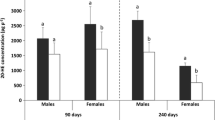
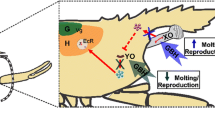
Abstract
Endocrine disruption compounds (EDC) are known to affect reproduction, development, and growth of exposed organisms. Although in vertebrates, EDCs mainly act through steroid receptors (e.g. androgen and estrogen receptors), their absence in many invertebrates suggests the involvement of another biological pathway in endocrine disruption effects. As retinoid signaling pathway is present in almost all Metazoa and its involvement in the endocrine disruption of gastropods (i.e. imposex) has been demonstrated, the present work was devoted to investigating the relative mRNA variations of two retinoid receptors genes, retinoid X receptor (RXR) and retinoid acid receptor (RAR), in the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus exposed for 6, 12 and 24 h to flutamide, fenitrothion and cyproterone acetate, three anti-androgens known to disrupt sexual reproduction of Brachionus sp. Results revealed that fenitrothion did not affect the relative mRNA levels RXR and RAR in B. calyciflorus, whereas RXR and RAR mRNA levels could be significantly increased by 2 to 4.5-fold and from 2 to 7-fold after exposure to flutamide and cyproterone acetate, respectively. Moreover, the effects of flutamide and cyproterone acetate were measured from 6 and 12 h of exposure, respectively. Cyproterone acetate caused the highest increase of RXR and RAR mRNA levels, probably due to its progestin activity in addition to its anti-androgenic activity and the potential presence of a membrane-associated progesterone receptor as reported in Brachionus manjavacas. Consequently, although it is still difficult to evaluate the hormonal pathways involved in the endocrine disruption in Brachionus sp., this work suggests that the retinoid signaling pathway appears to be a good starting point to try to elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in sexual reproductive dysfunction in Brachionidae.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidli S, Castro LFC, Lahbib Y, Reis-Henriques MA, El Menif NT, Santos MM (2013) Imposex development in Hexaplex trunculus (Gastropoda: Caenogastropoda) involves changes in the transcription levels of the retinoid X receptor (RXR). Chemosphere 93(6):1161–1167
Addinsoft (2019) XLSTAT 2019: data analysis and statistical solution for Microsoft Excel. Paris, France
Allenby G, Bocquel MT, Saunders M, Kazmer S, Speck J, Rosenberger M, Lovey A, Kastner P, Grippo JF, Chambon P (1993) Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90(1):30–34
André A, Ruivo R, Fonseca E, Froufe E, Castro LFC, Santos MM (2019) The retinoic acid receptor (RAR) in molluscs: function, evolution and endocrine disruption insights. Aquat Toxicol 208:80–89
Bettin C, Oehlmann J, Stroben E (1996) TBT-induced imposex in marine neogastropods is mediated by an increasing androgen level. Helgoländer Meeresun 50(3):299–317
Cui J, Wu L, Chan SM, Chu KH (2013) cDNA cloning and mRNA expression of retinoid-X-receptor in the ovary of the shrimp Metapenaeus ensis. Mol Biol Rep 40(11):6233–6244
Dawson MI, Xia Z (2012) The retinoid X receptors and their ligands. BBA-Mol Cell Biol L 1821(1):21–56
Ferrando MD, Sancho E, Andreu-Moliner E (1996) Chronic toxicity of fenitrothion to an algae (Nannochloris oculata), a rotifer (Brachionus calyciflorus), and the cladoceran (Daphnia magna). Ecotox Environ Safe 35(2):112–120
Gallardo WG, Hagiwara A, Tomita Y, Soyano K, Snell TW (1997) Effect of some vertebrate and invertebrate hormones on the population growth, mictic female production, and body size of the marine rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Müller. Hydrobiologia 358(1–3):113–120
Germain P, Altucci L, Bourguet W, Rochette-Egly C, Gronemeyer H (2003) Nuclear receptor superfamily: principles of signaling Pureand Applied Chemistry 75(11-12):1619–1664
Gilbert JJ (2003) Environmental and endogenous control of sexuality in a rotifer life cycle: developmental and population biology. Evol Dev 5(1):19–24
Gismondi E, Cauchie HM, Cruciani V, Joaquim-Justo C (2019) Targeted impact of cyproterone acetate on the sexual reproduction of female rotifers. Ecotoxicology 28(6), 643–649
Haeba MH, Hilscherová K, Mazurová E, Bláha L (2008) Selected endocrine disrupting compounds (vinclozolin, flutamide, ketoconazole and dicofol): effects on survival, occurrence of males, growth, molting and reproduction of Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Pollut R 15(3):222
Handberg-Thorsager M, Gutierrez-Mazariegos J, Arold ST, Nadendla EK, Bertucci PY, Germain P, Tomançak P, Pierzchalski K, Jones JW, Albalat R, Kane MA, Bourguet W, Laudet V, Arendt D, Schubert M (2018) The ancestral retinoic acid receptor was a low-affinity sensor triggering neuronal differentiation. Science Adv 4(2):eaao1261
Kamei Y, Kawada T, Kazuki R, Sugimoto E (1993) Retinoic acid receptor γ 2 gene expression is up-regulated by retinoic acid in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Biochem J 293(3):807–812
Kim DH, Kim HS, Hwang DS, Kim HJ, Hagiwara A, Lee JS, Jeong CB (2017) Genome-wide identification of nuclear receptor (NR) genes and the evolutionary significance of the NR1O subfamily in the monogonont rotifer Brachionus spp. Gen Comp Endocr 252:219–225
Lee MC, Fonseca E, Park JC, Yoon DS, Choi H, Kim M, Han J, Cho HC, Shin KH, Santos ML, Jung JH, Castro LFC, Lee JS (2019) Tributyltin affects retinoid X receptor-mediated lipid metabolism in the marine rotifer Brachionus koreanus. Environ Sci Technol 53(13):7830–7839
Lima D, Reis-Henriques MA, Silva R, Santos AI, Castro LFC, Santos MM (2011) Tributyltin-induced imposex in marine gastropods involves tissue-specific modulation of the retinoid X receptor. Aquat Toxicol 101(1):221–227
Litoff EJ, Garriott TE, Ginjupalli GK, Butler L, Gay C, Scott K, Baldwin WS (2014) Annotation of the Daphnia magna nuclear receptors: comparison to Daphnia pulex. Gene 552(1):116–125
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−▵▵CT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lv L, Snell TW, Yang J, Li S, Zhu W (2010) Effects of fenitrothion on life history parameters of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. J Freshwater Ecol 25(4):589–598
Lv L, Dong X, Lv F, Zhao W, Yu Y, Yang W (2017) Molecular cloning and characterization of an estrogen receptor gene in the marine polychaete Perinereis aibuhitensis. Comp Biochem Phys B 207:15–21
Mangelsdorf DJ, Borgmeyer U, Heyman RA, Zhou JY, Ong ES, Oro AE, Kakizuka A, Evans RM (1992) Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev 6(3):329–344
Matthiessen P (2003) Endocrine disruption in marine fish. Pure Appl Chem 75(11–12):2249–2261
Matthiessen P, Sumpter JP (1998) Effects of estrogenic substances in the aquatic environment. In: Fish ecotoxicology. Birkhäuser, Basel, p 319–335
Nishikawa JI, Mamiya S, Kanayama T, Nishikawa T, Shiraishi F, Horiguchi T (2004) Involvement of the retinoid X receptor in the development of imposex caused by organotins in gastropods. Environ Sci Tech 38(23):6271–6276
Novák J, Beníšek M, Hilscherová K (2008) Disruption of retinoid transport, metabolism and signaling by environmental pollutants. Environ Int 34(6):898–913
Novák J, Jálová V, Giesy JP, Hilscherová K (2009) Pollutants in particulate and gaseous fractions of ambient air interfere with multiple signaling pathways in vitro. Environ Int 35:43–49
Ooms‐Wilms AL, Postema G, Gulati RD (1999) Population dynamics of planktonic rotifers in Lake Loosdrecht, the Netherlands, in relation to their potential food and predators. Freshwater Biol 42(1):77–97
Poyet P, Labrie F (1985) Comparison of the antiandrogenic/androgenic activities of flutamide, cyproterone acetate and megestrol acetate. Mol Cell Endocrinol 42(3):283–288
Preston BL, Snell TW, Robertson TL, Dingmann BJ (2000) Use of freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus in screening assay for potential endocrine disruptors. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(12):2923–2928
Santos MM, Reis-Henriques MA, Castro LFC (2012) Lipid homeostasis perturbation by organotins: effects on vertebrates and invertebrates in biochemical and biological effects of organotins. In: Pagliarani A, Trombetti F, Ventrella V (eds) Biochemical and biological effects of organotins. Bentham Science, Italy, p 83–96
Smallridge RC, Carr FE, Fein HG (1991) Diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) reduces serum prolactin, thyrotropin, luteinizing hormone, and growth hormone and increases adrenocorticotropin and corticosterone in rats: involvement of dopaminergic and somatostatinergic as well as cholinergic pathways. Toxicol Applied Pharm 108(2):284–295
Smith HA, Welch DBM, Snell TW (2011) Molecular evolution of the membrane associated progesterone receptor in the Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera, Monogononta) species complex. Hydrobiologia 662(1):99–106
Snell TW, Moffat BD, Janssen C, Persoone G (1991) Acute toxicity tests using rotifers: IV. Effects of cyst age, temperature, and salinity on the sensitivity of Brachionus calyciflorus. Ecotox Environ Saf 21(3):308–317
Snell TW, Carmona MJ (1995) Comparative toxicant sensitivity of sexual and asexual reproduction in the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. Environ Toxicol Chem 14(3):415–420
Snell TW, Joaquim-Justo C (2007) Workshop on rotifers in ecotoxicology. Hydrobiologia 593(1):227–232
Stange D, Sieratowicz A, Oehlmann J (2012) Imposex development in Nucella lapillus–evidence for the involvement of retinoid X receptor and androgen signalling pathways in vivo. Aquat Toxicol 106:20–24
Stout EP, La Clair JJ, Snell TW, Shearer TL, Kubanek J (2010) Conservation of progesterone hormone function in invertebrate reproduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(26):11859–11864
Taib IS, Budin SB, Ghazali AR, Jayusman PA, Louis SR, Mohamed J (2013) Fenitrothion induced oxidative stress and morphological alterations of sperm and testes in male sprague-dawley rats. Clinics 68(1):93–100
Thomson SA, Baldwin WA, Wang YH, Kwon G, LeBlanc GA (2009) Annotation, phylogenetics, and expression of the nuclear receptors in Daphnia pulex. BMC Genom 10(1):500
Thornton JW (2003) Resurrecting the ancestral steroid receptor: ancient origin of estrogen signaling. Science 301:1714–1717
Titley-O’Neal CP, Munkittrick KR, MacDonald BA (2011) The effects of organotin on female gastropods. J Environ Monit 13(9):2360–2388
Venkaiah K, Thathapudi D, Sainath SB (2019) Detection and mode of action of retinoids on ovarian development in the mud crab, Scylla serrata. Int J Aquat Biol 7(5):245–253
Viroux L (1999) Zooplankton distribution in flowing waters and its implications for sampling: case studies in the River Meuse (Belgium) and the River Moselle (France, Luxembourg). J Plankton Res 21(7):1231–1248
World Health Organization (WHO) (2002) Global assessment of the state-of-the-science of endocrine disruptors. International Program on Chemical Safety, Geneva, Switzerland, p 180
Xi YL, Feng LK (2004) Effects of thiophanate-methyl and glyphosate on asexual and sexual reproduction in the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73(4):644–651
Zhang H, Pan L, Zhang L (2012) Molecular cloning and characterization of estrogen receptor gene in the Scallop Chlamys farreri: expression profiles in response to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Comp Biochem Phys C 156:51–57
Zhou Y, Zhang D, Hu D, Liu B, Peng J, Shen L, Chunlan L, Yihang H, Yuanyuan Z, Xing L, Xu T, Peter T, Tao L, Dawei H, Guanghui W (2019) Retinoic acid: a potential therapeutic agent for cryptorchidism infertility based on investigation of flutamide-induced cryptorchid rats in vivo and in vitro. Reprod Toxicol 87:108–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
All authors are willing to submit the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joaquim-Justo, C., Gismondi, E. Expression variations of two retinoid signaling pathway receptors in the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus exposed to three endocrine disruptors. Ecotoxicology 30, 343–350 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02339-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02339-5