Abstract
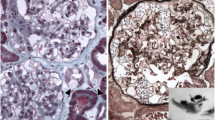
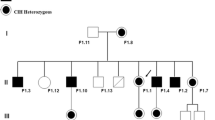
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare X-linked glycosphingolipidosis caused by mutations in GLA, a gene responsible for encoding α-galactosidase A, an enzyme required for degradation of glycosphingolipids, mainly globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) in all cells of the body. FD patients present a broad spectrum of clinical phenotype and many symptoms are shared with other diseases, making diagnosis challenging. Here we describe a novel GLA variant located in the 5′ splice site of the intron 3, in four members of a family with neuropsychiatric symptoms. Analysis of the RNA showed the variant promotes alteration of the wild type donor site, affecting splicing and producing two aberrant transcripts. The functional characterization showed absence of enzymatic activity in cells expressing both transcripts, confirming their pathogenicity. The family presents mild signs of FD, as angiokeratoma, cornea verticillata, acroparesthesia, tinnitus, vertigo, as well as accumulation of plasma lyso-Gb3 and urinary Gb3. Interestingly, the man and two women present psychiatric symptoms, as depression or schizophrenia. Although psychiatric illnesses, especially depression, are frequently reported in patients with FD and studies have shown that the hippocampus is an affected brain structure in these patients, it is not clear whether the Gb3 accumulation in the brain is responsible for these symptoms or they are secondary. Therefore, new studies are needed to understand whether the accumulation of Gb3 could produce neuronal alterations leading to psychiatric symptoms.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abramowicz A, Gos M (2018) Splicing mutations in human genetic disorders: examples, detection, and confirmation. J Appl Genet 59:253–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-018-0444-7
Arends M, Wanner C, Hughes D, Mehta A, Oder D, Watkinson OT et al (2017) Characterization of classical and nonclassical Fabry disease: a multicenter study. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(5):1631–1164. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016090964
Barch DM, Tillmanb R, Kelly D, Whalen D, Gilbert K, Luby JL (2019) Hippocampal volume and depression among young children. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 288:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2019.04.012
Bolsover FE, Murphy E, Cipolotti L, Werring DJ, Lachmann RH (2014) Cognitive dysfunction and depression in Fabry disease: a systematic review. J Inherit Metab Dis 37(2):177–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9643-x
Chen F, Bertelsen AB, Holm IE, Nyengaard JR, Rosenberg R, Dorph-Petersen KA (2019) Hippocampal volume and cell number in depression, schizophrenia, and suicide subjects. Brain Res 1727:146546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146546
Cole AL, Lee PJ, Hughes DA, Deegan PB, Waldek S, Lachmann RH (2007) Depression in adults with Fabry disease: a common and under-diagnosed problem. J Inherit Metab Dis 30(6):943–951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-007-0708-6
Crosbie TW, Packman W, Packman S (2009) Psychological aspects of patients with Fabry disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 32(6):745–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-009-1254-1
Desmet FO, Hamroun D, Lalande M, Collod-Beround G, Claustre M, Beround C (2009) Human splicing finder: an online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res 37(9):e67. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp215
deVeber GA, Schwarting GA, Kolodny EH, Kowall NW (1992) Fabry disease: immunocytochemical characterization of neuronal involvement. Ann Neurol 31(4):409–415. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410310410
Fellgiebel A, Wolf DO, Kolodny E, Müller MJ (2012) Hippocampal atrophy as a surrogate of neuronal involvement in Fabry disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 35(2):363–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-011-9390-9
Filoni C, Caciotti A, Carraresi L, Cavicchi C, Parini R, Antuzzi D et al (2010) Functional studies of new GLA gene mutations leading to conformational Fabry disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.11.003
Gairing S, Wiest R, Metzler S, Theodoridou A, Hoff P (2011) Fabry's disease and psychosis: causality or coincidence? Psychopathology. 44(3):201–204. https://doi.org/10.1159/000322794
Hamilton B (2006) State of depression in America. Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance (DBSA). Available online at: https://www.dbsalliance.org/pdfs/wpsearchable.pdf. Accessed 04/11/20
Hilz MJ, Kolodny EH, Brys M, Stemper B, Haendl T, Marthol H (2004) Reduced cerebral blood flow velocity and impaired cerebral autoregulation in patients with Fabry disease. J Neurol 251(5):564–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-004-0364-9
Juchniewicz P, Kloska A, Tylki-Szymańska A, Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka J, Węgrzyn G et al (2018) Female Fabry disease patients and X-chromosome inactivation. Gene 641:259–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.10.064
Kalmady SV, Shivakumar V, Arasappa R, Subramaniam A, Gautham S, Venkatasubramanian G et al (2017) Clinical correlates of hippocampus volume and shape in antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 263:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.03.014
Karczewski KJ, Francioli LC, Tiao G et al (2020) The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 581:434–443. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2308-7
Körver S, Geurtsen GJ, Hollak CEM, van Schaik IN, Longo MGF, Lima MR et al (2020) Depressive symptoms in Fabry disease: the importance of coping, subjective health perception and pain. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 15(1):28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-020-1307-y
Laney DA, Bennett RL, Clarke V, Fox A, Hopkin RJ, Johnson J et al (2013) Fabry disease practice guidelines: recommendations of the National Society of genetic counselors. J Genet Couns 22(5):555–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10897-013-9613-3
Lelieveld IM, Böttcher A, Hennermann JB, Beck M, Fellgiebel A (2015) Eight-year follow-up of neuropsychiatric symptoms and brain structural changes in Fabry disease. PLoS One 10(9):e0137603. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137603
Liston EH, Levine MD, Philippart M (1973) Psychosis in Fabry disease and treatment with phenoxybenzamine. Arch Gen Psychiatry 29(3):402–403. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1973.04200030090014
Löhle M, Hughes D, Milligan A, Richfield L, Reichmann H, Mehta A et al (2015) Clinical prodromes of neurodegeneration in Anderson-Fabry disease. Neurology 84(14):1454–1464. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001450
Lukas J, Giese AK, Markoff A, Grittner U, Kolodny E, Mascher H et al (2013) Functional characterization of alpha-galactosidase a mutation as a basis for a new classification system in fabry disease. PLoS Genet 9(8):e1003632. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003632
McGrath J, Saha S, Welham J et al (2004) A systematic review of the incidence of schizophrenia: the distribution of rates and the influence of sex, urbanicity, migrant status and methodology. BMC Med 2:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-2-13
Mckenna MC, Schuck PF, Ferreira GC (2019) Fundamentals of CNS energy metabolism and alterations in lysosomal storage diseases. J Neurochem 148(5):590–599. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14577
Moore DF, Ye F, Brennan ML, Gupta S, Barshop BA, Steiner RD, Rhead WJ, Brady RO et al (2004) Ascorbate decreases Fabry cerebral hyperperfusion suggesting a reactive oxygen species abnormality: an arterial spin tagging study. J Magn Reson Imaging 20(4):674–683. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.20162
Moore DF, Kaneski CR, Askari H, Schiffmann R (2007) The cerebral vasculopathy of Fabry disease. J Neurol Sci 257(1–2):258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2007.01.053
Muller KB, Rodrigues MDB, Pereira VG, Martins AM, D’Almeida V (2010) Reference values for lysosomal enzyme activities using dried blood spots samples – a Brazilian experience. Diagn Pathol 5:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-5-65
Naslavsky MS, Yamamoto GL, de Almeida TF, Ezquina ASM, Sunaga DY, Pho N et al (2017) Exomic variants of an elderly cohort of Brazilians in the ABraOM database. Hum Mutat 38(7):751–763. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23220
Nelson MP, Tse TE, O'Quinn DB, Percival SM, Jaimes EA, Warnock DG, et. al. (2014). Autophagy-lysosome pathway associated neuropathology and axonal degeneration in the brains of alpha-galactosidase A-deficient mice. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2:20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/2051-5960-2-20
Okeda R, Nisihara M (2008) An autopsy case of Fabry disease with neuropathological investigation of the pathogenesis of associated dementia. Neuropathology. 28(5):532–540. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1789.2008.00883.x
Okumiya T, Ishii S, Kase R, Kamei S, Sakuraba H, Suzuki Y (1995) Alpha-galactosidase gene mutations in Fabry disease: heterogeneous expressions of mutant enzyme proteins. Hum Genet 95:557–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223869
Oliveira JP, Ferreira S (2019) Multiple phenotypic domains of Fabry disease and their relevance for establishing genotype– phenotype correlations. Appl Clin Genet 12:35–50. https://doi.org/10.2147/TACG.S146022
Ploos van Amstel JK, Jansen RP, de Jong JG, Hamel BC, Wevers RA (1994) Six novel mutations in the alpha-galactosidase a gene in families with Fabry disease. Hum Mol Genet 3:503–505. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/3.3.503
Santos MAO, Bezerra LS, Carvalho A, Brainer-Lima AM (2018) Global hippocampal atrophy in major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Trends Psychiatry Psychother 40(4):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1590/2237-6089-2017-0130
Sawada J, Katayama T, Kano K, Asanome A, Takahashi K, Saito T et al (2015) A sporadic case of Fabry disease involving repeated fever, psychiatric symptoms, headache, and ischemic stroke in an adult Japanese woman. Intern Med 54(23):3069–3074. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.54.4719
Schafer E, Baron K, Widmer U, Deegan P, Neumann HP, Sunder-Plassmann G et al (2005) Thirty-four novel mutations of the GLA gene in 121 patients with Fabry disease. Hum Mutat 25:412. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.9327
Schermuly I, Müller MJ, Müller KM, Albrecht J, Keller I, Yakushev I et al (2011) Neuropsychiatric symptoms and brain structural alterations in Fabry disease. Eur J Neurol 18(2):347–353. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03155.x
Segal P, Kohn Y, Pollak Y, Altarescu G, Galili-Weisstub E, Raas-Rothschild A (2010) Psychiatric and cognitive profile in Anderson-Fabry patients: a preliminary study. J Inherit Metab Dis 33(4):429–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-010-9133-3
Shabbeer J, Robinson M, Desnick RJ (2005) Detection of alpha galactosidase a mutations causing Fabry disease by denaturing highperformance liquid chromatography. Hum Mutat 25(3):299–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20144
Shen YC, Haw-Ming L, Lin CC, Chen CH (2007) Psychosis in a patient with Fabry's disease and treatment with aripiprazole. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31(3):779–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.11.017
Sterne-Weiler T, Sanford JR (2014) Exon identity crisis: disease-causing mutations that disrupt the splicing code. Genome Biol 15(1):201. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb4150
Turaça LT, Pessoa JG, Motta FL, Muñoz Rojas MV, Müller KB et al (2012) New mutations in the GLA gene in Brazilian families with Fabry disease. J Hum Genet 57(6):347–351. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2012.32
Varela P, Caldas MM, Pesquero JB (2019) Novel GLA mutation promotes intron inclusion leading to Fabry disease. Front Genet 10:783. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00783
Varela P, Mastroianni-Kirsztajn G, Ferrer H, Aranda C, Wallbach K, Ferreira da Mata G et al (2020a) Functional characterization and pharmacological evaluation of a novel GLA missense mutation found in a severely affected Fabry disease family. Nephron. 144(3):147–155. https://doi.org/10.1159/000503998
Varela P, Mastroianni-Kirsztajn G, Motta FL, Martin RP, Turaça LT, Ferrer HLF et al (2020b) Correlation between GLA variants and alpha-galactosidase a profile in dried blood spot: an observational study in Brazilian patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis 15(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1274-3
Wang, R.Y., Lelis, A., Mirocha, J., Wilcox, W.R. (2007). Heterozygous Fabry women are not just carriers, but have a significant burden of disease and impaired quality of life. Genet Med;9(1):34–45. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/gim.0b013e31802d8321
Wise T, Radua J, Via E, Cardoner N, Abe O, Adams TM et al (2017) Common and distinct patterns of grey-matter volume alteration in major depression and bipolar disorder: evidence from voxel-based meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 22:1455–1463. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.72
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2014/27198-8) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2014/27198–8) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PhD. Patricia Varela: conceptualized and designed the study, designed the data collection experiments, drafted the initial manuscript, carried out the analyses, reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
MD. Gerson Carvalho: providing the samples analyzed in this work, analyzed the clinical symptoms of patients, reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
PhD. Renan Paulo Martin: carried out the initial analyses, reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
PhD. Joao Bosco Pesquero: conceptualized and designed the study, drafted the initial manuscript, carried out the initial analyses, reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. Corresponding author and guarantor for the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest and confirm independence from the sponsors. The sponsors have not influenced the content of the article.
Ethical approval and patient consent statement
The Research Ethics Committee of the Federal University of São Paulo, Brazil approved this protocol (0585/07 and 0354/18). All procedures were followed in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2013. All subjects involved in this study were older than 16 year at the time of the study. All four patients gave written informed consent agreeing to participate in the study and for the publication of their clinical cases. The consent was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varela, P., Carvalho, G., Martin, R.P. et al. Fabry disease: GLA deletion alters a canonical splice site in a family with neuropsychiatric manifestations. Metab Brain Dis 36, 265–272 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00640-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00640-0