Abstract
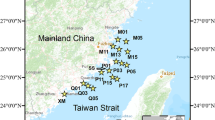
Sea surface temperature fronts in the Northeastern Arabian Sea (NEAS) facilitate nutrient enhancement in the surface layers, resulting in high primary production. Such high production areas contribute to the accumulation of fresh organic matter rich in carbohydrates, thereby supporting higher heterotrophic metabolism. Transparent exopolysaccharides (TEP) are one of the carbohydrate polymers released as exudates during primary production or decaying process and their breakdown is mediated by a set of ectoenzymes that includes glucosidases and chitinases. Observations were carried out in different aged NEAS fronts to elucidate the influence of frontal age on the abundance of TEP, bacterial nucleic acid content (high nucleic acid content, HNA and low nucleic acid content, LNA), and ectoenzymatic activities. The fronts were classified as younger and older, depending on their first appearance and sampling day. A clear transition from HNA to LNA bacteria, variations in TEP and related ectoenzymatic activities in the fronts was influenced by the frontal age. The younger fronts were dominated by HNA bacteria, α-glucosidase, and chitinase activity. In contrast, an acceleration in β-glucosidase activity, bacterial production, which was related to TEP concentration, was evident in the older fronts. Further, a significant increase in protist numbers in older fronts was related to effective grazing on HNA bacteria and TEP. The active turnover of TEP by bacteria and protists facilitates strong microbial loop in NEAS frontal regions. Elucidating contribution of such changes in the frontal areas will provide a basis for a better understanding of microbial carbon cycling.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnosti C (2004) Speed bumps and barricades in the carbon cycle: substrate structural effects on carbon cycling. Mar Chem 92:263–273
Arnous MB, Courcol N, Carrias JF (2010) The significance of transparent exopolymeric particles in the vertical distribution of bacteria and heterotrophic nanoflagellates in Lake Pavin. Aquat sci 72:245–253
Azam F, Fenchel T, Field JG, Gray JS, Meyer-Reil LA, Thingstad F (1983) The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 10:257–263
Ballen-Segura M, Felip M, Catalan J (2017) Some mixotrophic flagellate species selectively graze on Archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e02317-e2416
Barman TE (1969) Enzyme handbook, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, p 510
Bar-Zeev E, Rahav E (2015) Microbial metabolism of transparent exopolymer particles during the summer months along a eutrophic estuary system. Front Microbiol 6:403
Beier S, Bertilsson S (2013) Bacterial chitin degradation—mechanisms and ecophysiological strategies. Front Microbiol 4:149
Belkin IM, Cornillon PC, Sherman K (2009) Fronts in large marine ecosystems. Prog Oceanogr 81:223–236
Benner R, Pakulski JD, McCarthy M, Hedges JI, Hatcher PG (1992) Bulk chemical characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the ocean. Science 255:1561–1564
Bhaskar PV, Grossart HP, Bhosle NB, Simon M (2005) Production of macroaggregates from dissolved exopolymeric substances (EPS) of bacterial and diatom origin. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:255–264
Biddanda B, Benner R (1997) Carbon, nitrogen, and carbohydrate fluxes during the production of particulate and dissolved organic matter by marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 42:506–518
Brown MR (1991) The amino-acid and sugar composition of 16 species of microalgae used in mariculture. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 145:79–99
Brunner E, Richthammer P, Ehrlich H, Paasch S, Simon P, Ueberlein S, Van Pée KH (2009) Chitin-based organic networks: an integral part of cell wall biosilica in the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:9724–9727
Busch K, Endres S, Iversen MH, Michels J, Nöthig EM, Engel A (2017) Bacterial colonization and vertical distribution of marine gel particles (TEP and CSP) in the Arctic Fram Strait. Front Mar Sci 4:166
Cauchie HM (2002) Chitin production by arthropods in the hydrosphere. Hydrobiologia 470:63–95
Chitari RR (2019) Studies on ecology of microphytoplankton from the Northern Indian Ocean. Ph.D. thesis, Goa University, Goa, India.
Christaki U, Courties C, Massana R, Catala P, Lebaron P, Gasol JM, Zubkov MV (2011) Optimized routine flow cytometric enumeration of heterotrophic flagellates using SYBR Green I. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 9:329–339
Christian JR, Karl DM (1995) Bacterial ectoenzymes in marine waters: activity ratios and temperature responses in three oceanographic provinces. Limnol Oceanogr 40:1042–1049
Chróst RJ (1989) Characterization and significance of β-glucosidase activity in lake water. Limnol Oceanogr 34:660–672
Chróst RJ (1990) Microbial ectoenzymes in aquatic environments. Aquatic microbial ecology. Springer, New York, pp 47–78
Chróst RJ (1992) Significance of bacterial ectoenzymes in aquatic environments. Hydrobiologia 243:61–70
Chrost RJ (1991) Environmental control of the synthesis and activity of aquatic microbial ectoenzymes. Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer, New York, pp 29–59
Croot PL, Passow U, Assmy P, Jansen S, Strass VH (2007) Surface active substances in the upper water column during a Southern Ocean Iron Fertilization Experiment (EIFEX). Geophys Res Lett 34:1–5
De La Rocha CL, Nowald N, Passow U (2008) Interactions between diatom aggregates, minerals, particulate organic carbon, and dissolved organic matter: further implications for the ballast hypothesis. Global Biogeochem Cycles 22:1–10
Decho AW (1990) Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments: their role(s) in food webs and marine processes. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 28:73–153
Ducklow HW, Carlson CA, Smith WO (1998) Bacterial growth in experimental plankton assemblages and seawater cultures from the Phaeocystis antarctica bloom in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Aquat Microb Ecol 168:229–244
Durkin CA, Mock T, Armbrust EV (2009) Chitin in diatoms and its association with the cell wall. Eukaryot Cell 8:1038–1050
Dutz J, Breteler WK, Kramer G (2005) Inhibition of copepod feeding by exudates and transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) derived from a Phaeocystis globosa dominated phytoplankton community. Harmful Algae 4:929–940
Engel A (2004) Distribution of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in the northeast Atlantic Ocean and their potential significance for aggregation processes. Deep Sea Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap 51:83–92
Eswaran R, Khandeparker L (2017) Seasonal variation in bacterial community composition and β-glucosidase expression in a tropical monsoon-influenced estuary. Aquat Microb Ecol 80:273–287
Fernández M, Bianchi M, Van Wambeke F (1994) Bacterial biomass, heterotrophic production and utilization of dissolved organic matter photosynthetically produced in the Almeria-Oran front. J Mar Syst 5:313–325
Fiala M, Sournia A, Claustre H, Marty JC, Prieur L, Vétion G (1994) Gradients of phytoplankton abundance, composition and photosynthetic pigments across the Almeria-Oran front (SW Mediterranean Sea). J Mar Syst 5:223–233
Garrison DL, Gowing MM, Hughes MP, Campbell L, Caron DA, Dennett MR, Shalapyonok A, Olson RJ, Landry MR, Brown SL, Liu HB (2000) Microbial food web structure in the Arabian Sea: a US JGOFS study. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 47:1387–1422
Gasol JM, Zweifel UL, Peters F, Fuhrman JA, Hagström Å (1999) Significance of size and nucleic acid content heterogeneity as measured by flow cytometry in natural planktonic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4475–4483
Giroldo D, Henriques Vieira AA, Paulsen BS (2003) relative increase of deoxy sugars during microbial degradation of an extracellular polysaccharide released by a tropical freshwater Thalassiosira sp. (Bacillariophyceae). J Phycol 39:1109–1115
Gooday GW (1990) The ecology of chitin degradation. Advances in microbial ecology. Springer, Boston, pp 387–430
Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (1983) Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Verlag Chemie, New York
Grossart HP, Czub G, Simon M (2006) Algae–bacteria interactions and their effects on aggregation and organic matter flux in the sea. Environ Microbiol 8:1074–1084
Gügi B, Le Costaouec T, Burel C, Lerouge P, Helbert W, Bardor M (2015) Diatom-specific oligosaccharide and polysaccharide structures help to unravel biosynthetic capabilities in diatoms. Mar Drugs 13:5993–6018
Hahn MW, Höfle MG (2001) Grazing of protozoa and its effect on populations of aquatic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:113–121
Harlay J, De Bodt C, Engel A, Jansen S, d’Hoop Q, Piontek J, Van Oostende N, Groom S, Sabbe K, Chou L (2009) Abundance and size distribution of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in a coccolithophorid bloom in the northern Bay of Biscay. Deep Sea Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap 56:1251–1265
Helbert W (2017) Marine polysaccharide sulfatases. Front Mar Sci 4:6
Holloway CF, Cowen JP (1997) Development of a scanning confocal laser microscopic technique to examine the structure and composition of marine snow. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1340–1352
Hoppe HG (1993) Use of fluorogenic model substrates for extracellular enzyme activity (EEA) measurement of bacteria. Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology. CRC Press, Cambridge, pp 423–431
Hoppe HG, Arnosti C, Herndl GJ (2002) Ecological significance of bacterial enzymes in the marine environment. Enzymes in the environment: activity, ecology, and applications. Marcel Decker, New York, pp 73–107
Jackson GA (1995) TEP and coagulation during a mesocosm experiment. Deep Sea Res II 42:215–222
Janse I, Van Rijssel M, Gottschal JC, Lancelot C, Gieskes WW (1996) Carbohydrates in the North Sea during spring blooms of Phaeocystis: a specific fingerprint. Aquat Microb Ecol 10:97–103
Khandeparker L, Eswaran R, Hede N, Anil AC (2018) Significance of metabolically active bacterioplankton in the frontal regions of the Northeastern Arabian Sea. Aquat sci 80:38
Klein C, Claquin P, Pannard A, Napoléon C, Le Roy B, Véron B (2011) Dynamics of soluble extracellular polymeric substances and transparent exopolymer particle pools in coastal ecosystems. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 427:13–27
Krishna MS, Mukherjee J, Dalabehera HB, Sarma VVSS (2018) Particulate organic carbon composition in temperature fronts of the northeastern Arabian Sea during winter. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 123:463–478
Lebaron P, Servais P, Baudoux AC, Bourrain M, Courties C, Parthuisot N (2002) Variations of bacterial-specific activity with cell size and nucleic acid content assessed by flow cytometry. Aquat Microb Ecol 28:131–140
Ling SC, Alldredge AL (2003) Does the marine copepod Calanus pacificus consume transparent exopolymer particles (TEP)? J Plankton Res 25:507–515
Madhupratap M, Prasanna Kumar S, Bhattathiri PMA, Dileep Kumar M, Raghukumar S, Nair KKC, Ramaiah N (1996) Mechanism of the biological response to winter cooling in the northeastern Arabian Sea. Nature 384:549–552
Mari X, Rassoulzadegan F (2004) Role of TEP in the microbial food web structure. I. Grazing behavior of a bacterivorous pelagic ciliate. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 279:13–22
Misic C, Fabiano M (2006) Ectoenzymatic activity and its relationship to chlorophyll-a and bacteria in the Gulf of Genoa (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean). J Mar Syst 60:193–206
Monticelli LS, Caruso G, Decembrini F, Caroppo C, Fiesoletti F (2014) Role of prokaryotic biomasses and activities in carbon and phosphorus cycles at a coastal, thermohaline front and in offshore waters (Gulf of Manfredonia, Southern Adriatic Sea). Microb Ecol 67:501–519
Mopper K, Ramana KS, Drapeau DT (1995) The role of surface-active carbohydrates in the flocculation of a diatom bloom in a mesocosm. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 42:47–73
Myklestad S, Haug A (1972) Production of carbohydrates by the marine diatom Chaetoceros affinis var. willei (Gran) Hustedt. I. Effect of the concentration of nutrients in the culture medium. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 9:125–136
Nosaka Y, Yamashita Y, Suzuki K (2017) Dynamics and origin of transparent exopolymer particles in the Oyashio Region of the Western Subarctic Pacific during the Spring diatom bloom. Front Mar Sci 4:79
Ortega-Retuerta E, Duarte CM, Reche I (2010) Significance of bacterial activity for the distribution and dynamics of transparent exopolymer particles in the Mediterranean Sea. Microb Ecol 59:808–818
Ortega-Retuerta E, Marrasé C, Muñoz-Fernández A, Sala MM, Simó R, Gasol JM (2018) Seasonal dynamics of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and their drivers in the coastal NW Mediterranean Sea. Sci Total Environ 631:180–190
Passow U (2000) Formation of transparent exopolymer particles, TEP, from dissolved precursor material. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 192:1–11
Passow U (2002) Transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in aquatic environments. Prog Oceanogr 55:287–333
Passow U, Alldredge AL, Logan BE (1994) The role of particulate carbohydrate exudates in the flocculation of diatom blooms. Deep Sea Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap 41:335–357
Passow U, Shipe RF, Murray A, Pak DK, Brzezinski MA, Alldredge AL (2001) The origin of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) and their role in the sedimentation of particulate matter. Cont Shelf Res 21:327–346
Pedrotti ML, Peters F, Beauvais S, Vidal M, Egge J, Jacobsen A, Marrasé C (2010) Effects of nutrients and turbulence on the production of transparent exopolymer particles: a mesocosm study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 419:57–69
Pernthaler J, Sattler B, Simek K, Schwarzenbacher A, Psenner R (1996) Top-down effects on the size-biomass distribution of a freshwater bacterioplankton community. Aquat Microb Ecol 10:255–263
Piontek J, Händel N, De Bodt C, Harlay J, Chou L, Engel A (2011) The utilization of polysaccharides by heterotrophic bacterioplankton in the Bay of Biscay (North Atlantic Ocean). J Plankton Res 33:1719–1735
Prieto L, Navarro G, Cozar A, Echevarria F, Garcia CM (2006) Distribution of TEP in the euphotic and upper mesopelagic zones of the southern Iberian coasts. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 53:1314–1328
Pugnetti A, Armeni M, Camatti E, Crevatin E, Dell’Anno A, Del Negro P, Milandri A, Socal G, Umani SF, Danovaro R (2005) Imbalance between phytoplankton production and bacterial carbon demand in relation to mucilage formation in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Sci Total Environ 353:162–177
Ramseier MK, von Gunten U, Freihofer P, Hammes F (2011) Kinetics of membrane damage to high (HNA) and low (LNA) nucleic acid bacterial clusters in drinking water by ozone, chlorine, chlorine dioxide, monochloramine, ferrate (VI), and permanganate. Water Res 45:1490–1500
Rgens KJ, Massana R (2008) Protistan grazing on marine bacterioplankton. Microbial ecology of the oceans. Wiley, Hoboken, p 383
Roy R, Anil AC (2015) Complex interplay of physical forcing and Prochlorococcus population in ocean. Prog Oceanogr 137:250–260
Roy R, Chitari R, Kulkarni V, Krishna MS, Sarma VVSS, Anil AC (2015) CHEMTAX-derived phytoplankton community structure associated with temperature fronts in the northeastern Arabian Sea. J Mar Syst 144:81–91
Samo TJ, Pedler BE, Ball GI, Pasulka AL, Taylor AG, Aluwihare LI, Azam F, Ralf G, Landry MR (2012) Microbial distribution and activity across a water mass frontal zone in the California current ecosystem. J Plankton Res 34:802–814
Sanders RW, Caron DA, Berninger UG (1992) Relationships between bacteria and heterotrophic nanoplankton in marine and fresh waters: an inter-ecosystem comparison. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 86:1–14
Sarma VVSS, Desai DV, Patil JS, Khandeparker L, Aparna SG, Shankar D, D’Souza S, Dalabehera HB, Mukherjee J, Sudharani P, Anil AC (2018) Ecosystem response in temperature fronts in the northeastern Arabian Sea. Prog Oceanogr 165:317–331
Schattenhofer M, Wulf J, Kostadinov I, Glöckner FO, Zubkov MV, Fuchs BM (2011) Phylogenetic characterisation of picoplanktonic populations with high and low nucleic acid content in the North Atlantic Ocean. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:470–475
Schuster S, Herndl GJ (1995) Formation and significance of transparent exopolymeric particles in the northern Adriatic Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 124:227–236
Šimek K, Kasalický V, Jezbera J, Horňák K, Nedoma J, Hahn MW, Bass D, Jost S, Boenigk J (2013) Differential freshwater flagellate community response to bacterial food quality with a focus on Limnohabitans bacteria. ISME J 7:1519
Sintes E, del Giorgio PA (2014) Feedbacks between protistan single-cell activity and bacterial physiological structure reinforce the predator/prey link in microbial foodwebs. Front Microbiol 5:453
Smestad B, Haug A, Myklestad S (1975) Structural studies of the extracellular polysaccharide produced by the diatom Chaeotoceros curvisetus cleve. Acta Chem Scand B 29:337–340
Smucker RA, Dawson R (1986) Products of photosynthesis by marine phytoplankton: chitin in TCA “protein” precipitates. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 104:143–152
Somville M (1984) Measurement and study of substrate specificity of exoglucosidase activity in eutrophic water. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:1181–1185
Størseth TR, Kirkvold S, Skjermo J, Reitan KI (2006) A branched β-d-(1→ 3, 1→ 6)-glucan from the marine diatom Chaetoceros debilis (Bacillariophyceae) characterized by NMR. Carbohydr Res 341:2108–2114
Tang KW, Turk V, Grossart HP (2010) Linkage between crustacean zooplankton and aquatic bacteria. Aquat Microb Ecol 61:261–277
ter Braak CJ, Smilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user's guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). https://www.canoco.com.
Thornton DC (2004) Formation of transparent exopolymeric particles (TEP) from macroalgal detritus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 282:1–12
Vipin P, Sarkar K, Aparna SG, Shankar D, Sarma VVSS, Gracias DG, Krishna MS, Srikanth G, Mandal R, Rao ER, Rao NS (2015) Evolution and sub-surface characteristics of a sea-surface temperature filament and front in the northeastern Arabian Sea during November–December 2012. J Mar Syst 150:1–11
Wang Y, Hammes F, Boon N, Chami M, Egli T (2009) Isolation and characterization of low nucleic acid (LNA)-content bacteria. ISME J 3:889–902
Woodson CB, Litvin SY (2015) Ocean fronts drive marine fishery production and biogeochemical cycling. PNAS 112:1710–1715
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank The Director, NIO, for his support and the captain, officers and crew members of SSK # 060 cruise for helping us on-board. We also thank other members of the cruise and Ocean Finder teammates. The present study was supported by the OCEAN FINDER programme PSC 0105 of CSIR-NIO. R.E. acknowledges CSIR for the award of Senior Research Fellowship (SRF award no: 31/26(282)/2015-EMRI). He is a registered doctoral student in the School of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, Goa University. This is a NIO contribution No. 6655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
27_2020_770_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1 Spatial and vertical profiles of a) HNA-complexity (SSC) b) LNA-complexity (SSC), c) HNA-DNA content (FL1), d) LNA-DNA content (FL1), e) variation in DNA content ratio of HNA and LNA bacteria, f) variation between complexity ratio of HNA and LNA bacteria along the cruise transect. Profiles with a symbol are "frontal"; unmarked profiles are "non-frontal" stations in each transect (PDF 4110 KB)
27_2020_770_MOESM2_ESM.eps
Supplementary file2 Response of abiotic and biotic variables in the non-front and fronts of different regions in the NEAS. All values are expressed as a depth-integrated; X-axis indicate different variables; Different Y-axis represent the units for different variables. (EPS 1617 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khandeparker, L., Eswaran, R. & Anil, A.C. How does frontal age influence physiological status of bacteria: a case study from the Northeastern Arabian Sea. Aquat Sci 83, 17 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-020-00770-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-020-00770-8