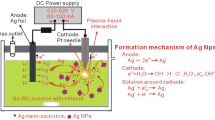
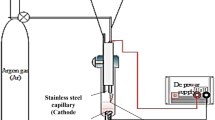
Abstract
The method of contact glow discharge with the using of “sacrificial” silver anodes have been proposed for synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) stabilized by polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). Using transmission electron microscopy, it was found that the mean size of AgNPs decrease from 10 to 5 nm with increasing of PVP concentration from 2.5 to 10 g/L. At the same time, the polydispersity index of AgNPs non-monotonically depends on concentration of stabilizer and the narrowest size distribution (less than 15%) was observed at PVP concentration equal to 5 g/L. The electrochemical investigations of Ag anodic dissolution associated with the recorded UV-Vis spectra of the obtained AgNPs solutions suggest that (i) the rate of silver dissolution depend on the nature of regulating agent—NaOH or CH3COONa; (ii) silver anodes are not passivated in the presence of PVP; (iii) unlike to the process of chemical reduction of silver ions by PVP using of the contact glow discharge technique provides a pseudo-stationary process mode, i.e., the stability of rates of nucleation and growth of AgNPs via stability both of Ag+ and solvated electrons concentrations that leads to formation of nearly monodisperse nanoparticles.









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04859-w
References
Natsuki J, Natsuki T, Hashimot Y (2015) A review of silver nanoparticles: synthesis methods, properties and applications. Int J Mater Sci Appl 4:325–332. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijmsa.20150405.17
Paramasivam G, Kayambu N, Rabel AM, Sundramoorthy AK, Sundaramurthy A (2017) Anisotropic noble metal nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functionalization and applications in biosensing, bioimaging, drug delivery and theranostics. Acta Biomater 49:45–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.066
Zhang Z, Shen W, Xue J, Liu Y, Liu Y, Yan P, Liu J, Tang J (2018) Recent advances in synthetic methods and applications of silver nanostructures. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2450-4
Chaiendoo K, Boonchiangma S, Promarak V, Ngeontae W (2018) New sensitive strategy for formaldehyde sensing by in situ generation of luminescent silver nanoclusters. Colloid Polym Sci 296(12):1995–2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4427-3
Srikar SK, Giri DD, Pal DB, Mishra PK, Upadhyay SN (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: a review. Green Sustain Chem 6:34–56. https://doi.org/10.4236/gsc.2016.61004
Pareek V, Bhargava A, Gupta R, Jain N, Panwar J (2017) Synthesis and applications of noble metal nanoparticles: a review. Adv Sci Eng Med 9:527–544. https://doi.org/10.1166/asem.2017.2027
Besenhard MO, Baber R, LaGrow AP, Mazzei L, Thanh NTK, Gavriilidis A (2018) New insight into the effect of mass transfer on the synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. CrystEngComm 20:7082–7093. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ce01014e
Xi Z, Ye H, Xia X (2018) Engineered noble-metal nanostructures for in vitro diagnostics. Chem Mater 30:8391–8414. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b04152
Kinnear C, Moore TL, Rodriguez-Lorenzo L, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Petri-Fink A (2017) Form follows function: nanoparticle shape and its implications for nanomedicine. Chem Rev 117:11476–11521. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00194
Fox CM, Yu T, Breslin CB (2020) Electrochemical formation of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic activity immobilised in a hydrogel matrix. Colloid Polym Sci 298:549–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04624-5
Blandón L, Vázquez MV, Benjumea DM, Ciro G (2012) Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their potential use as antimicrobial agent: a case study on Escherichia coli. Port Electrochim Acta 30(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.201202135
Dobre N, Petica A, Buda M, Anicăi L, Vişan T (2014) Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles in aqueous electrolytes. UPB Sci Bull Ser B 76:127–136
Yanilkin VV, Nasretdinova GR, Kokorekin VA (2018) Mediated electrochemical synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Russ Chem Rev 87:1080–1110. https://doi.org/10.1070/RCR4827
Kuntyi OI, Kytsya AR, Mertsalo IP, Mazur AS, Zozula GI, Bazylyak LI, Topchak RV (2019) Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles by reversible current in solutions of sodium polyacrylate. Colloid Polym Sci 297:689–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-019-04488-4
Kuntyi O, Mazur A, Kytsya A, Karpenko O, Bazylyak L, Mertsalo I, Pokynbroda T, Prokopalo A (2020) Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles in solutions of rhamnolipid. Micro Nano Lett 15(12):802–807. https://doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2020.0195
Toriyabe Y, Watanabe S, Yatsu S, Shibayama T, Mizuno T (2007) Controlled formation of metallic nanoballs during plasma electrolysis. Appl Phys Lett 91:041501–041503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2760042
Lal A, Bleuler H, Wüthrich R (2008) Fabrication of metallic nanoparticles by electrochemical discharges. Electrochem Commun 10:488–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2008.01.017
Wüthrich R, Allagui A (2010) Building micro and nanosystems with electrochemical discharges. Electrochim Acta 55:8189–8196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.01.096
Tochikubo F, Shimokawa Y, Shirai N, Uchida S (2014) Chemical reactions in liquid induced by atmospheric-pressure dc glow discharge in contact with liquid. Jpn J Appl Phys 53:126201–126208. https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.53.126201
Shirai N, Uchida S, Tochikubo F (2014) Synthesis of metal nanoparticles by dual plasma electrolysis using atmospheric dc glow discharge in contact with liquid. Jpn J Appl Phys 53:046202–046205. https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.53.046202
Oka Y, Kuroshima T, Sawachika K, Yamashita M, Sakao M, Ohnishi K, Asami K, Yatsuzuka M (2019) Preparation of silver nanocolloidal solution by cavitation bubble plasma. Vacuum 167:530–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.05.013
Rumbach P, Go DB (2017) Perspectives on plasmas in contact with liquids for chemical processing and materials synthesis. Top Catal 60:799–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-017-0745-9
Lin L, Starostin SA, Li S, Hessel V (2018) Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by microplasma. Phys Sci Rev 3:1–91. https://doi.org/10.1515/psr-2017-0121
Tseng K-H, Chen YC, Shyue JJ (2011) Continuous synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles by electrochemical discharge in aqueous solutions. J Nanopart Res 13:1865–1872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9937-y
Ashkarran AA (2010) A novel method for synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles by arc discharge in liquid. Curr Appl Phys 10:1442–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2010.05.010
Zhang YT, Guo Y, Ma TC (2011) Plasma catalytic synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Chin Phys Lett 28:105201–105203. https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/28/10/105201
Sato S, Mori K, Ariyada O, Atsushi H, Yonezawa T (2011) Synthesis of nanoparticles of silver and platinum by microwave-induced plasma in liquid. Surf Coat Technol 206:955–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.03.110
Shi Q, Vitchuli N, Nowak J, Caldwell JM, Breidt F, Bourham M, Zhang X, McCord M (2011) Durable antibacterial Ag/polyacrylonitrile (Ag/PAN) hybrid nanofibers prepared by atmospheric plasma treatment and electrospinning. Eur Polym J 47:1402–1409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2011.04.002
Nam S, Ali DM, Kim J (2016) Characterization of alginate/silver nanobiocomposites synthesized by solution plasma process and their antimicrobial properties. J Nanomater 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4712813
Huang XZ, Zhong XX, Lu Y, Li YS, Rider AE, Furman SA, Ostrikov K (2013) Plasmonic Ag nanoparticles via environment-benign atmospheric microplasma electrochemistry. Nanotechnol 24:095604. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/9/095604
Kim SC, Kim SM, Yoon GJ, Nam SW, Lee SY, Kim JW (2014) Gelatin-based sponge with Ag nanoparticles prepared by solution plasma: fabrication, characteristics, and their bactericidal effect. Curr Appl Phys 14:S172–S179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2013.12.032
Jin SH, Kim SM, Lee SY, Kim JW (2014) Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using a solution plasma process. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14:8094–8097. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.9428
Zhang Z, Zhao B, Hu L (1996) PVP protective mechanism of ultrafine silver powder synthesized by chemical reduction processes. J Solid State Chem 121:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1006/jssc.1996.0015
Malina D, Sobczak-Kupiec A, Wzorek Z, Kowalski Z (2012) Silver nanoparticles synthesis with different concentrations of polyvinylpyrrolidone. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 7:1527–1534
Yin B, Ma H, Wang S, Chen S (2003) Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles under protection of poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone). J Phys Chem B 107:8898–8904. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0349031
Wang H, Qiao X, Chen J, Wang X, Ding S (2005) Mechanisms of PVP in the preparation of silver nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 94(2-3):449–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.05.005
Hoppe CE, Lazzari M, Pardinas-Blanco I, López-Quintela MA (2006) One-step synthesis of gold and silver hydrosols using poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) as a reducing agent. Langmuir 22:7027–7034. https://doi.org/10.1021/la060885d
Slistan-Grijalva A, Herrera-Urbina R, Rivas-Silva JF, Ávalos-Borja M, Castillón-Barraza FF, Posada-Amarillas A (2005) Classical theoretical characterization of the surface plasmon absorption band for silver spherical nanoparticles suspended in water and ethylene glycol. Phys E 27:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2004.10.014
Kytsya AR, Reshetnyak OV, Bazylyak LI, Hrynda YM (2014) UV/VIS-spectra of silver nanoparticles as characteristics of their sizes and sizes distribution. In: Zaikov GE, Bazylyak LI, Haghi AK (eds) Functional polymer blends and nanocomposites: a practical engineering approach1st edn. Apple Academic Press, New York, pp 231–239. https://doi.org/10.1201/b16895
Sandoe HE, Watzky MA, Diaz SA (2019) Experimental probes of silver metal nanoparticle formation kinetics: comparing indirect versus more direct methods. Int J Chem Kinet 51:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1002/kin.21315
Patakfalvi R, Papp S, Dekany I (2007) The kinetics of homogeneous nucleation of silver nanoparticles stabilized by polymers. J Nanopart Res 9:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-006-9139-9
Kytsya A, Bazylyak L, Simon P, Zelenina I, Antonyshyn I (2019) Kinetics of Ag300 nanoclusters formation: the catalytically effective nucleus via a steady-state approach. Int J Chem Kinet 51:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1002/kin.20913
Funding
This work was carried out with the partial financial support of the National Research Foundation of Ukraine (Agreement 165/02.2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 282 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuntyi, O.I., Kytsya, А.R., Bondarenko, A.B. et al. Microplasma synthesis of silver nanoparticles in PVP solutions using sacrificial silver anodes. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 855–863 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04811-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04811-y