Abstract
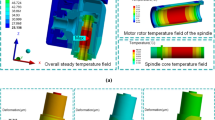
To ensure the stability of precision of the motorized spindle for five-axis machining center, the thermal error of five-axis machining center was investigated, and the temperature rise-thermal deformation model of a thin-wall ring type rotary elastomer was built on the basis of thermo-elastic property. Thus, a model of radial thermal error was con-structed. The relationship between radial error and axial error was also investigated in this paper and the total radial errors were gotten. In addition, the thermal error of the motorized spindle of five-axis machining center was measured by the ball bar in the experiment of thermal error. The motorized spindle total radial error was achieved by this experiment and radial total error analytical model. Finally, a BP neural network algorithm was introduced for thermal error prediction of five-axis machining center, and the precision of prediction of these models was compared and analyzed. The analysis shows that this method is practical and effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- σ r :
-
Radial normal stress
- σ θ :
-
Radian normal stress; is shear stress.
- E :
-
Elastic modulus of the material
- μ :
-
Poisson ratio of the material
- α :
-
Linear expansion coefficient of the material
- μ 1 :
-
Bearing’s radial thermal error
- μ 2 :
-
Radial thermal error caused by axial deformation
- Δ :
-
Axial thermal error
- μ r :
-
Radial total thermal error
- δ X :
-
x direction measurement thermal error
- δ y :
-
y direction measurement thermal error
- δ z :
-
z direction measurement thermal error
References
Y. Li, W. Zhao and S. Lan, A review on spindle thermal error compensation in machine tools, Int. J. Mach. Tools & Manuf., 95 (2015) 20–38.
B. Bossmanns and J. F. Tu, A thermal model for high speed motorized spindles, Int. J. Mach. Tools & Manuf., 39(9) (1990) 1345–1366.
J. Lee, D. H. Kim and C. M. Lee, A study on the thermal characteristics and experiments of high-speed spindle for machine tools, International J. of Precision Eng. and Manuf., 16(2) (2015) 293–299.
Z. F. Liu, M. H. Pan and A. P. Zhang, Thermal characteristic analysis of high-speed motorized spindle system based on thermal contact resistance and thermal-conduction resistance, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 76(9) (2015) 1913–1926.
A. Zivkovic, M. Zeljkovic and S. Tabakovic, Mathematical modeling and experimental testing of high-speed spindle behavior, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 77(5) (2015) 107–1086.
H. Su, L. Lu and Y. Liang, Thermal analysis of the hydrostatic spindle system by the finite volume element method, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 71(9–12) (2014) 1949–1959.
C. Ma, J. Yang and L. Zhao, Simulation and experimental study on the thermally induced deformations of high-speed spindle system, Applied Thermal Engineering, 86 (2015) 251–268.
C. Ma, X. Mei and J. Yang, Thermal characteristics analysis and experimental study on the high-speed spindle system, J. of Zhejiang University, 79(1–4) (2015) 469–489.
Y. Li, W. Zhao, W. Wu and B. Lu, Boundary conditions optimization of spindle thermal error analysis and thermal key points selection based on inverse heat conduction, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 90(9–12) (2017) 2803–2812.
Y. Cui, H. Li, T. Li and L. Chen, An accurate thermal performance modeling and simulation method for motorized spindle of machine tool based on thermal contact resistance analysis, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 96(2) (2018) 1–13.
L. Zhang, W. Gong, K. Zhang, Y. Wu, D. An and H. Shi, Thermal deformation prediction of high-speed motorized spindle based on biogeography optimization algorithm, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 97(5–8) (2018) 1–11.
Z. F. Liu, M. H. Pan, A. P. Zhang, Y. S. Zhao, Y. Yang and C. Y. Ma, Thermal characteristic analysis of high-speed motorized spindle system based on thermal contact resistance and thermalconduction resistance, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 76 (2015) 1913–1926.
T. Liu, W. G. Gao, D. W. Zhang, Y. F. Zhang, W. F. Chang, C. M. Liang and Y. L. Tian, Analytical modeling for thermal errors of motorized spindle unit, Int. J. Mach. Tool Manu., 112 (2016) 53–70.
Q. Li and H. Li, A general method for thermal error measurement and modeling in CNC machine tools’ spindle, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 103(5–8) (2019) 2739–2749.
A. Statham, Assessing the thermal distortion caused by spindle rotation of a machining centre using the draft standard ISO/DIS 230-3, Laser Metrology & Machine Performance III (2014).
Z. S. Yan, W. H. Lin and C. H. Liu, Measurement of the thermal elongation of high speed spindles in real time using a cat’s eye reflector based optical sensor, Sensors & Actuators A Physical, 221(10) (2015) 154–160.
K. Liu, T. Li, H. Liu, Y. Liu and Y. Wang, Analysis and prediction for spindle thermal bending deformations of a vertical milling machine, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 16(3) (2020) 1549–1558.
X. Qi, D. Zhang and H. Zhang, The control system design of thermal experimental platform for high-speed spindle based PLC, International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation, IEEE Computer Society (2010) 639–642.
H. Lu, Q. Wu and S. Wu, A new spindle rotation error measurement system based on three point method, Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, IEEE (2016) 2003–2008.
S. D. Ashok and G. L. Samuel, Modeling, measurement, and evaluation of spindle radial errors in a miniaturized machine tool, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 59(5–8) (2012) 445–461.
C. W. Wu, C. F. Chang and Y. S. Shiao, Thermal error compensation method for machine center, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 59(5–8) (2012) 681–689.
Y. Li, W. Zhao and W. Wu, Thermal error modeling of the spindle based on multiple variables for the precision machine tool, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 72(9–12) (2014) 1415–1427.
K. Liu, T. Li and T. Li, Thermal behavior analysis of horizontal CNC lathe spindle and compensation for radial thermal drift error, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 95(1–4) (2018) 1293–1301.
T. M. Li, F. C. Li, Y. Jiang and H. T. Wang, Thermal error modeling and compensation of a heavy gantry-type machine tool and its verification in machining, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 92 (2017) 3073–3092.
B. M. Wang, X. S. Mei, Z. X. Wu and F. Zhu, Dynamic modeling for thermal error in motorized spindles, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 78 (2015) 1141–1146.
J. Yang, H. Shi, B. Feng, L. Zhao, C. Ma and X. S. Mei, Thermal error modeling and compensation for a high-speed motorized spindle, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 77 (2015) 1005–1017.
Q. Yin, F. Tan, H. Chen and G. Yin, Spindle thermal error modeling based on selective ensemble bp neural networks, The Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 101(5–8) (2019) 1699–1713.
B. Jian et al., Predicting spindle displacement caused by heat using the general regression neural network, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 104(9–12) (2019) 4665–4674.
B. L. Jian, Y. S. Guo, C. H. Hu, L. W. Wu and H. T. Yau, Prediction of spindle thermal deformation and displacement using back propagation neural network, Sensors and Materials, 32(1) (2020) 431–445.
W. Tian, G. Wang, L. Yang and W. Gao, The application of a regularization method to the estimation of geometric errors of a three-axis machine tool using a double ball bar, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 32(10) (2018) 4871–4881.
Z. Zhao, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Z. Wang and C. Quan, Dynamic thermal behavior and thermal error prediction of spindle due to periodic jump motions in a large precision die-sinking edm machine, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 33(7) (2019) 3397–3405.
B. Rengui, Q. Pingz and Y. Can, Elasto-plastic analysis for static and dynamic performance of rolling element bearings, J. of Jishou University (Natural Sciences Edition), 40(5) (2019) 37–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaofeng Wang is a Post Doctor of Jilin University. He received his Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from Jilin University. His research interests include manufacturing equipment reliability and thermal balance design of precision machine tools.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, X., Zhu, X. et al. Thermal error prediction of motorized spindle for five-axis machining center based on analytical modeling and BP neural network. J Mech Sci Technol 35, 281–292 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-020-1228-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-020-1228-7