Abstract
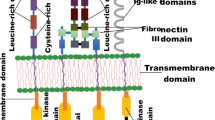
Cancer is the 2nd most fatal disease around the globe. Various receptors have been showed to be overexpressed and/or mutated in numerous cancers. Discoidin domain receptors 1 (DDR1) and 2 (DDR2) are one of the novel receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), which have been proved to regulate various cellular signaling pathways, cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, matrix remodeling, and dysregulation of these receptors may lead to metastatic cancer progressions. These receptors belong to unique category of RTKs, which require collagen binding for its activation. Yet the mechanism of this extracellular collagen binding and activation of cytosolic kinase domain of the receptors is not clear. Like other RTKs, these receptors also showed its extensive implications in numerous cancers like lung, breast, ovarian, pancreatic cancer and many others. Therefore DDR1 and DDR2 emerge as potential therapeutic targets in preventing cancer. Various small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been developed against these two receptors and proved to be highly efficacious in reducing tumor progressions. This review would highlight the detailed structure, functions, mechanism of action, signaling pathways of DDR1 and DDR2, their roles in cancer developments and the inhibition of these receptors with numerous inhibitors can be a promising strategy to combat this hefty menace.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Cancer. 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
Falzone L, Salomone S, Libra M. Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the third millennium. Front Pharm. 2018;9:1300 https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01300.
Arruebo M, Vilaboa N, Sáez-Gutierrez B, Lambea J, Tres A, Valladares M, et al. Assessment of the evolution of cancer treatment therapies. Cancers. 2011;3:3279–330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3033279.
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2010;141:1117–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.011.
Lu P, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. 2012;196:395–406. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201102147.
Shrivastava A, Radziejewski C, Campbell E, Kovac L, McGlynn M, Ryan TE, et al. An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol Cell. 1997;1:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80004-0.
Vogel W, Gish GD, Alves F, Pawson T. The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol Cell. 1997;1:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80003-9.
Kiedzierska A, Smietana K, Czepczynska H, Otlewski J. Structural similarities and functional diversity of eukaryotic discoidin-like domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1774:1069–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.07.007.
Rammal H, Saby C, Magnien K, Van-Gulick L, Garnotel R, Buache E, et al. Discoidin domain receptors: potential actors and targets in cancer. Front Pharm. 2016;7:55. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00055.
Johnson JD, Edman JC, Rutter WJ. A receptor tyrosine kinase found in breast carcinoma cells has an extracellular discoidin I-like domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:5677–81. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.12.5677.
Alves F, Vogel W, Mossie K, Millauer B, Höfler H, Ullrich A. Distinct structural characteristics of discoidin I subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases and complementary expression in human cancer. Oncogene. 1995;10:609–18.
Valiathan RR, Marco M, Leitinger B, Kleer CG, Fridman R. Discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases: new players in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31:295–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9346-z.
Leitinger B. Molecular analysis of collagen binding by the human discoidin domain receptors, DDR1 and DDR2 identification of collagen binding sites in DDR2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16761–9. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m301370200.
Hou G, Vogel W, Bendeck MP. The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase DDR1 in arterial wound repair. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:727–35. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci10720.
Leitinger B, Steplewski A, Fertala A. The D2 period of collagen II contains a specific binding site for the human discoidin domain receptor, DDR2. J Mol Biol. 2004;344:993–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.089.
Leitinger B, Kwan AP. The discoidin domain receptor DDR2 is a receptor for type X collagen. Matrix Biol. 2006;25:355–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2006.05.006.
Leitinger B. Transmembrane collagen receptors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:265–90. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154013.
Carafoli F, Hohenester E. Collagen recognition and transmembrane signalling by discoidin domain receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834:2187–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014.
Alves F, Saupe S, Ledwon M, Schaub F, Hiddemann W, Vogel W. Identification of two novel, kinase-deficient variants of discoidin domain receptor 1: differential expression in human colon cancer cell lines. FASEB J. 2001;15:1321–3. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.00-0626fje.
Playford MP, Butler RJ, Wang XC, Katso RM, Cooke IE, Ganesan TS. The genomic structure of discoidin receptor tyrosine kinase. Genome Res. 1996;6:620–7. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.6.7.620.
Dengjel J, Akimov V, Olsen JV, Bunkenborg J, Mann M, Blagoev B, et al. Quantitative proteomic assessment of very early cellular signaling events. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:566–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1301.
Gu TL, Deng X, Huang F, Tucker M, Crosby K, Rimkunas V, et al. Survey of tyrosine kinase signaling reveals ROS kinase fusions in human cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e15640. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015640.
Farndale RW, Lisman T, Bihan D, Hamaia S, Smerling CS, Pugh N, et al. Cell–collagen interactions: the use of peptide Toolkits to investigate collagen–receptor interactions. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:241–50. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0360241.
Konitsiotis AD, Raynal N, Bihan D, Hohenester E, Farndale RW, Leitinger B. Characterization of high affinity binding motifs for the discoidin domain receptor DDR2 in collagen. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:6861–8. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m709290200.
Xu H, Raynal N, Stathopoulos S, Myllyharju J, Farndale RW, Leitinger B. Collagen binding specificity of the discoidin domain receptors: binding sites on collagens II and III and molecular determinants for collagen IV recognition by DDR1. Matrix Biol. 2011;30:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2010.10.004.
Ichikawa O, Osawa M, Nishida N, Goshima N, Nomura N, Shimada I. Structural basis of the collagen-binding mode of discoidin domain receptor 2. EMBO J. 2007;26:4168–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601833.
Dejmek J, Dib K, Jönsson M, Andersson T. Wnt-5a and G-protein signaling are required for collagen-induced DDR1 receptor activation and normal mammary cell adhesion. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:344–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.10752.
Jönsson M, Andersson T. Repression of Wnt-5a impairs DDR1 phosphorylation and modifies adhesion and migration of mammary cells. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:2043–53.
Kim HG, Hwang SY, Aaronson SA, Mandinova A, Lee SW. DDR1 receptor tyrosine kinase promotes prosurvival pathway through Notch1 activation. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:17672–81. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m111.236612.
Iwai LK, Chang F, Huang PH. Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies insulin enhancement of discoidin domain receptor 2 phosphorylation. Cell Adh Migr. 2013;7:161–4. https://doi.org/10.4161/cam.22572.
Lu KK, Trcka D, Bendeck MP. Collagen stimulates discoidin domain receptor 1-mediated migration of smooth muscle cells through Src. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2011;20:71–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2009.12.006.
Ikeda K, Wang LH, Torres R, Zhao H, Olaso E, Eng FJ, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 2 interacts with Src and Shc following its activation by type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:19206–12. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m201078200.
Koo DH, McFadden C, Huang Y, Abdulhussein R, Friese-Hamim M, Vogel WF. Pinpointing phosphotyrosine-dependent interactions downstream of the collagen receptor DDR1. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2005.11.035.
Wang CZ, Su HW, Hsu YC, Shen MR, Tang MJ. A discoidin domain receptor 1/SHP-2 signaling complex inhibits α2β1-integrin–mediated signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/3 activation and cell migration. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:2839–52. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E05-11-1068.
Yang G, Li Q, Ren S, Lu X, Fang L, Zhou W, et al. Proteomic, functional and motif-based analysis of C-terminal Src kinase-interacting proteins. Proteomics. 2009;9:4944–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200800762.
Huang Y, Arora P, McCulloch CA, Vogel WF. The collagen receptor DDR1 regulates cell spreading and motility by associating with myosin IIA. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:1637–46. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.046219.
Shintani Y, Fukumoto Y, Chaika N, Svoboda R, Wheelock MJ, Johnson KR. Collagen I–mediated up-regulation of N-cadherin requires cooperative signals from integrins and discoidin domain receptor 1. J Cell Biol. 2008;180:1277–89. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200708137.
Das S, Ongusaha PP, Yang YS, Park JM, Aaronson SA, Lee SW. Discoidin domain receptor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase induces cyclooxygenase-2 and promotes chemoresistance through nuclear factor-κB pathway activation. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8123–30. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-06-1215.
Yeh YC, Wang CZ, Tang MJ. Discoidin domain receptor 1 activation suppresses α2β1 integrin-dependent cell spreading through inhibition of Cdc42 activity. J Cell Physiol. 2009;218:146–56. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21578.
Su J, Yu J, Ren T, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 2 is associated with the increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009;330:141–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-009-0127-0.
Lemeer S, Bluwstein A, Wu Z, Leberfinger J, Müller K, Kramer K, et al. Phosphotyrosine mediated protein interactions of the discoidin domain receptor 1. J Proteom. 2012;75:3465–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2011.10.007.
Ongusaha PP, Kim JI, Fang L, Wong TW, Yancopoulos GD, Aaronson SA, et al. p53 induction and activation of DDR1 kinase counteract p53-mediated apoptosis and influence p53 regulation through a positive feedback loop. EMBO J. 2003;22:1289–301. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg129.
Das S, Ongusaha PP, Yang YS, Park JM, Aaronson SA, Lee SW. Discoidin domain receptor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase induces cyclooxygenase-2 and promotes chemoresistance through nuclear factor-κB pathway activation. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8123–30. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1215.
Payne LS, Huang PH. Discoidin domain receptor 2 signaling networks and therapy in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:900–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000164.
Iwai LK, Payne LS, Luczynski MT, Chang F, Xu H, Clinton RW, et al. Phosphoproteomics of collagen receptor networks reveals SHP-2 phosphorylation downstream of wild-type DDR2 and its lung cancer mutants. Biochem J. 2013;454:501–13. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20121750.
Ford CE, Lau SK, Zhu CQ, Andersson T, Tsao MS, Vogel WF. Expression and mutation analysis of the discoidin domain receptors 1 and 2 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:808–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6603614.
Yang SH, Baek HA, Lee HJ, Park HS, Jang KY, Kang MJ, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 2010;24:311–9. https://doi.org/10.3892/or_00000861.
Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.025.
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER, McLellan MD, Cibulskis K, et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2008;455:1069–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07423.
Davies H, Hunter C, Smith R, Stephens P, Greenman C, Bignell G, et al. Somatic mutations of the protein kinase gene family in human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7591–5. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-1855.
Hammerman PS, Sos ML, Ramos AH, Xu C, Dutt A, Zhou W, et al. Mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic target in squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8274.cd-11-0005.
Miao L, Wang Y, Zhu S, Shi M, Li Y, Ding J, et al. Identification of novel driver mutations of the discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) gene in squamous cell lung cancer of Chinese patients. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:369 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-369.
Kobayashi-Watanabe N, Sato A, Watanabe T, Abe T, Nakashima C, Sueoka E, et al. Functional analysis of Discoidin domain receptor 2 mutation and expression in squamous cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2017;110:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.05.017.
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Baumforth K, Wei W, Dziechciarkova M, Ehrmann J, et al. Novel markers for differentiation of lobular and ductal invasive breast carcinomas by laser microdissection and microarray analysis. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-7-55.
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Ehrmann J, Fridman E, Skarda J, Kolara Z. Novel immunohistochemical markers for the differentiation of lobular and ductal invasive breast carcinomas. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2007;151:59–64. https://doi.org/10.5507/bp.2007.010.
Barker KT, Martindale JE, Mitchell PJ, Kamalati T, Page MJ, Phippard DJ, et al. Expression patterns of the novel receptor-like tyrosine kinase, DDR, in human breast tumours. Oncogene. 1995;10:569–75.
Neuhaus B, Bühren S, Böck B, Alves F, Vogel WF, Kiefer F. Migration inhibition of mammary epithelial cells by Syk is blocked in the presence of DDR1 receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68:3757–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0676-8.
Zhang K, Corsa CA, Ponik SM, Prior JL, Piwnica-Worms D, Eliceiri KW, et al. The collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor 2 stabilizes SNAIL1 to facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:677–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2743.
Ren T, Zhang W, Liu X, Zhao H, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) promotes breast cancer cell metastasis and the mechanism implicates epithelial–mesenchymal transition programme under hypoxia. J Pathol. 2014;234:526–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4415.
Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA, Gardiner-Garden M, Henshall SM, Scurry J, Scolyer RA, Davies MJ, et al. Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecules DDR1, Claudin 3, and Ep-CAM in metaplastic ovarian epithelium and ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4427–36. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-04-0073.
Quan J, Yahata T, Adachi S, Yoshihara K, Tanaka K. Identification of receptor tyrosine kinase, discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1), as a potential biomarker for serous ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:971–82. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12020971.
Colas E, Perez C, Cabrera S, Pedrola N, Monge M, Castellvi J, et al. Molecular markers of endometrial carcinoma detected in uterine aspirates. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:2435–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25901.
Shen Q, Cicinnati VR, Zhang X, Iacob S, Weber F, Sotiropoulos GC, et al. Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:227. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-9-227.
Couvelard A, Hu J, Steers G, Dermot OT, Sauvanet A, Belghiti J, et al. Identification of potential therapeutic targets by gene-expression profiling in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1597–610. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.09.007.
Weiner HL, Huang H, Zagzag D, Boyce H, Lichtenbaum R, Ziff EB. Consistent and selective expression of the discoidin domain receptor-1 tyrosine kinase in human brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:1400–9.
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Ishida E, Higuchi T, Yamamoto H, Tsujikawa K, et al. Prostate cancer antigen-1 contributes to cell survival and invasion though discoidin receptor 1 in human prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00655.x.
Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Hooper S, Chaudhry SI, Williamson P, Harrington K, Leitinger B, et al. Collective cell migration requires suppression of actomyosin at cell–cell contacts mediated by DDR1 and the cell polarity regulators Par3 and Par6. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2133.
Nemoto T, Ohashi K, Akashi T, Johnson JD, Hirokawa K. Overexpression of protein tyrosine kinases in human esophageal cancer. Pathobiology. 1997;65:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1159/000164123.
Chua HH, Yeh TH, Wang YP, Huang YT, Sheen TS, Lo YC, et al. Upregulation of discoidin domain receptor 2 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck-J Sci Spec. 2008;30:427–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20724.
Rodrigues R, Roque L, Espadinha C, Pinto A, Domingues R, Dinis J, et al. Comparative genomic hybridization, BRAF, RAS, RET, and oligo-array analysis in aneuploid papillary thyroid carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:917–26.
Renné C, Willenbrock K, Ku¨ppers R, Hansmann ML, Bra¨uninger A. Autocrine-and paracrine-activated receptor tyrosine kinases in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2005;105:4051–9. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-10-4008.
von Mässenhausen A, Sanders C, Brägelmann J, Konantz M, Queisser A, Vogel W, et al. Targeting DDR2 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with dasatinib. Int J Cancer. 2016;139:2359–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30279.
Tomasson MH, Xiang Z, Walgren R, Zhao Y, Kasai Y, Miner T, et al. Somatic mutations and germline sequence variants in the expressed tyrosine kinase genes of patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;111:4797–808. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-09-113027.
Loriaux MM, Levine RL, Tyner JW, Fröhling S, Scholl C, Stoffregen EP, et al. High-throughput sequence analysis of the tyrosine kinome in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;111:4788–96. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-07-101394.
Siddiqui K, Kim GW, Lee DH, Shin HR, Yang EG, Lee NT, et al. Actinomycin D identified as an inhibitor of discoidin domain receptor 2 interaction with collagen through an insect cell based screening of a drug compound library. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32:136–41. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.32.136.
Carafoli F, Mayer MC, Shiraishi K, Pecheva MA, Chan LY, Nan R, et al. Structure of the discoidin domain receptor 1 extracellular region bound to an inhibitory Fab fragment reveals features important for signaling. Structure. 2012;20:688–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.02.011.
Ram R, Lorente G, Nikolich K, Urfer R, Foehr E, Nagavarapu U. Discoidin domain receptor-1a (DDR1a) promotes glioma cell invasion and adhesion in association with matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Neurooncol. 2006;76:239–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-6874-1.
Castro-Sanchez L, Soto-Guzman A, Navarro-Tito N, Martinez-Orozco R, Salazar EP. Native type IV collagen induces cell migration through a CD9 and DDR1-dependent pathway in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010;89:843–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.07.004.
Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2559.
Modi V, Dunbrack RL. Clustering of the structures of protein kinase activation loops: a new nomenclature for active and inactive kinase structures. 2018:395723. https://doi.org/10.1101/395723.
Hanson SM, Georghiou G, Thakur MK, Miller WT, Rest JS, Chodera JD, et al. What makes a kinase promiscuous for inhibitors? Cell Chem Biol. 2019;26:390–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.11.005.
Day E, Waters B, Spiegel K, Alnadaf T, Manley PW, Buchdunger E, et al. Inhibition of collagen-induced discoidin domain receptor 1 and 2 activation by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Eur J Pharm. 2008;599:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.014.
Safran H, Dipetrillo T, Khurshid H, Ng T, Mantripragada K, Birnbaum A, et al. A phase I study of dasatinib with concurrent chemoradiation for stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2012;2:56. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2012.00056.
Brunner AM, Costa DB, Heist RS, Garcia E, Lindeman NI, Sholl LM, et al. Treatment-related toxicities in a phase II trial of dasatinib in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8:1434–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0b013e3182a47162.
Canning P, Tan L, Chu K, Lee SW, Gray NS, Bullock AN, et al. Structural mechanisms determining inhibition of the collagen receptor DDR1 by selective and multi-targeted type II kinase inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 2014;426:2457–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2014.04.014.
Rix U, Rix LR, Terker AS, Fernbach NV, Hantschel O, Planyavsky M, et al. A comprehensive target selectivity survey of the BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor INNO-406 by kinase profiling and chemical proteomics in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2010;24:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.228.
Sun X, Phan TN, Jung SH, Kim SY, Cho JU, Lee H, et al. LCB 03-0110, a novel pan-discoidin domain receptor/c-Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses scar formation by inhibiting fibroblast and macrophage activation. J Pharm Exp Ther. 2012;340:510–19. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.111.187328.
Liu L, Hussain M, Luo J, Duan A, Chen C, Tu Z, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel dasatinib analogues as potent DDR 1 and DDR 2 kinase inhibitors. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2017;89:420–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.12863.
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Pinkas DM, Fox AE, Luo J, Huang H, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 3-(Imidazo [1, 2-a] pyrazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-isopropyl-N-(3-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl) benzamide as a dual inhibitor of discoidin domain receptors 1 and 2. J Med Chem. 2018;61:7977–90. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01045.
Gao M, Duan L, Luo J, Zhang L, Lu X, Zhang Y, et al. Discovery and optimization of 3-(2-(Pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidin-6-yl) ethynyl) benzamides as novel selective and orally bioavailable discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2013;56:3281–95. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm301824k.
Kim HG, Tan L, Weisberg EL, Liu F, Canning P, Choi HG, et al. Discovery of a potent and selective DDR1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8:2145–50. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb400430t.
Richters A, Nguyen HD, Phan T, Simard JR, Gru¨tter C, Engel J, et al. Identification of type II and III DDR2 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2014;57:4252–62. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm500167q.
Terai H, Tan L, Beauchamp EM, Hatcher JM, Liu Q, Meyerson M, et al. Characterization of DDR2 inhibitors for the treatment of DDR2 mutated nonsmall cell lung cancer. ACS Chem Biol. 2015;10:2687–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00655.
Wang Z, Bian H, Bartual SG, Du W, Luo J, Zhao H, et al. Structure-based design of tetrahydroisoquinoline-7-carboxamides as selective discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2016;59:5911–16. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00140.
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Bartual SG, Luo J, Xu T, Du W, et al. Tetrahydroisoquinoline-7-carboxamide derivatives as new selective discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017;8:327–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00497.
Wang Q, Dai Y, Ji Y, Shi H, Guo Z, Chen D, et al. Discovery and optimization of a series of 3-substituted indazole derivatives as multi-target kinase inhibitors for the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;163:671–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.12.015.
Zhu D, Huang H, Pinkas DM, Luo J, Ganguly D, Fox AE, et al. 2-Amino-2,3-dihydro-1 H-indene-5-carboxamide-based discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors: design, synthesis, and in vivo antipancreatic cancer efficacy. J Med Chem. 2019;62:7431–44. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00365.
Mo C, Zhang Z, Li Y, Huang M, Zou J, Luo J, et al. Design and optimization of 3’-(imidazo [1, 2-a] pyrazin-3-yl)-[1, 1’-biphenyl]-3-carboxamides as selective DDR1 inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00495.
Murray CW, Berdini V, Buck IM, Carr ME, Cleasby A, Coyle JE, et al. Fragment-based discovery of potent and selective DDR1/2 inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015;6:798–803. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00143.
Richter H, Satz AL, Bedoucha M, Buettelmann B, Petersen AC, Harmeier A, et al. DNA-encoded library-derived DDR1 inhibitor prevents fibrosis and renal function loss in a genetic mouse model of Alport syndrome. ACS Chem Biol. 2018;14:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.8b00866.
Carafoli F, Bihan D, Stathopoulos S, Konitsiotis AD, Kvansakul M, Farndale RW, et al. Crystallographic insight into collagen recognition by discoidin domain receptor 2. Structure. 2009;17:1573–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2009.10.012.
Acknowledgements
The authors declare their deep and sincere gratitude to the Principal, faculty staffs, management and all the members of Pharmaceutical Chemistry Department of Acharya & BM Reddy College of Pharmacy, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India, for their widest support in successful accomplishment of this review work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matada, G.S.P., Das, A., Dhiwar, P.S. et al. DDR1 and DDR2: a review on signaling pathway and small molecule inhibitors as an anticancer agent. Med Chem Res 30, 535–551 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02694-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02694-2