nigg, J. T., Faraone, S. V., & Pennington, B. F. (2005). Validity of the executive function theory of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analytic review. Biological Psychiatry, 57(11), 1336–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.02.006.
Zelazo, P. D., & Cunningham, W. A. (2007). Executive Function: Mechanisms Underlying Emotion Regulation. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of emotion regulation (p. 135–158). The Guilford Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the regional ethics committee.
Conflict of Interest
Edmund J S Sonuga-Barke declares the following competing interests: Fees for speaking, consultancy, research funding and conference support from Shire Pharma; Speaker fees from Janssen Cilag, Medice & Qbtech; Book royalties from OUP and Jessica Kingsley; Consultancy from Neurotech solutions.
Marina Danckaerts declares the following competing interests: Fees for speaking, consultancy, research funding and conference support from Shire and Janssen Cilag Pharma; Book royalties from OUP and Van Gorcum; Consultancy from Neurotech solutions.
Saskia van der Oord has been involved in the development, implementation, and trialing of an executive functioning game training for children with ADHD, and a cognitive behavioral planning intervention for adolescents with ADHD. She has no financial interests in either of these interventions. She was a speaker for Medice & Shire.
The present study is unrelated to the above grants and relationships. The other author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Liefferinge, D., Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S., Danckaerts, M. et al. Do Childhood Emotional Lability and ADHD Symptoms Have Shared Neuropsychological Roots?. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 43, 491–505 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-020-09859-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-020-09859-8