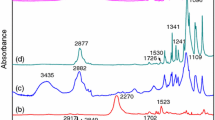
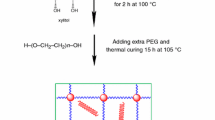
Abstract
The different molecular weights of polyurethane (PU), using as solid-solid phase change materials, were synthesized by different molar ratios of polyethylene glycol (PEG, Mn = 8000), 4,4’-methylenebis (cyclohexyl isocyanate) (H12MDI), and Emulsogen TS200 (tristyrylphenol polyglycol ether), through solvent-free bulk polymerization method. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD), and polarization optical microscopy (POM) were applied to examine the characteristics of phase transition and crystalline morphology. According to the results of examination, both latent heat and crystalline structure were affected by the molecular weight. The enthalpies of fusion and crystallization reached up to 129.59 and 105.45 J/g, respectively, suggesting a promising future for this phase change material to be applied in thermal energy storage.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarbu I, Dorca A (2019) Review on heat transfer analysis in thermal energy storage using latent heat storage systems and phase change materials. Int J Energy Res 43(1):29–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4196
de Gracia A, Cabeza LF (2015) Phase change materials and thermal energy storage for buildings. Energy Build 103:414–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.06.007
Wang T, Wang S, Luo R et al (2016) Microencapsulation of phase change materials with binary cores and calcium carbonate shell for thermal energy storage. Appl Energy 171:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.037
Prieto C, Rodríguez A, Patiño D et al (2018) Thermal energy storage evaluation in direct steam generation solar plants. Sol Energy 159:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.11.00.
Alizadeh M, Sadrameli SM (2016) Development of free cooling based ventilation technology for buildings: thermal energy storage (TES) unit, performance enhancement techniques and design considerations–A review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:619–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.168
Zalba B, Marı́n JM, Cabeza LF et al (2003) Review on thermal energy storage with phase change: materials, heat transfer analysis and applications. Appl Thermal Eng 23(3):251–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-4311(02)00192-8
Abhat A (1983) Low temperature latent heat thermal energy storage: heat storage materials. Sol Energy 30:313–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(83)90186-X
Pirasaci T, Goswami DY (2016) Influence of design on performance of a latent heat storage system for a direct steam generation power plant. Appl Energy 162:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.105
Bhagat K, Saha SK (2016) Numerical analysis of latent heat thermal energy storage using encapsulated phase change mterial for solar thermal power plant. Renew Energy 95:323–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.04.018
Mao Q (2016) Recent developments in geometrical configurations of thermal energy storage for concentrating solar power plant. Renew Sust Energ Rev 59:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.355
Korth T, Loistl F, Storch A et al (2019) Capacity enhancement of air conditioning systems by direct integration of a latent heat storage unit. Appl Therm Eng 167:114727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114727
Sonnenrein G, Elsner A, Baumhögger E et al (2015) Reducing the power consumption of household refrigerators through the integration of latent heat storage elements in wire-and-tube condensers. Int J Refrig 51:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2014.12.011
Berardi U, Soudian S (2019) Experimental investigation of latent heat thermal energy storage using PCMs with different melting temperatures for building retrofit. Energy Build 185:180–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.12.016
Sarı A, Alkan C, Özcan AN (2015) Synthesis and characterization of micro/nano capsules of PMMA/capric–stearic acid eutectic mixture for low temperature-thermal energy storage in buildings. Energy Build 90:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.01.013
Subramanian A, Appukuttan S (2019) Microencapsulation of stearic acid into strontium titanate shell by sol-gel approach for thermal energy storage. ChemistrySelect 4(27):7818–7823. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201901505
Han GGD, Li H, Grossman JC (2017) Optically-controlled long-term storage and release of thermal energy in phase-change materials. Na Commun 8(1):1446. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01608-y
Xi P, Gu X, Cheng B et al (2009) Preparation and characterization of a novel polymeric based solid–solid phase change heat storage material. Energy Convers Manag 50(6):1522–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.02.013
Meng Q, Hu JJ (2008) A poly (ethylene glycol)-based smart phase change material. Sol Energy Mat Sol C 92(10):1260–1268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2008.04.026
Fu X, Kong W, Zhang Y et al (2015) Novel solid–solid phase change materials with biodegradable trihydroxy surfactants for thermal energy storage. RSC Adv 5(84):68881–68889. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA11842E
Li W, Ding E (2007) Preparation and characterization of cross-linking PEG/MDI/PE copolymer as solid–solid phase change heat storage material. Sol Energy Ma Sol C 91(9):764–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2007.01.011
Su J, Liu P (2006) A novel solid–solid phase change heat storage material with polyurethane block copolymer structure. Energy Convers Manag 47(18):3185–3191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2006.02.022
Zhou X (2009) Preparation and characterization of PEG/MDI/PVA copolymer as solid–solid phase change heat storage material. J Appl Polym Sci 113(3):2041–2045. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29923
Chen C, Liu W, Wang Z et al (2015) Novel form stable phase change materials based on the composites of polyethylene glycol/polymeric solid-solid phase change material. Sol Energy Mat Sol C 134:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2011.01.022
Sarı A, Alkan C, Biçer A (2012) Synthesis and thermal properties of polystyrene-graft-PEG copolymers as new kinds of solid–solid phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Mater Chem Phys 133(1):87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.12.056
Alkan C, Günther E, Hiebler S et al (2012) Polyurethanes as solid–solid phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy 86(6):1761–1769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2012.03.012
Cao Q, Liu P (2006) Hyperbranched polyurethane as novel solid–solid phase change material for thermal energy storage. Eur Polym J 42(11):2931–2939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2006.07.020
Chen C, Liu W, Wang H et al (2015) Synthesis and performances of novel solid–solid phase change materials with hexahydroxy compounds for thermal energy storage. Appl Energy 152:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.004
Sundararajan S, Samui AB, Kulkarni PS (2019) Crosslinked polymer networks of poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) and hydroxyl terminated poly (dimethyl siloxane) (HTPDMS) as polymeric phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy 181:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.01.091
Du X, Wang H, Du Z et al (2017) Synthesis and thermal properties of novel solid-solid phase change materials with comb-polyurethane block copolymer structure for thermal energy storage. Thermochim Acta 651:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2017.02.012
Kong W, Fu X, Liu Z et al (2017) A facile synthesis of solid-solid phase change material for thermal energy storage. Appl Therm Eng 117:622–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.10.088
Lu X, Fang C, Sheng X et al (2019) One-step and solvent-free synthesis of polyethylene glycol-based polyurethane As solid–solid phase change materials for solar thermal energy storage. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(8):3024–3032. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b05903
Yang Y, Ren Y, Li W et al (2019) Preparation and characterization of novel form stable phase change materials based on stearic acid (SA)/hollow glass microsphere (HGS) with low supercooling. J Therm Anal Calorim 136(5):1905–1913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7854-y
Sundararajan S, Samui AB, Kulkarni PS (2016) Interpenetrating phase change polymer networks based on crosslinked polyethylene glycol and poly (hydroxyethyl methacrylate). Sol Energy Mat Sol C 149:266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.12.040
Sundararajan S, Samui AB, Kulkarni PS (2017) Thermal energy storage using poly (ethylene glycol) incorporated hyperbranched polyurethane as solid–solid phase change material. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(49):14401–14409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b03330
Peng K, Chen C, Pan W, et al. (2016) Preparation and properties of β-cyclodextrin/4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate/polyethylene glycol (β-CD/MDI/PEG) crosslinking copolymers as polymeric solid–solid phase change materials. Sol Energ Mat Sol C, 145: 238-247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.10.031.
Chen C, Liu W, Wang H et al (2016) Synthesis and characterization of novel solid–solid phase change materials with a polyurethaneurea copolymer structure for thermal energy storage. RSC Adv 6(105):102997–103005. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA23141A
Chen K, Yu X, Tian C et al (2014) Preparation and characterization of form-stable paraffin/polyurethane composites as phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Energy Convers Manag 77:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.09.015
Zhou Y, Sheng D, Liu X et al (2018) Synthesis and properties of crosslinking halloysite nanotubes/polyurethane-based solid-solid phase change materials. Sol Energ Mat Sol C 174:84–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2017.08.031
Funding
It is acknowledged that this work was supported by the National key research and development program (No.2018YFC1801503), the Shanghai Colleges and Universities Experimental Technology Construction Plan (No.A4-0100-19-SDJH0403), the Shanghai Sailing Program (No.19YF1417800), and the Start-Up Funds of Shanghai University of Engineering Science (No.E3-0507-19-05111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Pu, Z., Zhu, M. et al. Solvent-free synthesis of PEG modified polyurethane solid-solid phase change materials with different Mw for thermal energy storage. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 835–843 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04804-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04804-3