Abstract
Key message
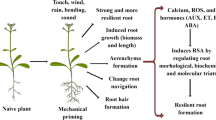
We found that mutations in a Ca 2+ -permeable mechanosensitive channel MCA1, an ethylene-regulated microtubule-associated protein WDL5, and a versatile co-receptor BAK1 affect root growth response to mechanical stress.
Abstract
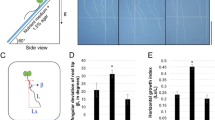
Plant root tips exposed to mechanical impedance show a temporal reduction in the elongation growth. The process involves a transient Ca2+ increase in the cytoplasm followed by ethylene signaling. To dissect the molecular mechanisms underlying this response, we examined the root growth of a series of Arabidopsis mutants with potentially altered response to mechanical stress after transfer from vertical to horizontal plates that were covered by dialysis membrane as an impedance. Among the plant hormone-response mutants tested, the ethylene-insensitive mutant ein3 was confirmed to show no growth reduction after the transfer. The root growth reduction was attenuated in a mutant of MCA1 encoding a Ca2+-permeable mechanosensitive channel and that of WDL5 encoding an ethylene-regulated microtubule-associated protein. We also found that the growth reduction was enhanced in a mutant of BAK1 encoding a co-receptor that pairs with numerous leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases to modulate growth and immunity. These results suggest the root growth reduction in response to mechanical stress involves ethylene-mediated microtubule reorganization and also transmembrane receptor-mediated signal transduction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arteca JM, Arteca RN (1999) A multi-responsive gene encoding 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase (ACS6) in mature Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Mol Biol 19:209–219
Bengough AG, Mullins CE (1990) Mechanical impedance to root growth: a review of experimental techniques and root growth responses. J Soil Sci 41:341–358
Cao H, Glazebrook J, Clarke JD, Volko S, Dong X (1997) The Arabidopsis NPR1 gene that controls systemic acquired resistance encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin repeats. Cell 88:57–63
Chehab EW, Yao C, Henderson Z, Kim S, Braam J (2012) Arabidopsis touch-induced morphogenesis is jasmonate mediated and protects against pests. Curr Biol 22:701–706
Chinchilla D, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Kemmerling B, Nürnberger T, Jones JD, Felix G, Boller T (2007) A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 448:497–500
Chinchilla D, Shan L, He P, de Vries S, Kemmerling B (2009) One for all: the receptor-associated kinase BAK1. Trends Plant Sci 14:535–541
Dodd AN, Kudla J, Sanders D (2010) The language of calcium signaling. Ann Rev Plant Biol 61:593–620
Dou L, He K, Higaki T, Wang X, Mao T (2018) Ethylene signaling modulates cortical microtubule reassembly in response to salt stress. Plant Physiol 176:2071–2081
Dressano K, Ceciliato PHO, Silva AL, Guerrero-Abad JC, Bergonci T, Ortiz-Morea FA, Bürger M, Silva-Filho MC, Moura DS (2017) BAK1 is involved in AtRALF1-induced inhibition of root cell expansion. PLoS Genet 13:e1007053
Ellis C, Turner JG (2002) A conditionally fertile coi1 allele reveals cross talk between plant hormone signalling pathways in Arabidopsis seeds and young seedlings. Planta 215:549–556
Escobar-Restrepo JM, Huck N, Kessler S, Gagliardini V, Gheyselinck J, Yang WC, Grossniklaus U (2007) The FERONIA receptor-like kinase mediates male–female interactions during pollen tube reception. Science 317:656–660
Feng W, Kita D, Peaucelle A, Cartwright HN, Doan V, Duan Q, Liu MC, Maman J, Steinhorst L, Schmitz-Thom I et al (2018) The FERONIA receptor kinase maintains cell-wall integrity during salt stress through Ca2+ signaling. Curr Biol 28:666–675
Franck CM, Westermann J, Boisson-Dernier A (2018) Plant malectin-like receptor kinases: from cell wall integrity to immunity and beyond. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69:301–328
Gonneau M, Desprez T, Martin M, Doblas VG, Bacete L, Miart F, Sormani R, Hematy K, Renou J, Landrein B et al (2018) Receptor kinase THESEUS1 is a rapid alkalinization factor 34 receptor in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 28:2452–2458
Guo H, Ecker JR (2003) Plant responses to ethylene gas are mediated by SCF (EBF1/EBF2)-dependent proteolysis of EIN3 transcription factor. Cell 115:667–677
Guzmán P, Ecker JR (1990) Exploiting the triple response of Arabidopsis to identify ethylene-related mutants. Plant Cell 2:513–523
Hamada T (2014) Microtubule organization and microtubule-associated proteins in plant cells. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 312:1–52
Hamant O, Haswell ES (2017) Life behind the wall: sensing mechanical cues in plants. BMC Biol 15:59–67
Haruta M, Sabat G, Stecker K, Minkoff BB, Sussman MR (2014) A peptide hormone and its receptor protein kinase regulate plant cell expansion. Science 343:408–411
He K, Gou X, Yuan T, Lin H, Asami T, Yoshida S, Russell SD, Li J (2007) BAK1 and BKK1 regulate brassinosteroid-dependent growth and brassinosteroid-independent cell-death pathways. Curr Biol 17:1109–1115
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada JP, Hartog MV, Schmidt ED, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Hématy K, Sado PE, Van Tuinen A, Rochange S, Desnos T, Balzergue S, Pelletier S, Renou JP, Höfte H (2007) A receptor-like kinase mediates the response of Arabidopsis cells to the inhibition of cellulose synthesis. Curr Biol 17:922–931
Ju C, Yoon GM, Shemansky JM, Lin DY, Ying ZI, Chang J, Garrett WM, Kessenbrock M, Groth G, Tucker ML et al (2012) CTR1 phosphorylates the central regulator EIN2 to control ethylene hormone signaling from the ER membrane to the nucleus in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:19486–19491
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48:452–458
Kurusu T, Kuchitsu K, Nakano M, Nakayama Y, Iida H (2013) Plant mechanosensing and Ca2+ transport. Trends Plant Sci 18:227–233
Ladwig F, Dahlke RI, Stührwohldt N, Hartmann J, Harter K, Sauter M (2015) Phytosulfokine regulates growth in Arabidopsis through a response module at the plasma membrane that includes CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE-GATED CHANNEL17, H+-ATPase, and BAK1. Plant Cell 27:1718–1729
Lee D, Polisensky DH, Braam J (2005) Genome-wide identification of touch- and darkness-regulated Arabidopsis genes: a focus on calmodulin-like and XTH genes. New Phytol 165:429–444
Li J, Wen J, Lease KA, Doke JT, Tax FE, Walker JC (2002) BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110:213–222
Li C, Yeh FL, Cheung AY, Duan Q, Kita D, Liu MC, Maman J, Luu EJ, Wu BW, Gates L et al (2015) Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins as chaperones and co-receptors for FERONIA receptor kinase signaling in Arabidopsis. eLife 4:e06587
Lian N, Liu X, Wang X, Zhou Y, Li H, Li J, Mao T (2017) COP1 mediates dark-specific degradation of microtubule-associated protein WDL3 in regulating Arabidopsis hypocotyl elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:12321–12326
Lorenzo O, Piqueras R, Sánchez-Serrano JJ, Solano R (2003) ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 integrates signals from ethylene and jasmonate pathways in plant defense. Plant Cell 15:165–178
Ma Q, Sun J, Mao T (2016) Microtubule bundling plays a role in ethylene-mediated cortical microtubule reorientation in etiolated hypocotyls. J Cell Sci 129:2043–2051
Massa GD, Gilroy S (2003) Touch modulates gravity sensing to regulate the growth of primary roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 33:435–445
Monshausen GB, Gilroy S (2009) Feeling green: mechanosensing in plants. Trends Cell Biol 19:228–235
Nakagawa Y, Katagiri T, Shinozaki K, Qi Z, Tatsumi H, Furuichi T, Kishigami A, Sokabe M, Kojima I, Sato S et al (2007) Arabidopsis plasma membrane protein crucial for Ca2+ influx and touch sensing in roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3639–3644
Okamoto T, Takahashi T (2019) Ethylene signaling plays a pivotal role in mechanical-stress-induced root-growth cessation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 14:e1669417
Okamoto T, Tsurumi S, Shibasaki K, Obana Y, Takaji H, Oono Y, Rahman A (2008) Genetic dissection of hormonal responses in the roots of Arabidopsis grown under continuous mechanical impedance. Plant Physiol 146:1651–1662
Okamoto T, Takatani S, Noutoshi Y, Motose H, Takahashi T (2018) Omeprazole enhances mechanical stress-induced root growth reduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 59:1581–1591
Perrin RM, Wang Y, Yuen CY, Will J, Masson PH (2007) WVD2 is a novel microtubule-associated protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 49:961–971
Pickett FB, Wilson AK, Estelle M (1990) The aux1 mutation of Arabidopsis confers both auxin and ethylene resistance. Plant Physiol 94:1462–1466
Postel S, Küfner I, Beuter C, Mazzotta S, Schwedt A, Borlotti A, Halter T, Kemmerling B, Nürnberger T (2010) The multifunctional leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase BAK1 is implicated in Arabidopsis development and immunity. Eur J Cell Biol 89:169–174
Roman G, Lubarsky B, Kieber JJ, Rothenberg M, Ecker JR (1995) Genetic analysis of ethylene signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana: five novel mutant loci integrated into a stress response pathway. Genetics 139:1393–1409
Russinova E, Borst JW, Kwaaitaal M, Cano-Delgado A, Yin Y, Chory J, de Vries SC (2004) Heterodimerization and endocytosis of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptors BRI1 and AtSERK3 (BAK1). Plant Cell 16:3216–3229
Shih HW, Miller ND, Dai C, Spalding EP, Monshausen GB (2014) The receptor-like kinase FERONIA is required for mechanical signal transduction in Arabidopsis seedlings. Curr Biol 24:1887–1892
Solano R, Stepanova A, Chao Q, Ecker JR (1998) Nuclear events in ethylene signaling: a transcriptional cascade mediated by ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1. Genes Dev 12:3703–3714
Stegmann M, Monaghan J, Smakowska-Luzan E, Rovenich H, Lehner A, Holton N, Belkhadir Y, Zipfel C (2017) The receptor kinase FER is a RALF-regulated scaffold controlling plant immune signaling. Science 355:287–289
Sun J, Ma Q, Mao T (2015) Ethylene regulates the Arabidopsis microtubule-associated protein WAVE-DAMPENED2-LIKE5 in etiolated hypocotyl elongation. Plant Physiol 169:325–337
Swarbreck SM, Colaço R, Davis JM (2013) Plant calcium-permeable channels. Plant Physiol 163:514–522
Tsugama D, Liu S, Takano T (2016) The bZIP protein VIP1 is involved in touch responses in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 171:1355–1365
Wang NN, Shih MC, Li N (2005) The GUS reporter-aided analysis of the promoter activities of Arabidopsis ACC synthase genes AtACS4, AtACS5, and AtACS7 induced by hormones and stresses. J Exp Bot 56:909–920
Yamanaka T, Nakagawa Y, Mori K, Nakano M, Imamura T, Kataoka H, Terashima A, Iida K, Kojima I, Katagiri T et al (2010) MCA1 and MCA2 that mediate Ca2+ uptake have distinct and overlapping roles in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152:1284–1296
Yasuda S, Okada K, Saijo Y (2017) A look at plant immunity through the window of the multitasking coreceptor BAK1. Curr Opin Plant Biol 38:10–18
Yu X, Xu G, Li L, Vespoli L, Liu H, Moeder W, Chen S, de Oliveira MVV, de Souza SA, Shao W et al (2019) The receptor kinases BAK1/SERK4 regulate Ca2+ channel mediated cellular homeostasis for cell death containment. Curr Biol 29:3778–3790
Yuan F, Yang H, Xue Y, Kong D, Ye R, Li C, Zhang J, Theprungsirikul L, Shrift T, Krichilsky B et al (2014) OSCA1 mediates osmotic-stress-evoked Ca2+ increases vital for osmosensing in Arabidopsis. Nature 514:367–371
Zhong S, Shi H, Xue C, Wang L, Xi Y, Li J, Quail PH, Deng XW, Guo H (2012) A molecular framework of light-controlled phytohormone action in Arabidopsis. Cur Biol 22:1530–1535
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Nakahara Research and Education Foundation (to TO), by Ryobi Teien Memory Foundation (to TO) and by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research [no. 16H0124518] from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (to TT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TO and ST performed the experiments. TO, HM and TT designed the research, analyzed the data and carried out statistical analyses. TO, HI and TT wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Qiaochun Wang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Movie. S1 Time-lapse movie of 5-day-old wild-type seedlings grown under mechanically impeded conditions. Time stamp shown in upper left of the movie represents the time (h:min) after the seedlings were placed on the plate (AVI 495 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, T., Takatani, S., Motose, H. et al. The root growth reduction in response to mechanical stress involves ethylene-mediated microtubule reorganization and transmembrane receptor-mediated signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 40, 575–582 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02653-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02653-6