Abstract
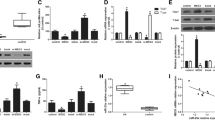
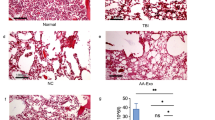
MiR-150-5p is an immune-related miRNA and elevated in the plasma of patients with aplastic anemia (AA), but its role in T cell activation in patients with severe aplastic anemia (SAA) is unclear. This study aims to explore the role of miR-150-5p in T cell activation of SAA. RT-PCR and Western blot were used to detect the expression of mRNA and protein. The cell proportion was detected by flow cytometry. The lentiviruses expressing miR-150-5p inhibitor and Bach2 shRNA were respectively infected to produce stable miR-150-5p or Bach2 knockout cells. Brdu incorporation method was used to detect T cell proliferation. SAA mouse model was induced with cyclophosphamide and busulfan, and intravenous injection of LV inhibitor NC and LV-miR-150-5p inhibitor. The miR-150-5p expression is up-regulated in SAA, which is negatively correlated with Bach2. Inhibition of miR-150-5p reduces the activation of T cells. MiR-150-5p directly targeted 3′UTR of Bach2. Moreover, the expression of miR-150-5p and the activation of T cells were decreased in SAA mouse model. MiR-150-5p promotes T cell activation in SAA by targeting Bach2. Targeting miR-150-5p may be a new molecular therapy for SAA patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akihiko M, Kyoko O, Yoshitaka K, Ari IN, Calame KL, Dai I, Satoshi T, Kazuhiko I (2014) Bach2 represses plasma cell gene regulatory network in B cells to promote antibody class switch. EMBO J 29:4048–4061
Alves AC, Bruhn S, Ramasamy A, Wang H, Holloway JW, Hartikainen AL, Jarvelin MR, Benson M, Balding DJ, Coin LJM (2013) Dysregulation of complement system and CD4+ T cell activation pathways implicated in allergic response. Plos One 8.
Ban YH, Oh SC, Seo SH, Kim SM, Choi IP, Greenberg PD, Chang J, Kim TD, Ha SJ (2017) miR-150-mediated Foxo1 regulation programs CD8 T cell differentiation. Cell Rep 20:2598–2611
Bart-Jan K, Nato T, Katarzyna SC, Elisabeth B, Boots AMH, Anke VDB, Joost K (2015) Immuno-miRs: critical regulators of T-cell development, function and ageing. Immunology 144:1–10
Chen Z, Stelekati E, Kurachi M, Yu S, Cai Z, Manne S, Khan O, Yang X, Wherry EJ (2017) miR-150 regulates memory CD8 T cell differentiation via c-Myb. Cell Rep 20:2584–2597
F S, N S, Y J, Y M, H D, Q Z, F Y, W L, (2019) Aberrant expression of imprinted lncRNA MEG8 causes trophoblast dysfunction and abortion. J Cell Biochem 120:17378–17390
Hosokawa K, Kajigaya S, Feng X, Desierto MJ, Fernandez Ibanez MD, Rios O, Weinstein B, Scheinberg P, Townsley DM, Young NS (2017) A plasma microRNA signature as a biomarker for acquired aplastic anemia. Haematologica 102:69–78
Jang E, Lee HR, Lee GH, Oh AR, Cha JY, Igarashi K, Youn J (2017) Bach2 represses the AP-1-driven induction of interleukin-2 gene transcription in CD4+T cells. BMB Rep 50:472–477
Kim TD, Jung HR, Seo SH, Oh SC, Ban Y, Tan X, Min KJ, Hyun Lee S, Koh DS, Jung H, Park YJ, Ran YS, Doh J, Ha SJ, Choi I, Greenberg PD (2017) MicroRNA-150 modulates intracellular Ca levels in naïve CD8 T cells by targeting TMEM20. Sci Rep 7:2623
Kohei H, Pawel M, Xingmin F, Keyvan K, Townsley DM, Bogdan D, Jichun C, Sachiko K, Taylor JG, Hourigan CS (2015) Identification of novel microRNA signatures linked to acquired aplastic anemia. Haematologica 100:1534–1545
Lahmann A, Kuhrau J, Fuhrmann F, Heinrich F, Bauer L, Durek P, Mashreghi MF, Hutloff A (2019) Bach2 controls T follicular helper cells by direct repression of Bcl-6. J Immunol 202:2229–2239
Pt P, K V, S J, LH R, H T, S M, O V, TP A, (2011) A functional complement system is required for normal T helper cell differentiation. Immunobiology 216:737–743
Pyaram K, Yadav VN, Reza MJ (2010) Sahu A Virus–complement interactions: an assiduous struggle for dominance. Future Virology 5:709–730
Richer MJ, Lang ML, Butler NS (2016) T cell fates zipped up: how the Bach2 basic leucine zipper transcriptional repressor directs T cell differentiation and function. J Immunol 197:1009–1015
Shallis RM, Ahmad R, Zeidan AM (2018) Aplastic anemia: etiology, molecular pathogenesis, and emerging concepts. Eur J Haematol 101:711–720
Shin-Ichi T, Midori U, Akihiko M, Arata T, Kohei K, Tomohiro K, Kazuhiko I, Takashi S (2013) Bach2 maintains T cells in a naive state by suppressing effector memory-related genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:10735–10740
Yu X, Lao Y, Teng XL, Li S, Zhou Y, Wang F, Guo X, Deng S, Chang Y, Wu X, Liu Z, Chen L, Lu LM, Cheng J, Li B, Su B, Jiang J, Li HB, Huang C, Yi J, Zou Q (2018) SENP3 maintains the stability and function of regulatory T cells via BACH2 deSUMOylation. Nat Commun 9:3157
Funding
This study was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1804192) and Key Scientific Research Project Plan of Institutions of Higher Learning of Henan Province (19A320046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All protocols were authorized by the Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yu, J., Wang, F. et al. MiR-150-5p regulate T cell activation in severe aplastic anemia by targeting Bach2. Cell Tissue Res 384, 423–434 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03373-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03373-9