Abstract
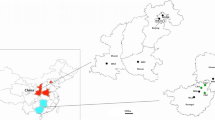
Rhododendron brachycarpum is an ecologically important tree species with a narrow, fragmented geographic range in East Asia. R. brachycarpum is distributed primarily in Korea and Japan, with two small isolated populations in the Russian Far East. We obtained 124 samples from seven populations of R. brachycarpum, representing all geographical regions of its entire natural range, and we utilized microsatellite markers to estimate the level of genetic variation within and between populations. A total of 200 alleles based on 14 nuclear microsatellites loci were identified. High diversity (He = 0.556–0.626) was observed in populations from Korea and Japan. In contrast, in peripheral populations from Russia diversity was quite low (He = 0.100–0.369) with a high coefficient of inbreeding (FIS = 0.471–0.526). Strong population differentiation (FST = 0.356) and clear distinction among the geographical groups (FCT = 0.227) were revealed. Bayesian clustering and principal coordinate analyses indicated that two Russian populations, Sikhote-Alin and Iturup Island, represent extremes of two different migration routes, with one derived from the mainland and one from Japan.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data (microsatellite genotypes) available in Supplemental data.
References
Aizawa M, Yoshimaru H, Saito H, Katsuki T, Kawahara T, Kitamura K, Shi F, Kaji M (2007) Phylogeography of a northeast Asian spruce, Picea jezoensis, inferred from variation observed in organelle DNA markers. Molec Ecol 16:3393–3405. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03391.x
Aizawa M, Yoshimaru H, Takahashi M, Kawahara T, Sugita H, Saito H, Sabirov R (2015) Genetic structure of Sakhalin spruce (Picea glehnii) in northern Japan and adjacent regions revealed by nuclear microsatellites and mitochondrial gene sequences. J Pl Res 128:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-014-0682-7
Altman J, Ukhvatkina ON, Omelko AM, Macek M, Plener T, Pejcha V, Cerny T, Petrik P, Srutek SJS, Zhmerenetsky AA, Vozmishcheva AS, Krestov PV, Petrenko TY, Treydte K, Dolezal J (2018) Pole ward migration of the destructive effects of tropical cyclones during the 20th century. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:11543–11548. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1808979115
Arnaud-Haond S, Belkhir K (2007) GenClone: a computer program to analyse genotipyc data, test for clonality and describe spatial clonal organization. Molec Ecol Notes 7:15–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01522.x
Association of wildlife research, office envision on conservation of environment (2004–2019). Search system of Japanese red data. Available at: http://jpnrdb.com/. Accessed 9 Feb 2019.
Averkova GP (2008) Rhododendron brachycarpum The red data book of Russian federation (Plants and fungi). KMK Scientific Press, Moscow
Barkalov VYu (2009) Flora of the Kuril Islands. Dalnauka, Vladivostok pp 125–126 (in Russian)
Bondarchuk SN (2014) Features of flowering and fruiting of Rhododendron fauriei Franch. in the Sikhote-Alin Reserve. In: Pugachevsky (ed) Current status, development trends, rational use and preservation of the biological diversity of the plant world: materials of the Intern. scientific conf. Ecoperspectiva, Minsk, pp 174–177 (in Russian)
Brookfield J (1996) A simple new method for estimating null allele frequency from heterozygote deficiency. Molec Ecol 5:453–455. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.1996.00098.x
Chamberlain DF, Hyam R, Argent G, Fairweather G, Walter KS (1996) The genus Rhododendron–its classification and synonymy. Royal Botanical Garden of Edinburgh Press, Edinburgh
Charrier O, Dupont P, Pornon A, Escaravage N (2014) Microsatellite marker analysis reveals the complex phylogeographic history of Rhododendron ferrugineum (Ericaceae) in the Pyrenees. PLoS ONE 9:e92976. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092976
Chung MY, López-Pujol J, Chung MG (2014) Comparative genetic structure between Sedum ussuriense and S. kamtschaticum (Crassulaceae), two stonecrops co-occurring on rocky cliffs. Amer J Bot 101:46–956. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1400108
Chung MY, López-Pujol J, Chung MG (2016) Is the Baekdudaegan “the Southern Appalachians of the East”? A comparison between these mountain systems, focusing on their role as glacial refugia. Keran J Pl Taxon 46:337–347. https://doi.org/10.11110/kjpt.2016.46.4.337
Chung MY, López-Pujol J, Chung MG (2017) The role of the Baekdudaegan (Korean Peninsula) as a major glacial refugium for plant species: a priority for conservation. Biol Conserv 206:236–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.11.040
Devey ME, Bell JC, Smith DN, Neale DB, Moran GF (1996) A genetic linkage map for Pinus radiata based on RFLP, RAPD and microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 92:673–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226088
Doleshy F (1983) Distribution and classiication of certain Japanese Rhododendrons. JARS 37:2. Available at: https://scholar.lib.vt.edu/ejournals/JARS/v37n2/v37n2-doleshy.htm
Escaravage N, Questiau S, Pornon A, Doche B, Taberlet P (1998) Clonal diversity in Rhododendron ferrugineum L. (Ericaceae) population inferred from AFLP markers. Molec Ecol 7:975–982. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.1998.00415.x
Earl DA, von Holdt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resources 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Molec Ecol 14:2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365294X.2005.02553.x
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distance among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Flyagina IA (1972) Rhododendron fauriei Franch. in the Sikhote-Alin Reserve. Bulletin GBS 85:29–31 (in Russian)
Frichot E, Mathieu F, Trouillon T, Bouchard G, François O (2014) Fast and efficient estimation of individual ancestry coefficients. Genetics 196:973–983. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.113.160572
Frichot E, François O (2015) LEA: An R package for landscape and ecological association studies. Meth Ecol Evol 6:925–929. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12382
Fujii N, Senni K (2006) Phylogeography of Japanese alpine plants: biogeographic importance of alpine region of Central Honshu in Japan. Taxon 55:43–52. https://doi.org/10.2307/25065527
Galanin AV (2004) Rhododendron fauriei. Flora of the Sikhote-Alin Biosphere Reserve (vascular plants). BGI FEB RAS, Vladivostok, pp 137–145
Gromyko MN, Pimenova EA, Smirnova EA, Astafiev AA (2010) Fires and their influence to the natural ecosystems of the Central Sikhote-Alin. Dalnauka, Vladivostok (in Russian)
Hampe A, Petit RJ (2005) Conserving biodiversity under climate change: the rear edge matters. Ecol Lett 8:461–467. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00739.x
Hamrick JL (2004) Response of forest trees to global environmental changes. Forest Ecol Managem 197:323–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2004.05.023
Hewitt G (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature 405(6789):907–913
Hirao AS (2010) Kinship between parents reduces offspring fitness in a natural population of Rhododendron brachycarpum. Ann Bot (Oxford) 105:637–646. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq018
Ikeda H, Senni K, Fujii N, Setoguchi H (2009) High mountains of the Japanese archipelago as refugia for arctic-alpine plants: phylogeography of Loiseleuria procumbens (L.) Desvaux (Ericaceae). Biol J Linn Soc 97:403–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2009.01177.x
Kalinowski ST (2005) HP-RARE 1.0: a computer program for performing rarefaction on measures of allelic richness. Molec Ecol Notes 5:187–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00845.x
Khasa DP, Jaramillo-Correa JP, Jaquish B, Bousquet J (2006) Contrasting microsatellite variation between subalpine and western larch, two closely related species with different distribution patterns. Molec Ecol 15:3907–3918. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.03066.x
Kohn C, Conrad K, Kramer M, Pooler M (2018) Genetic diversity of Magnolia ashei characterized by SSR markers. Conserv Genet 19:923–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-018-1065-8
Kong WS, Watts P (1993) The plant geography of Korea with an emphasis on the alpine zones. geobotany 19. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Koskinen MT, Hirvonen H, Landry PA, Primmer CR (2004) The benefits of increasing the number of microsatellites utilized in genetic population studies: an empirical perspective. Hereditas 141:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.2004.01804.x
Krestov PV, Barkalov VYu, Omelko AM, Yakubov VV, Nakamura Yu, Sato K (2009) Relic vegetation complexes in the modern refugia of Northeast Asia. VL Komarov Mem Lectures 56:5–63 (in Russian)
Kurashige Y (2017) Genus Rhododendron. In: Ohashi H, Kadota Y, Kihara H, Murata J, Yonekura K (eds) Wild flowers of Japan 4. Heibonsha, Tokyo, pp 232–250 (in Japanese)
Kwak M, Won H, Hong J, Lee BY (2015) Isolation and characterization of 19 novel microsatellite loci in Rhododendron aureum and Rhododendron brachycarpum (Ericaceae). Biochem Syst Ecol 61:520–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2015.07.011
Lee BC (2009) Rare plants. Data book of Korea. Korean National arboretum. Geobook Publishing Co., Pocheon
Lee SW, Kim YM, Kim WW, Jang SS, Chung JM (2002) Genetic variation and structure of Rhododendron brachycarpum D. Don, a rare and endangered tree species in Korea. Silvae Genet 51:215–219
Lee BC, Shim IS (2011) Environmental and ecological characteristics distribution of natural growth region in Rhododendron brachycarpum. J Environm Sci 10:1319–1328. https://doi.org/10.5322/JES.2011.20.10.1319
Lesica P, Allendorf F (1995) When are peripheral populations valuable for conservation. Conserv Biol 9:753–760
Li LF, Song N, Tang EH, Xiao HX (2011) Genomic and EST microsatellites for Rhododendron aureum (Ericaceae) and cross-amplification in other congeneric species. Amer J Bot 98:250–252. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1100153
Linnik EV, Fukuda T, Terenteva EI (2018) Molecular phylogeny of Rhododendron brachycarpum D.Don ex G. Don fil. On the Kunashir island. Contributions to the 5th Moscow International Conference «Molecular Phylogenetics and Biodiversity Biobanking» (MolPhy-5) August 25–28. Torus Press, Moscow, pp 86–88.
Liu YF, Xing M, Zhao W, Fan RJ, Luo S, Chen X (2012) Genetic diversity analysis of Rhododendron aureum Georgi (Ericaceae) located on Changbai Mountain using ISSR and RAPD markers. Pl Syst Evol 298:921–930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-012-0601-0
Long C, Ni Y, Zhang X, Xin T, Long B (2015) Biodiversity of Chinese ornamentals. Acta Hortic 1087:209–220. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1087.25
Maekawa F (1974) Origin and characteristics of Japan’s flora. In: Numata M (ed) The flora and vegetation of Japan. Kodansha, Tokyo
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Moriguchi Y, Kang KC, Lee KY, Lee SW, Kim YY (2009) Genetic variation of Picea jezoensis populations in South Korea revealed by chloroplast, mitochondrial and nuclear DNA markers. J Pl Res 122:153–160
Naganuma Y, Sakio H, Masuzawa T (2006) Comparison of community structure and growth between the alpine dwarf shrubs Rhododendron aureum and R.brachycarpum on the Yatsugatake range, central Japan. Jap J Environm 48:77–84. https://doi.org/10.18922/jjfe.48.2_77
Naito K, Isagi Y, Kameyama Y, Nakagoshi N (1999) Population structure in Rhododendron metternichii var. hondoense assessed with microsatellite and their implication for conservation. J Pl Res 112:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013895
Neel MC, Cummings MC (2003) Effectiveness of conservation targets in capturing genetic diversity. Conserv Biol 17:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.2003.01352.x
Nei M, Tajima F, Tateno Y (1983) Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular-data II: gene-frequency data. J Molec Evol 19:153–170
Nitzelius T (1972) Rhododendron brachycarpum D. Don Ex G. Don ssp. tigerstedtii, A new subspecies (Preliminary Report). Quart Bull Amer Rhododendron Soc 26: 3. https://scholar.lib.vt.edu/ejournals/JARS/v26n3/v26n3-nitzelius.htm
Oh SH, Chen L, Kim SH, Kim YD, Shin H (2010) Phylogenetic relationship of Physocarpus insularis (Rosaceae) endemic on Ulleung Island: implications for conservation biology. J Pl Biol 53:94–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-009-9093-z
Ohwi J (1965) Flora of Japan. Smitsonian Institution, Washington
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Petit RJ, Aguinagalde I, Beaulieu JL, Bittkau C, Brewer S, Cheddadi R et al (2003) Glacial refugia: hotspots but not melting pots of genetic diversity. Science 300:1563–1565. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1083264
Polezhaeva MA, Semerikov VL, Pimenova EA (2013) Genetic diversity of larch at the north of Primorskii Krai and distribution limits of Larix olgensis A. Henry. Russ J Genet 49:497–502. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795413030149
Polezhaeva MA, Pimenova EA, Tikhonova NA, Korchagina OS (2018) Plastid DNA diversity and genetic divergence within Rhododendron dauricum s.l. (R. dauricum s.s., R. ledebourii, R. sichotense and R. mucronulatum; Ericaceae). Pl Syst Evol 304:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-018-1508-1
Raymond M, Rousset F (1995) GENEPOP (Version 1.2): population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J Heredity 86:248–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01931.x
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSTSpc: Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System. version 2.02. Exeter Software, Setauket
Shemetova NS (1970) Rhododendron fauriei Franch.–New species for the flora of the Continental part of Far East. Bot J 55:550–551
Takahashi H (2015) Genus Rhododendron. In: Plants of the Kuril Islands. Hokkaido University Press, Sapporo (in Japanese). pp 291–292
Takayama K, Sun BY, Stuessy TF (2013) Anagenetic speciation in Ullung Island, Korea: genetic diversity and structure in the island endemic species, Acer takesimense(Sapindaceae). J Pl Res 126:323–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-012-0529-z
Tamaki S, Isoda K, Takahashi M, Yamada H, Yamashita Y (2018) Genetic structure and diversity in relation to the recently reduced population size of the rare conifer, Pseudotsuga japonica, endemic to Japan. Conserv Genet 19:1243–1255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-018-1092-5
Tatewaki M (1957) Geobotanical studies on the Kurile Islands. Acta Horti Gotoburg 21:43–123
van Oosterhout C, Hutchinson WF, Wills DPM, Shipley P (2004) MICRO-CHECKER: software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Molec Ecol Notes 4:535–538. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2004.00684.x
Vorob’yev DP, (1963) Flora of the Kuril Islands. Academy of Sciences, Moscow-Leningrad (in Russian)
Waits LP, Luikart G, Taberlet P (2001) Estimating the probability of identity among genotypes in natural populations: cautions and guidelines. Molec Ecol 10:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01185.x
Wang X, Huanga Y, Long C (2013) Assessing the genetic consequences of flower-harvesting in Rhododendron decorum Franchet (Ericaceae) using microsatellite markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 50:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2013.04.009
Wang X, Zhao W, Li L, You J, Ni B, Chen X (2018) Clonal plasticity and diversity facilitates the adaptation of Rhododendron aureum Georgi to alpine environment. PLoS ONE 13:e0197089. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197089
Wu F, Shen S, Zhang X, Yang G, Wang Y (2017) Inferences of genetic structure and demographic history of Rhododendron protistum var. giganteum–The world’s largest Rhododendron using microsatellite markers. Flora 233:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flora.2017.04.009
Yamazaki T (1996) A revision of the genus Rhododendron in Japan, Taiwan, Korea and Sakhalin. Tsumura Laboratory, Tokyo
Yang J, Yoon HS, Pak JH (2012) Phylogeny of Korean Rubus (Rosaceae) based on the second intron of the LEAFY gene. Canad J Pl Sci 92:461–472. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps2011-180
Yu F, Wang T, Groen T, Skidmore A, Yang X, Ma K, Wu Z (2019) Climate and land use changes will degrade the distribution of Rhododendrons in China. Sci Total Environm 659:515–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.223
Zhou W, Oh J, Li W, Kim DW, Lee SH, Na M (2013) Phytochemical studies of Korean endangered plants: a new flavone from Rhododendron brachycarpum G.Don. Bull Korean Chem Soc 34:2535–2538. https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.8.2535
Zhou W, Oh J, Li W, Kim DW, Yang MH, Jang J-H, Ahn JS, Lee SH, Na M (2014) Chemical constituents of the Korean endangered species Rhododendron brachycarpum. Biochem Syst Ecol 56:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.06.003
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mikhail Gromyko for the help with collecting of samples from Sikhote-Alin Reserve, to Evgeniy Tabalykin for the material from Iturup Island, Hee-Young Gil and students of Sungkyunkwan University for the samples from the BDDG of South Korea and Svetlana Semerikova for the sample from the Mustila Arboretum. We also thank anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. This study was performed within the frameworks of a state contract with the Institute of Plant and Animal Ecology, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, and partly supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 20-04-00417 A)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ying-xun Qiu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1. Detailed information on genotypes of 98 individuals of Rhododendron brachycarpum at 14 loci.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polezhaeva, M.A., Marchuk, E.A., Modorov, M.V. et al. Insights into the genetic diversity and population structure of Rhododendron brachycarpum (Ericaceae) in East Asia as characterized by SSR markers. Plant Syst Evol 307, 9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01726-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01726-z