Abstract
Objective and design
Retinoblastoma is the most common primary intraocular malignancy of childhood, which brings a heavy burden to the countries across the world, especially the developing countries. It has been shown that lncRNA muscleblind-like 1 antisense RNA 1 (MBNL1-AS1) exerts anti-tumor effects in various cancers, including bladder cancer, papillary thyroid cancer, and retinoblastoma. In the present study, we hypothesized that MBNL1-AS1 might play a protective role against retinoblastoma.
Methods
The expression of MBNL1-AS1 and its potential target miR-338-5p were evaluated in retinoblastoma cell line by real-time quantitative PCR and western blot. The involvement of MBNL1-AS1-miR-338-5p in the cell proliferation was evaluated by cell counting kit-8 (CCK8), and colony formation assay. The cell migration was evaluated by Transwell assay in Y79 cells, a retinoblastoma cell line. The involvement of MBNL1-AS1-miR-338-5p in tumor formation was also evaluated in mice.
Results
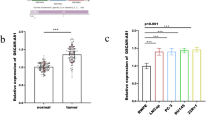
It was found that MBNL1-AS1 overexpression inhibited proliferation and migration in Y79 cells. In addition, the inhibitory effects of MBNL1-AS1 on Y79 cells were significantly reversed in the presence of miR-338-5p mimics, and MBNL1-AS1 overexpression significantly decreased miR-338-5p level in Y79 cells. Furthermore, MBNL1-AS1 overexpression significantly inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and this inhibitory effect was almost lost in the presence of miR-338-5p mimics. Finally, our in vivo study showed that MBNL1-AS1 overexpression significantly inhibited Y79-induced retinoblastoma in mice, and this inhibitory effect was lost in the presence of miR-338-5p mimics.
Conclusion
Our study shows that MBNL1-AS1 exerts its anti-tumor effect by targeting miR-338-5p, thereby inactivating wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in retinoblastoma.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hao F, Mou Y, Zhang L, Wang S, Yang Y. LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 is a prognostic biomarker and serves as oncogenic role in retinoblastoma. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(3):BSR20180384.
Fabian ID, Onadim Z, Karaa E, et al. The management of retinoblastoma. Oncogene. 2018;37(12):1551–60.
Rao R, Honavar SG. Retinoblastoma. Indian J Pediatr. 2017;84(12):937–44.
Wei X, Wang B, Wang Q, et al. MiR-362-5p, which is regulated by long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1, promotes the cell proliferation and tumor growth of bladder cancer by targeting QKI. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:164.
Fu XM, Guo W, Li N, et al. The expression and function of long noncoding RNA lncRNA-ATB in papillary thyroid cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(14):3239–46.
Yang G, Fu Y, Lu X, Wang M, Dong H, Li Q. LncRNA HOTAIR/miR-613/c-met axis modulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinoblastoma cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(10):5083–96.
Wei X, Yang X, Wang B, et al. LncRNA MBNL1-AS1 represses cell proliferation and enhances cell apoptosis via targeting miR-135a-5p/PHLPP2/FOXO1 axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Med. 2020;9(2):724–36.
Zhu K, Wang Y, Liu L, Li S, Yu W. Long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1 regulates proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer stem cells in colon cancer by interacting with MYL9 via sponging microRNA-412-3p. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2020;44(1):101–14.
Wang JH, Zhang L, Huang ST, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of MYL9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(4):e0175280.
Li P, Xing W, Xu J, et al. microRNA-301b-3p downregulation underlies a novel inhibitory role of long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):144.
Zhou P, Li X. Serum miR-338-5p has potential for use as a tumor marker for retinoblastoma. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(1):307–13.
Gao Y, Lu X. Decreased expression of MEG3 contributes to retinoblastoma progression and affects retinoblastoma cell growth by regulating the activity of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(2):1461–9.
Wu T, Wang LN, Tang DR, Sun FY. SOST silencing promotes proliferation and invasion and reduces apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Gene Ther. 2017;24(7):399–407.
Yang M, Li Y, Wei W. MicroRNA-188-5p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ID4 through Wnt/betacatenin signaling in retinoblastoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:10251–62.
Oshikawa M, Tsutsui C, Ikegami T, et al. Full-length transcriptome analysis of human retina-derived cell lines ARPE-19 and Y79 using the vector-capping method. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(9):6662–70.
Liu Y, Hu H, Liang M, et al. Regulated differentiation of WERI-Rb-1 cells into retinal neuron-like cells. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(4):1172–84.
Xu L, Li W, Shi Q, et al. MicroRNA936 inhibits the malignant phenotype of retinoblastoma by directly targeting HDAC9 and deactivating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(2):635–45.
Ju C, Zhou R, Sun J, et al. LncRNA SNHG5 promotes the progression of osteosarcoma by sponging the miR-212-3p/SGK3 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2018;18:141.
Li J, Guo Y, Duan L, et al. AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via activation of ERK signaling. Oncotarget. 2017;8(20):33694–703.
Wu XZ, Cui HP, Lv HJ, Feng L. Knockdown of lncRNA PVT1 inhibits retinoblastoma progression by sponging miR-488–3p. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108627.
Huo Y, Wang Q, Liu Y, et al. A temperature-sensitive phase-change hydrogel of topotecan achieves a long-term sustained antitumor effect on retinoblastoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:6069–82.
Aldred SF, Collins P, Trinklein N. Identifying targets of human micrornas with the LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System using 3’UTR-reporter constructs and a microRNA mimic in adherent cells. J Vis Exp. 2011; (55).
Song B, Lin HX, Dong LL, Ma JJ, Jiang ZG. MicroRNA-338 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(5):1290–6.
Zhang T, Liu W, Zeng XC, et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-338–3p promoted angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:583–91.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LX and WRL contributed to the conception and design of the study; LX, SYZ and ADT performed the experiments and collected the data; SYZ and ADT performed the statistical analysis; LX and SYZ completed data interpretation; LX and WRL wrote the manuscript and revised manuscript; All authors contributed to reading and revising the manuscript and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest in this investigation.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Zhu, S., Tang, A. et al. LncRNA MBLN1-AS1 inhibits the progression of retinoblastoma through targeting miR-338-5p-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Inflamm. Res. 70, 217–227 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01432-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-020-01432-z