Abstract
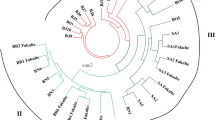
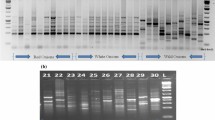
Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of germplasm collections provides an opportunity for plant breeders to develop new and improved cultivars. In this study, genotypic variation of 90 lentil genotypes was evaluated using 10 CAAT Box Derived Polymorphism (CBDP) markers. The polymorphism percentage was 100% with an average of 100% indicating a high polymorphism level. A total of 117 alleles were identified for different genetic locations and with an average of 13 alleles per primer. Among CBDP markers used, the highest allele amplified belonged to CBDP22 marker with 21 bands and the lowest allele amplified corresponded to CBDP3, CBDP6 and CBDP13 markers with 11 bands. The Polymorphic information content (PIC) ranged from 0.413 to 0.471 with an average of 0.448. Marker Index (MI) ranged from 4.85 to 9.90. The highest index for genetic diversity (PIC and MI) belonged to the CBDP22 indicating a high resolution for this marker as compared to other markers. Based on neighbor joining clustering for molecular data, genotypes were grouped into five distinct groups. Population structure analysis showed that the highest peak was at K = 3, indicating the presence of three major clusters. The results of this study showed that CBDP markers can be used as a useful tool for studying the genetic diversity of lentil germplasm.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alabboud, I., Szilagyi, L., and Roman, G.H.V., Assessment of genetic diversity in lentil (Lens culinary Medik) as revealed by RAPD markers, Sci. Pap., USAMV Bucharest, Ser. A, 2009, vol. LII.
Vicente, Joana G., Conway, J., Roberts, S.J., and Taylor, J.D., Identification and origin of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races and related pathovars, Phytopathology, 2001, 91, no. 5, 492–499.
Upadhyaya, H. D., and Ortiz, R., A mini core subset for capturing diversity and promoting utilization of chickpea genetic resources in crop improvement, Theor. Appl. Genet., 2001, vol. 102, no. 8, pp. 1292–1298.
Ghafoor, A., Sharif, A., Ahmad, Z., Zahid, M.A., and Rabbani, M.A., Genetic diversity in blackgram (Vigna mungo L. Hepper), Field Crops Res., 2001, vol. 69, no. 2, pp. 183–190.
Baldwin, S., Pither-Joyce, M., Wright, K., Chen, L., and McCallum, J., Development of robust genomic simple sequence repeat markers for estimation of genetic diversity within and among bulb onion (Allium cepa L.) populations, Mol. Breed., 2012, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 1401–1411.
Feghhi, S.M.A., Norouzi, P., Saidi, A., Zamani, K. and Amiri, R. Research Article Identification of SCAR and RAPD markers linked to Rz1 gene in Holly sugar beet using BSA and two genetic distance estimation methods, Electr. J. Plant Breed, 2012, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 598–605.
Altıntas, S., Toklu, F., Kafkas, S., Kilian, B., Brandolini, A., and Özkan, H., Estimating genetic diversity in durum and bread wheat cultivars from Turkey using AFLP and SAMPL markers, Plant Breed. 2008, vol. 127, no. 1, pp. 9–14.
Fatehi, R., Talebi, R. and Fayyaz, F., Characterization of Iranian landrace wheat accessions by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers, J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Sci., 2011, vol. 1, no. 10, pp. 432–436.
Hajibarat, Z., Saidi, A., Hajibarat, Z., and Talebi, R, Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of landrace and improved chickpea (Cicer arietinum) genotypes using morphological and microsatellite markers, Environ. Exp. Biol., 2014, vol. 12, pp. 161–166.
Saidi, A., Eghbalnegad, Y., and Hajibarat, Z., Study of genetic diversity in local rose varieties (Rosa spp.) using molecular markers, Banats J. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 8, pp. 148–157.
Singh, A.K., Rana, M.K., Singh, S., Kumar, S., Kumar, R, and Singh, R, CAAT box-derived polymorphism (CBDP): a novel promoter-targeted molecular marker for plants, J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 175–183.
Etminan, A., Pour-Aboughadareh, A., Mohammadi, R., Noori, A., and Ahmadi-Rad, A., Applicability of CAAT box-derived polymorphism (CBDP) markers for analysis of genetic diversity in durum wheat, Cereal Res. Commun., 2018, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 1–9.
Hajibarat, Z., Saidi, A., Hajibarat, Z. and Talebi, R., Characterization of genetic diversity in chickpea using SSR markers, start codon targeted polymorphism (SCoT) and conserved DNA-derived polymorphism (CDDP), Physiol. Mol. Boil. Plants, 2015, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 365–373.
Lassner, M.W., Peterson, P., and Yoder, J.I., Simultaneous amplification of multiple DNA fragments by polymerase chain reaction in the analysis of transgenic plants and their progeny, Plant Mol. Biol. Repr., 1989, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 116–128.
Lynch, M. and Walsh, J.B., Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits, Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates Inc., 1998.
Yeh, F.C., Yang, R.C., Boyle, T.B.J., Ye, Z.H., and Mao, J.X., POPGENE, the User Friendly Shareware for Population Genetic Analysis, Edmonton: Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. Center. Univ. Alberta, 1997.
Pritchard J.K., Stephens M., and Donnelly, P., Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data, Genetics, 2000, vol. 155, pp. 945–959.
Evanno, G., Regnaut, S., and Goudet, J., Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study, Mol. Ecol., 2005, vol. 14, no. 8, pp. 2611–2620.
Paterson A.H., Tanksley S.D., and Sorrells, M.E., DNA markers in plant improvement, Adv. Agron., 1991, vol. 46, pp. 39–90.
Collard, B.C.Y., Mackill, D.J., Conserved DNA-derived polymorphism (CDDP): a simple and novel method for generating DNA markers in plants, Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 2009, vol. 27, no. 4, p. 558.
Saidi, A., Daneshvar, Z., and Hajibarat, Z., Comparison of genetic variation of Anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum) cultivars using SCoT, CDDP and RAPD markers, Plant Tiss. Cult. Biotechnol., 2018, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 171–182.
Singh, A.K., Rana, M.K., Singh, S., Kumar, S., Kumar, R., and Singh, R., CAAT box-derived polymorphism (CBDP): a novel promoter-targeted molecular marker for plants, J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 175–183.
Heikrujam, M., Kumar, J., and Agrawal, V., Genetic diversity analysis among male and female Jojoba genotypes employing gene targeted molecular markers, Start Codon Targeted (SCoT) polymorphism and CAAT Box Derived Polymorphism (CBDP) markers, Meta Gene, 2015, vol. 5, pp. 90–97.
Tiwaria, G., Singha, R., Singha, N., Roy, Choudhurya, D., Paliwala, R., Kumarb, A., and Gupta., V., Study of arbitrarily amplified (RAPD and ISSR) and gene targeted (SCoT and CBDP) markers for genetic diversity and population structure in Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees), Industr. Crops Prod., 2016, vol. 86, pp. 1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Sarvmeili, J., Saidi, A., Farrokhi, N. et al. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure Analysis of Landrace and Wild Relatives of Lentil Germplasm Using CBDP Marker. Cytol. Genet. 54, 566–573 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452720060092
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452720060092