Abstract
The lysosome represents an important regulatory platform within numerous vesicle trafficking pathways including the endocytic, phagocytic, and autophagic pathways. Its ability to fuse with endosomes, phagosomes, and autophagosomes enables the lysosome to break down a wide range of both endogenous and exogenous cargo, including macromolecules, certain pathogens, and old or damaged organelles. Due to its center position in an intricate network of trafficking events, the lysosome has emerged as a central signaling node for sensing and orchestrating the cells metabolism and immune response, for inter-organelle and inter-cellular signaling and in membrane repair. This review highlights the current knowledge of general lysosome function and discusses these findings in their implication for renal glomerular cell types in health and disease including the involvement of glomerular cells in lysosomal storage diseases and the role of lysosomes in nongenetic glomerular injuries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The term “lysosome,” Greek for “lytic body” first appeared in print 65 years ago, when De Duve et al. set forward to unravel the intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver by tissue fractionation studies (De Duve et al. 1955). The typical lysosome is a single membrane-bound round structure of about 0.2–0.3 µm in diameter. Each mammalian cell comprises between 50 and 1000 lysosomes distributed throughout the cytoplasm. Lysosomes represent a highly dynamic cellular vesicular compartment within the late endocytic pathway, in which biological macromolecules are degraded (Bainton 1981; de Duve 2005). The cargo degraded by lysosomes differs depending on the route of delivery. The endocytic pathway brings small intracellular molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and endocytosed membrane proteins to lysosomes (Pryor and Luzio 2009), the autophagic pathway targets intracellular aggregates and dysfunctional organelles to lysosomes (Jegga et al. 2011), and the phagocytic pathway routes phagocytosed large (≥ 0.5 µm) particles such as bacteria to lysosomes for degradation (Herb et al. 2020). Besides the canonical role of lysosomes for the degradation of waste, emerging studies show a significant contribution of lysosomes to the sensing of the nutrient status of cells, to metabolism, membrane repair, and immune signaling (Saftig and Puertollano 2020). This review will broadly cover general lysosome biology, thereafter, focusing on our existing knowledge about lysosome function in glomerular health and disease. This review is based on many excellent expert reviews on lysosomal biology, we apologize to those many researchers, whose work could not be cited in this context.
Lysosomal composition and biogenesis
The complexity of lysosomes is emphasized by data from proteome analyses: Roughly 200 glycosylated and nonglycosylated integral membrane proteins have been identified (Fig. 1), which are crucial for the transport of metabolites and for the prevention of lysosomal membrane degradation (Saftig and Klumperman 2009; Saftig et al. 2010). Ion channels and transporters regulate the luminal ion composition (Calcraft et al. 2009; Zhang et al. 2009), tethering factors, and SNARE proteins at the membrane control fission and fusion with communicating cellular compartments (Brocker et al. 2010; Hong and Lev 2014). Lysosomal function is orchestrated by lysosomal degradative enzymes and by lysosomal membrane proteins (Saftig and Klumperma 2009; Schwake et al. 2013). The highly glycosylated transmembrane proteins lysosome-associated membrane proteins 1 and 2 (LAMP1 and LAMP2) are the most abundant lysosomal proteins and are thought to protect the membrane from degradation by lysosomal enzymes (Saftig and Klumperman 2009). The crucial and characteristic acidity of lysosomes is achieved by a dedicated H+-ATPase (Graves et al. 2008; Mindell 2012), which maintains the luminal acidic pH to stabilize and mediate the activity of the over 70 lysosomal degradative enzymes that have pH optima ranging from pH 3.5 to pH 5.5 (Lubke et al. 2009). Lysosomal degradative enzymes (also called acid hydrolases) may roughly be classified into substrate-specific groups such as glycosidases, proteases, nucleases, lipases, phosphatases, phospholipases, and sulfatases, which altogether break down various biological substances including glycans, lipids, glycogen, and proteins. Lysosomal ions and ion channels are indispensable for the regulation of the lysosomal pH, and of the ion flux or transport across the lysosomal membranes (Xiong and Zhu 2016).
The plethora of lysosomal proteins highlights the complexity of lysosomes and their central role for cellular function, signaling, and metabolism. Modified from Ballabio and Bonifacino 2020
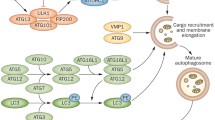
Lysosomal biogenesis involves maturation from other endocytic vesicles (early endosomes, late endosomes/multivesicular bodies, and intermediate vesicles) and targeting of lysosomal proteins to the lysosome. Basically, four different routes to lysosome formation have been described (reviewed in (Trivedi et al. 2020)). These include a “maturation,” a “vesicular transport,” a “fusion and fission,” and a “kiss and run” pathway (Fig. 2). The large arsenal of acid hydrolases, transmembrane proteins, and membrane-associated proteins are specifically recognized as lysosomal components postsynthesis and thereafter correctly sorted to lysosomes. The vesicular pathway is used for the transport of the majority of lysosome resident proteins to lysosomes. Lysosomal transmembrane proteins are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). After passage through the Golgi apparatus, they are either sorted directly from the trans-Golgi network (TGN) to the endosomes and lysosomes or indirectly, i.e., they are first sorted to the cell surface from where they enter the endocytic pathway. Most acid hydrolases are delivered to lysosomes via a mannose 6-phosphate (M6P)-dependent ER-to-lysosome trafficking pathway (Griffiths et al. 1988) following their synthesis in the ER. M6P allows enzymes to be recognized by M6P receptors (MPRs) in the TGN, which forms small vesicles that carry lysosomal resident proteins. These vesicles fuse with late endosomes/multivesicular bodies (MVBs), whose acidic environment causes dissociation of MPR from the cargos. While the MPRs recycle back to the TGN, lysosomal proteins continue their journey to lysosomes (Ghosh et al. 2003). Lysosomes can therefore be distinguished from endosomes due to their lack of MPR. Other soluble enzymes and nonenzymatic proteins are transported to lysosomes in an M6P-independent manner mediated by alternative receptors such as the lysosomal integral membrane protein LIMP-2 or sortilin (Reczek et al. 2007; Zhao et al. 2014).
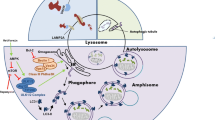
Lysosomal biogenesis is thought to occur through four different routes. In the maturation pathway, endocytosed cargo is first delivered to early endosomes, which progressively mature to late endosomes, endo-lysosomes, and subsequently into lysosomes. Thereby, endocytosis starts with the invagination of cargo-bound plasma membrane by either clathrin-dependent or clathrin-independent mechanisms. In the vesicular transport pathway, endosomal carrier vesicles/multivesicular bodies (MVBs) transfer cargo from early to late endosomes to lysosomes or directly from the matured late endosomes to lysosomes. In the fusion and fission pathway, the limiting membrane of late endosomes/MVBs and lysosomes fuses to form hybrid organelles, where the degradation of endocytosed macromolecules commences. These hybrid organelles subsequently reform to lysosomes. In the “kiss and run” pathway, late endosomes form a contact site (“kiss”) with lysosomes, transfer cargo and subsequently dissociate (“run”) again. Resident lysosomal proteins are synthesized in the ER. Sorting to lysosomes occurs through multiple pathways. 1. Most acid hydrolases are delivered to lysosomes via a mannose 6-phosphate (M6P) dependent ER-to-lysosome trafficking pathway. M6P modified proteins are recognized by M6P receptors (MPRs) in the trans-Golgi network (TGN), which forms small vesicles that carry lysosomal resident proteins. These vesicles fuse with late endosomes, the acidic environment of which causes dissociation of MPR from the cargos. While the MPRs recycle back to the TGN, lysosomal proteins continue their journey to lysosomes. 2. Lysosomal transmembrane proteins are either sorted directly from the ER-TGN to endosomes and lysosomes or indirectly, i.e., they are first sorted to the cell surface from where they enter the endocytic pathway. Both these direct and indirect routes rely on clathrin-coated vesicles to carry the proteins from the TGN or plasma membrane to the endosomes. Abbreviations: EE = early endosome, RE = recycling endosome, MVB = multi vesicular body, ILV = intraluminal vesicle, LE = late endosome, AP = autophagosome, LYS = lysosome, EL = endolysosome, APL = autophagolysosome, PL = protolysosome, MPR = mannose-6-phosphate receptor, light blue cylinder = lysosomal membrane protein, red star = lysosomal acid hydrolase, blue rod = plasma membrane protein, red oval = bacteria
Endocytosed cargo can escape degradation via recycling vesicles. One of the best understood recycling process at lysosomes/late endosomes is the cellular iron metabolism and iron recycling (reviewed in (Kurz et al. 2011)). Regeneration of consumed lysosomes occurs in a process called autophagic lysosome regeneration (ALR) (Yu et al. 2010). There, proto-lysosomes bud-off from autophagolysosomes through extrusion of tubular structures composed of lysosomal membrane components. Proto-lysosomes mature to nascent lysosomes by acquiring acidity and lysosomal luminal proteins (Chen and Yu 2017). Further, lysosomes are regenerated from hybrid organelles (endolysosomes), which are generated by fusion of late endosomes with lysosomes to (Huotari and Helenius 2011).
Cellular functions of lysosomes
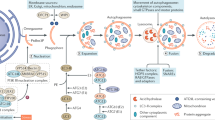
Lysosomes are involved in a multitude of cellular functions by far exceeding their role as degradative organelles. The most important lysosomal functions, namely exocytosis of proteins and of vesicles, plasma membrane repair, remodeling and growth, inter-organelle and inter-cellular signaling, metabolic sensing, lipid metabolism, and cell injury are discussed in the following paragraphs and summarized in Fig. 3.
Scheme depicting the plethora of lysosomal functions within a cell. 1. Depending on the trigger, lysosomes move with the help of a dynein/kinesin motor complex along microfilaments that are organized by the microtubule organizing center (MTOC) and localize in the cell periphery or at the cell center. Cell-homeostatic functions of lysosomes include 2. degradation of cargo delivered from the 2a. endocytic, 2b. autophagosomal and 2c. phagocytic pathways to peptides, 3. membrane repair, remodeling and growth, 4. receptor recycling, 5. bone resorption, immune modulation and cell–cell signaling through lysosomal secretion of 5a. enzymes or 5b. exosomes derived from multivesicular bodies, 6. metabolic sensing and control through autophagy and gene transcription regulation, 7. lipid metabolism, and 8. inter-organelle Ca2+ signaling. Lysosomes can induce chronic inflammation and trigger diverse sorts of cell-deaths by 9. lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) and 10. lysosomal secretion of pro-inflammatory factors. LMP is most frequently the consequence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) exposure (i.e., released from damaged mitochondria), which results in the leakage of lysosomal enzymes to the cytoplasm, inducing proinflammatory events such as inflammasome activation. Lysosomal dependent cell death is the consequence of massive lysosomal enzyme leakage
Protein exocytosis
Two types of lysosomes are described to exist physiologically, namely conventional degradative lysosomes and secretory lysosomes. Whereas conventional lysosomes primarily act as a waste disposal of phagocytosed and autophagocytosed debris (Klionsky and Emr 2000; Stuart and Ezekowitz 2005), the so-called secretory lysosomes (or lysosome-related organelles (LROs)) store and secrete proteins for cell-type-specific functions. Typical proteins secreted by lysosomes are lysosomal hydrolases, perforin, granzyme, histamine, serotonin, major basic protein, chemoattractant, clotting factors, and renin among others. The existence of secretory lysosomes is not restricted to a specific cell type anymore, as they have been described in hematopoietic cells, melanocytes, renal tubular cells, osteoclasts, and melanocytes (Blott and Griffiths 2002; Dell'Angelica et al. 2000; Lee and Ye 2018; Taugner et al. 1985). Some LROs are simply modified lysosomes, for instance in cytotoxic T lymphocytes, the lytic granules are the only lysosome-type organelle present. In other cells, such as melanocytes, both the melanosomes and the “conventional” lysosomes co-exist (Pryor and Luzio 2009). It is now widely accepted that secretory lysosomes move towards the plasma membrane, fuse with the plasma membrane and release their content into the extracellular space by exocytosis (Buratta et al. 2020). The exocytosis of lysosomal proteins is a ubiquitous Ca2+ regulated mechanism, which plays a crucial role in several physiological processes such as bone resorption by osteoclasts (Vaes 1968), melanocyte function during pigmentation, immune response and antigen presentation among others (Blott and Griffiths 2002; Buratta et al. 2020; Lee and Ye 2018).
Vesicle exocytosis
Besides the exocytosis of proteins from secretory lysosomes, “lysosomes” have been shown to exocytose small extracellular vesicles (EVs), termed exosomes from cells. EVs are now classified into 3 distinct populations including apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes (Thery et al. 2018). Among them, exosomes represent the smallest class of EVs (approximately 50–140 nm, despite no clear cutoff size to separate them from microvesicles) that originate from the inward budding of the membrane of late endosomes/lysosomes. Exosomes do not fuse with the late endosomal/lysosomal membrane but are released upon exocytosis as intact vesicles into the extracellular space and fluids (i.e. blood, synovial fluid, cerebrospinal liquor, and urine) (Buratta et al. 2020). In nonsecretory cells, this mode of exocytosis depends on membrane proximal lysosomes (Jaiswal et al. 2002). The process of exosome exocytosis is an important mechanism of cellular clearance, now also being more and more considered as an effective cell-to-cell communication mechanism, short and over long distance through fusion of exosomes with the membrane of other (neighboring) cells. Exosomes contain a plethora of cellar components from the donator cell, ranging from proteins, lipids, microRNA, RNA, and even DNA (Skotland et al. 2017). Interestingly, lysosomes have been suggested to restrict exosome exocytosis. In this process, MVBs were described to fuse to autophagosomes to form amphisomes. Amphisomes then fuse to lysosomes, which determine MVB fate and thereby reduce exosome release (Baixauli et al. 2014). Precisely, reduction of exosome release was found to occur in the setting of enhanced autophagy and enhanced LC3 levels (Fader et al. 2008).
Plasma membrane repair, remodeling, and growth
Plasma membrane disruption is a normal event in the life of a mammalian cell, especially in cells exposed to mechanical stress. Resealing is therefore a life assuring event for irreplaceable cells (i.e., cardiac myocytes and neurons) (McNeil and Kirchhausen 2005). Lysosome exocytosis has been found to be essential for the repair of damaged plasma membrane via fusion of the lysosomes situated in proximity of the injury site with the plasma membrane (McNeil and Kirchhausen 2005; Reddy et al. 2001). Mechanistically, this process is driven by a transient increase in intracellular Ca2+ and the Ca2+ sensing membrane protein synaptogamin VII, which associates with lysosomes by interacting with the SNARE complexes and plasma membrane phospholipids (Caler et al. 2001). Whether the fusion of lysosomal membrane with the plasma membrane is accompanied with the exocytosis of proteins or vesicles, or whether the fusing lysosomes are those originating from lysosomal recycling events is not known. However, the process of lysosomal exocytosis as a membrane donator is not only important for plasma membrane repair but also for specific membrane remodeling mechanisms (Czibener et al. 2006) and for the elongation of developing neuronal processes (Arantes and Andrews 2006).
Lysosomes as signaling nodes
Lysosomes can modulate cellular signaling through two principles: first, through their involvement in the recycling of receptors to the plasma membrane by the endocytic pathway; second, lysosomes have emerged as the second largest intracellular storage organelle for Ca2+, a ubiquitous primary signaling messenger in mammalian cells. Lysosomes typically comprise 2–3% of the cellular volume in mammalian cells, which suggests that although lysosomes have a high intraluminal Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]LYS ≈ 500–600 µM, which is about ~ 5000–6000 times the amount of free Ca2+ compared to the cytosol (Lloyd-Evans et al. 2010)), their overall contribution to cellular Ca2+ signaling is relatively low compared to the ER, which comprises about 11% of cellular volume and has an approximate Ca2+ concentration of [Ca2+]ER ≈ 12–2000 µM. Nonetheless, lysosomes have been shown to initiate local and global changes in cellular Ca2+ signaling. Local Ca2+ changes in the vicinity of lysosomes (through release of Ca2+ from the lysosome lumen) governs lysosomal transport and fusion events. Global Ca2+ release events appear to depend on the interplay between lysosomes and the ER. Thereby, a local lysosomal Ca2+ release at ER-lysosomal contact sites is thought to evolve into global Ca2+ release events. Further, ER-lysosomal contact might provide a source to refill depleted lysosomal Ca2+. Three main types of Ca2+ channels have been identified in mammalian lysosomes: transient receptor potential cation channels of the mucolipin family (TRPML), two-pore channels (TPR), and the trimeric Ca2+ two-transmembrane channel P2X4 (Li et al. 2019; Morgan et al. 2011). Lysosomal Ca2+ channel activities are most likely differentially modulated depending on the cell condition, thus allowing selective Ca2+ responses tailored to the cellular need, as they respond to a variety of stimuli, such as pH, nutrients, cellular stress, ATP, NAADP, and sphingosine. No actual candidate transporters or pumps have yet been identified in placental mammals that mediate the Ca2+ import into lysosomes necessary to obtain the high [Ca2+]LYS, however, SERCA3 (Lopez et al. 2008) and SLC24A5 (Na+/K+/Ca2+ exchanger (Lamason et al. 2005)) might represent potential candidates.
Lysosomes as metabolic sensors
Being the main mediator of cellular catabolism, the lysosome is in a unique position to integrate information on cellular degradation and recycling processes as a proxy to sense the cell’s nutritional status (Saftig and Puertollano 2020). The nutrient-regulated “mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1” (mTORC1), a key regulator of cellular biosynthesis pathways (Saxton and Sabatini 2017), dynamically associates with and is activated at lysosomes under specific conditions, especially in response to amino acids through involvement of heterodimeric Rag GTPases (RagA or RagB with RagC or RagD) at the lysosomal limiting membrane (reviewed in Ballabio and Bonifacino 2020; Lawrence and Zoncu 2019). mTORC1 recruitment is also inducible by cholesterol through involvement of the cholesterol-binding Niemann-Pick type C1 protein (NPC1). Activation of mTORC1 in response to nutrient availability increases the peripheral appearance of lysosomes to support cell anabolism and growth on the one side. On the other side, activation of mTORC1 inhibits catabolic pathways such as autophagy, which is visible in an inhibited fusion of lysosomes with autophagosomes. Of note, mTORC1 also regulates the re-formation of lysosomes during autophagy, a process that results in the restoration of a pool of functional lysosomes, which will be needed in the setting of starvation (Yu et al. 2010). mTORC1 is not the only nutrient-responsive molecule recruited to lysosomes. Rag-GTPases also mediate the recruitment of TSC (tuberous sclerosis complex) and FNIP (folliculin interacting protein 1) complexes, which both represent upstream regulators of mTOR.
Lysosomes sense the cellular nutrition state and transfer this information into an adaptive transcription of genes involved in several steps of the lysosome-autophagy pathway (Palmieri et al. 2011). This lysosome-to-nucleus signaling pathway is mediated through calcium signaling molecules such as transcription factor EB (TFEB) and the phosphatase calcineurin. TFEB dephosphorylation through calcineurin and protein phosphatase 2A (PPA2) (Martina and Puertollano 2018; Medina et al. 2015) mediates its translocation from the lysosomal limiting membrane to the nucleus. There, TFEB upregulates the transcription of CLEAR genes, such as hydrolases, lysosomal membrane proteins, the v-ATPase proton pump complex, and participates in the regulation of lysosome-related processes such as endocytosis, exocytosis, phagocytosis, and immune response (Sardiello et al. 2009). TFEB simultaneously controls the expression of autophagy genes and by this regulates both the initiation and the terminal steps of this essential homeostatic pathway (Raben and Puertollano 2016). TFEB nuclear translocation is promoted by a multitude of environmental stimuli, including starvation, bacterial infections, physical exercise, ER stress, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial damage. Transcription of autophagosomal-lysosomal genes is shut-off by the nuclear export and cytosolic retention of TFEB, which is regulated by its phosphorylation through the kinases mTORC1, and potentially also by Erk and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) (Li et al. 2018, 2016; Settembre et al. 2011).
Besides the capability of sensing the cells nutritional/metabolic status, lysosomes exhibit a cargo recognition response. In this response, lysosomes can sense the arrival of autophagosomes carrying damaged mitochondria or microbes by recognizing mitochondrial or microbial nucleic acid via toll-like receptors (TLRs) expressed at the lysosomal limiting membrane. Of the thirteen members of the TLR family, TLR3, TLR7/8, and TLR9 signal from endolysosomes. When activated by nucleic acids, these receptors initiate a proinflammatory signaling cascade through nuclear translocation of NF-κB or interferon regulatory factors to stimulate the production of cytokines and/or interferons. TLR9 dow nstream signaling events are further an important mechanism to adapt the degradative potential of a cell to the autophagic cargo (Ballabio and Bonifacino 2020).
Lysosomes in lipid metabolism
In line with their digestive function, lysosomes among other vesicles stand at the crossroad of lipid metabolism due to their ability to process and sort exogenous and endogenous lipids to various membrane compartments (reviewed in (Thelen and Zoncu 2017)). Exogenous sterols, triglycerides, and phospholipids, which are carried by LDL enter the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis and are processed by the lysosome (Goldstein and Brown 2015). Lysosomes also sort and recycle endogenous lipids, which have entered lysosomes through fusion (i.e., inner membrane of autophagosomes) or maturation (i.e., limiting membrane of intra luminal vesicles (ILVs) from MVBs). These intralysosomal membranes coalesce into membrane sheets or “whorls,” as their lipid composition is modified in the internal acidic environment of the lysosome (Schoneberg et al. 2017). They need to be removed from the lysosomal lumen and are inserted into the lysosomal membrane to be further delivered to other organelles by vesicular routes. One such receiving organelle is the ER, where the lipids may be esterified and stored in lipid droplets. Once within lysosomes, taken up LDL particles are attacked by the lysosomal acid lipase type A (LIPA), which de-esterifies the cholesterol and triglyceride molecules (Chang et al. 2006). Because the level of cholesterol in the limiting membrane of lysosomes is low (Kolter and Sandhoff 2005), a transport process across this membrane followed by delivery to another membrane is thought to exist. Export of cholesterol from lysosomes his mainly linked to the concerted action of Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) 1 and 2 (Infante et al. 2008) in parallel to LIMP2 (Heybrock et al. 2019). Possibly, LAMP1 and LAMP2 accept cholesterol from NPC2 to facilitate the flow of cholesterol (Li and Pfeffer 2016). Once cholesterol is deposited on the lysosomal membrane, its transport to extra-lysosomal locations is thought to occur rapidly.
Lysosomal lipid metabolism is directly synchronized to the cellular needs via mTORC1-TFEB pathway, which promotes de novo lipid synthesis and simultaneously suppresses lipid catabolism. Involved mechanisms for enhanced lipid synthesis are the mTORC1-dependent phosphorylation of S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) (Duvel et al. 2010) and the mTORC1-driven expression, trafficking and proteolytic processing of sterol-responsive element-binding proteins (SREBPs) SREBP1c and SREBP2, which are master regulators for the synthesis of fatty acids and sterols respectively (Thelen and Zoncu 2017). Lysosomal lipid catabolism is prevented by the mTORC1-TFEB pathway by inhibiting the breakdown of lipid droplets in a specialized autophagosomal process called lipophagy.
Lysosomal injury
Lysosomes exert a cytoprotective effect by removing damaged organelles such as mitochondria, which are delivered to lysosomes by the autophagosomal pathway. As damaged organelles release pro-apoptotic proteins, their removal protects from cell injury (Ravikumar et al. 2010). On the other side, most lysosomes contain relatively large amounts of redox-active iron and in combination with a lack of antioxidant enzymes are therefore unusually susceptible to oxidant-mediated membrane destabilization or rupture, which perpetuates cell injury (Kurz et al. 2008). Features of lysosomal dysfunction include changes in expression and/or activity of lysosomal enzymes, changes in lysosomal size/number/pH/cellular positioning/motility and changes in lysosomal membrane properties. Furthermore, lysosomal dysfunction can lead to the accumulation of undegraded material and give rise to blockade of lysosomal related pathways (especially autophagy). Lysosomal damage leads to a condition called lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP). This selective destabilization of the lysosomal membrane allows translocation of lysosomal contents, including ions and cathepsins to the cytoplasm through membrane ruptures. To cope with lysosomal injury, cells have developed “endolysosomal damage-response mechanisms,” of which 4 have been described to date: (1) creation of new lysosomes via the mTORC1-TFEB pathway; (2) repair of damaged lysosomes by membrane sealing; and removal of damaged lysosomes either by (3) lysophagy; and/or by (4) lysosome exocytosis (Samie and Xu 2014). Small (proton permeable) disruptions of the lysosomal limiting membrane activate lysosomal repair mechanisms which converge at an ESCRT-dependent resealing of the membrane (Skowyra et al. 2018). Strong ruptures of the lysosomal membrane (i.e., ruptures permeable to lysosomal proteins, which are then exposed at the cytosolic side of the lysosomal membrane, such as β-galactosidase) trigger the recruitment of cytosolic galectins to injured lysosomes. Galectins (Chauhan et al. 2016; Thurston et al. 2012) together with extensive lysosomal ubiquitination (Papadopoulos and Meyer 2017) recruit components of the autophagy machinery and thus orchestrate the removal of damaged lysosomes with their debris by a selective form of autophagy, a process called lysophagy (Maejima et al. 2013).
Massive and prolonged LMP leads to a special form of programmed cell death, called lysosome-dependent cell death (LDCD), of which the extruding cathepsin B and cathepsin D are the main executors (reviewed in (Wang et al. 2018)). These through LMP extruding proteases are thought to further proteolytically activate substrates such as Bid and Bax, which in turn promote mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and caspase activation resulting in the initiation of apoptosis (de Castro et al. 2016). In other cases, the release of lysosomal effectors through LMP can result in two other forms of cell death depending on the triggering effector, namely ferroptosis (iron as trigger), and pyroptosis (reactive oxygen species as trigger). Last but not least, total lysosomal rupture leads to the massive release of lysosomal enzymes and thereby to an uncontrolled cleavage of cellular components and cytosolic acidification culminating in necrosis. Lysosomal injury/impairment has been implicated in various disease conditions including lysosomal storage diseases, neurodegeneration, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
Lysosomes in glomerular health
The kidney glomerular filtration barrier represents a sophisticated syncytium of three individual cell types, namely podocytes, mesangial, and glomerular endothelial cells, which sustain the structure and regulate the function of the filtration barrier (Pavenstadt et al. 2003). The terminally differentiated podocytes embrace the glomerular capillaries and form an intricate mesh with their interdigitating processes that are interconnected by a modified form of adherens junction, the slit diaphragm, which ultimately bridges the filtration slits. Podocytes are thought to share many morphological features and proteins with neurons (Giardino et al. 2009; Rastaldi et al. 2003). The intraglomerular mesangial cells are situated in close contact with the endothelial cells and represent a specialized form of pericytes that provide structural support. The fenestrated endothelial cells line the glomerular capillaries and reside opposite from the podocytes separated by the glomerular basement membrane. Podocytes synthesize, maintain, stabilize the mature glomerular filtration barrier, and regulate glomerular filtration. Mesangial cells regulate the glomerular capillary flow and ultrafiltration surface, are responsible for the homeostasis of the mesangial matrix and are source and targets of growth factors, cytokines, and vasoactive agents. Further, they are phagocytic cells degrading glomerular basal lamina and immune complexes. Glomerular endothelial cells are involved in GBM production and contribute the hydraulic conductivity and size and charge selectivity of the glomerular filtration barrier (reviewed in (Meyer-Schwesinger, C., Huber, T.B. 2020). Malfunction of any of these cell types leads to loss of glomerular function and proteinuria leading to the concept that these glomerular cell types interact (Dimke et al. 2015).
Lysosomes in healthy glomerular cells
In comparison to the surrounding renal tubular system the glomerular compartment is less abundant in lysosomes and shows lower lysosomal activity (Lovett et al. 1982). Knowledge about the glomerular cell-type “inventory” of lysosome types is rudimentary to absent. Electron microscopic evaluations demonstrate that the podocyte cell body contains prominent lysosomes. The density of cell organelles in the podocyte cell body indicates a high level of anabolic as well as catabolic activity. In contrast to the cell body, podocyte processes contain only few organelles (Pavenstadt et al. 2003), which distinguishes them from neuronal processes. Mesangial cells are phagocytic cells (Gomez-Guerrero et al. 2002; Schlondorff 1987), and therefore should contain an evolved lysosomal system. As a pioneer in lysosomal discovery, the group of George Palade was the first to describe the occurrence of an enhanced lytic activity in mesangial cells in comparison to glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes (Miller and Palade 1964). The measurement of acidic lysosomal hydrolases (acid phosphatase, β-glucuronidase, cathepsin D, nonspecific esterase, and aryl sulfatases A and B) showed considerable lysosomal activities in the nonpodocyte fraction of glomeruli (Lovett et al. 1982; Yokota et al. 1985). Besides the abundance of lysosomal hydrolases in mesangial cells, the morphological dissection of the mesangial and glomerular endothelial cell lysosomal system has largely been neglected.
Glomerular cell-type-specific dependency of homeostatic degradation systems
One important feature has to be taken into consideration prior to reflecting about the individual contribution of lysosomes to the homeostasis of glomerular cell types. Whereas lipid catabolism is restricted to lysosomes, protein degradation is not solely achieved by lysosomes. In fact, the majority (about 80%) of cellular proteins are degraded by the ubiquitin proteasomal system (UPS), which interacts at multiple steps with the autophagosomal lysosomal pathway (Meyer-Schwesinger 2019). While lysosomes mostly degrade protein aggregates and membrane proteins delivered by the endocytic pathway, the proteasome is essential for the regulation of various cellular functions by degradation of mostly short-lived and regulatory proteins, or damaged and misfolded proteins (Meyer-Schwesinger 2019), and protein aggregates in case of lysosomal dysfunction (Hao et al. 2013; Hjerpe et al. 2016). Both degradation systems mutually compensate for the impairment of one another (Meyer-Schwesinger 2019). This can be nicely observed in a study, in which podocytes deficient for ATG5 (essential for autophagosome formation) compensate autophagosome deficiency by upregulation of the UPS (Hartleben et al. 2010), or in mice with the lysosomal storage disease mucolipidosis type III, where the glomerular UPS compensates for lysosome-associated degradation defects resulting from lysosomal enzyme missorting into the extracellular space (Sachs et al. 2020). Only upon impairment of the proteasome in aged mice do ubiquitinated nondegraded proteins accumulate, and does mild proteinuria occur in ATG5-deficient podocytes (Hartleben et al. 2010). Interestingly, mucolipidosis type III mice do not develop proteinuria with age, even though a multitude of lysosomal hydrolases are missorted and do not reach the lysosome (Sachs et al. 2020).
It is becoming more and more clear that glomerular cell types differentially depend on protein degradation systems. Of the three glomerular cell types, most research attention to this topic is centered around podocytes. Proteomic studies performed in cultured murine and human podocytes demonstrate a strong proteolytic shift from a predominant proteasomal activity to a lysosomal activity in the course of podocyte differentiation (Rinschen et al. 2016; Schroeter et al. 2018), which coincides with a globally increased stability of mitochondrial, cytoskeletal, and membrane proteins in differentiated podocytes (Schroeter et al. 2018). How far this finding can be transferred to the physiologic in vivo situation still needs to be determined, as possible skewers such as culture conditions could explain the proteolytic system shift from undifferentiated to differentiated podocytes. Nonetheless, the specific disruption of players of the endocytic system in podocytes using genetic approaches support a strong involvement of the lysosomes in podocyte health. Thereby, mice with a podocyte-specific deficiency of Vps34, which in yeast is essential for the sorting of hydrolases to yeast vacuoles (Herman and Emr 1990) and in mammals (as mVps34 (class III PI3K)) has been implicated in the regulation of autophagy (Itakura et al. 2008), develop severe glomerulosclerosis with enlarged vacuoles and increased autophagosomes in podocytes and die at 9 weeks of age (Chen et al. 2013). This phenotype appears to be the result of a direct lysosomal impairment rather than of a primary defect in autophagy, highlighting the complexity of the subject and the need for cell-type-specific investigations.
Dissection of the expression of lysosomal membrane proteins among glomerular cell types suggests the existence of different subsets of endocytic/lysosomal vesicles within podocytes, mesangial and glomerular endothelial cells. Thereby, Limp2-positive vesicles are predominantly found in mesangial and glomerular endothelial cells, whereas Lamp2 is evenly distributed within the glomerular cell types, however to a far lesser extent than in the surrounding parietal epithelial cells and proximal tubular cells (Sachs et al. 2020), Fig. 4a. The functional significance of this finding still needs to be evaluated. Recent data from our lab demonstrate that of all glomerular cell types, podocytes have an exceptional high dependence on a functioning proteasomal system in vivo. Thereby, a new technique enabling a reporter-free bulk separation of glomerular cell types from wild-type mice for protein biochemical investigations shows that podocytes express higher levels of proteasomal proteins in comparison to mesangial and glomerular endothelial cells, whereas lysosomal proteins are comparable between glomerular cell types (https://biorxiv.org/cgi/content/short/2020.08.22.262584v1).
Scheme of glomerular cell involvement of lysosomes in health and disease. (a) Normal lysosomal distribution within glomerular cell types. (b) Lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) with different kinds of accumulating undegraded lysosomal cargo, alteration of lysosomal morphology and function. (c) Membranous nephropathy is caused by the binding of autoantibodies directed against podocyte foot process proteins PLA2R1 and THSD7A. Subepithelial immune deposits and complement activation are thought to mediate podocyte injury. The membrane attack complex C5b-9 triggers ROS production and LMP. Lysosomal exocytosis of acid hydrolases is thought to mediate slow degradation of subepithelial deposits (c’). A specific upregulation of LIMP2-positive lysosomes occurs in MN, potentially to compensate for the impairment of proteasomal dysfunction. (d) Diabetic nephropathy with involvement of all three glomerular cell types. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which trigger lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) with the sequel of acid hydrolase release such as cathepsin L into the cytoplasm. Cathepsin L cleaves podocyte proteins synaptopodin, CD2AP, and dynamin, inducing cytoskeletal alterations (d’). Inflammasome activation and lysosomal exocytosis of exosomes and of IL-1 β is additionally thought to maintain a pro-inflammatory condition. (e) Autoantibodies to LAMP2 have been described in crescentic glomerulonephritis (GN). These autoantibodies bind at the plasma membrane and at the limiting membrane of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and proteinase 3 (PR3) containing lysosomes in neutrophils and bind to a structurally related membrane protein at the surface of glomerular and renal microvascular endothelial cells. Lysosomal exocytosis (e’) is thought to be a major contributor to inflammation. (f) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) can be the cause of mutations of SCARB2, encoding for LIMP2 in primary FSGS. Further, increased susceptibility of African Americans to FSGS have implicated variants of apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) to lysosomal dysfunction in podocytes. APOL1 can induce LMP and a continuous chloride influx (f’). The APOL1 risk-variants interfere with endosomal trafficking and block autophagic flux, ultimately leading to inflammatory-mediated podocyte death and glomerular scarring
Lessons learnt from lysosomal storage diseases
The role of lysosomes in glomerular cells can best be appreciated by analyzing the effects of primary lysosomal dysfunctions on the glomerulus. Lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) are a group of individually inherited metabolic disorders that are the most common cause of childhood neurodegeneration. These diseases are predominantly caused by (1) mutations in genes encoding for lysosomal enzymes or their accessory proteins; (2) mutations in genes encoding for lysosomal transmembrane proteins that include transporters, ion channels, proteins of unknown functions (reviewed in (Cox and Cachon-Gonzalez 2012)); and (3) mutations in genes encoding for the Golgi-resident GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase which tags lysosomal enzymes at the Golgi apparatus with M6P for proper trafficking to lysosomes (Kollmann et al. 2010; Velho et al. 2017). As different LSDs have different molecular causes, the effects on lysosomal storage and the (patho) biochemical consequences on lysosomal function strongly vary (Marques and Saftig 2019). Nonetheless, almost all associated diseases are characterized by similar changes in cell biology, which include intra-lysosomal accumulation of various substrates (lipids, proteins, gangliosides, glucosylceramides, glycogen, glycosaminoglycans, among others), defects in endocytosis, autophagy, and mitochondrial function (Cox and Cachon-Gonzalez 2012). These functional deficiencies impact multiple cell types, particularly neurons (resulting in neurodegenerative phenotypes), and in very rare cases glomerular cells.
Glomerular involvement in LSD
The susceptibility of glomerular cells to lysosomal impairment is far from being clear, as it strongly varies between the different types of LSDs and also within one type of LSD. LSDs most likely affect glomerular cell types differentially due to a potentially differing capacity in lysophagy, ESCRT mediated membrane repair, lysosome mobility, exocytosis, cholesterol homeostasis among others (reviewed in (Marques and Saftig 2019)) (Fig. 4b). Renal/glomerular involvement constitutes a key contributor to the morbidity and mortality in patients with Fabry disease (Kantola 2019). In other LSDs, glomerular/renal impairment is usually a rare condition. Nonetheless, renal dysfunction has been reported in single patients with nephrosialidosis (Roth et al. 1988), infantile sialic acid storage disease (Sperl et al. 1990), cystinosis (Langman 2019), mucopolysacharidosis I (MPS-I) (Taylor et al. 1986), as well as with mucolipidosis (Kerr et al. 2011; Kobayashi et al. 2011; Tang et al. 1995). A complete review is beyond the scope of this article, a subset of LSDs with rare occurrence of glomerular cell involvement is summarized in Table 1. Although rapid progress has been made in understanding the genetic basis of lysosomal storage disorders, the factors underlying the disruption of cell metabolic and signaling pathways associated with these conditions are less well understood. It is commonly accepted that despite the broad variability of LSDs, diseases that store similar types of macromolecules (sphingolipids, mucopolysaccharides or glycoproteins) often have similar biochemical, pathological, and clinical phenotypes, suggesting that the nature and distribution of the stored material is the major lesion defining factor (Bifsha et al. 2007). In line, the electron density of the accumulated storage material differs between podocytes, glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells in mouse models of LSD (Sachs et al. 2020), suggesting that distinct types of macromolecules accumulate in a glomerular cell-specific manner, as the metabolic requirements might differ between the glomerular cell types. This, however, is pure speculation, as no information exists about the metabolic preferences of mesangial and glomerular endothelial cells. Murine podocytes have recently been shown to largely depend on anaerobic glycolysis (Brinkkoetter et al. 2019). Further, the nature of accumulating macromolecules underlying the different deposits by electron microscopy are mostly not determined in a glomerular cell type manner.
Phenotypic discrepancies between murine models of LSD and human disease-related phenotypes
The phenotypic heterogeneity associated with a given genotype in LSDs demonstrates that even though disease originates from a single gene disorder, other (cell-type specific?) modifying factors must play a role. One such modifying factor could be the compensatory potential of the affected cell species in dealing with this storage stress, which could define/shape the characteristics of the clinical presentation. Of all glomerular cells, podocytes have most frequently been observed to exhibit an altered morphology in lysosomal storage disorders, usually described as a foamy appearance (Kerr et al. 2011; Kobayashi et al. 2011; Tuysuz et al. 2016), most likely due to the accumulation of storage material. However, this foamy podocyte appearance does not necessarily associate with a decreased renal/glomerular function in for example mucolipidosis patients (Kerr et al. 2011). In this setting, differential “rescue” mechanisms are activated within glomerular cell types to compensate for lysosomal dysfunction. These rescue mechanisms range from an activation of lysosomal biogenesis, an activation of the proteasomal system, a downregulation of mTORC1 signaling, and a downregulation of protein synthesis through the integrated stress response (Sachs et al. 2020), among others. An important fact that has hampered the unraveling of the nature of glomerular cell injury in the different forms of LSDs is that often the experimental animal models of LSD do not mirror the human disease-related phenotypes despite the fact that they carry the human genotype. This limitation is most likely due to possible species-based differences in glomerular cell metabolism (Abe et al. 2000; Mattocks et al. 2006).
Fabry disease
A prominent example of species difference in dealing with the sequel of a defined genetic lysosomal disorder is Fabry disease, an X-linked monogenic LSD caused by mutations in the GLA gene (Kantola 2019), which encodes for the lysosomal hydrolase α-galactosidase A. The lack of α -galactosidase A leads to the progressive accumulation of glycosphingolipids, such as globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) in lysosomes of a plethora of cell types (mainly in endothelial cells of the kidney, heart liver, and spleen) as well as in plasma. Even though the glomerular/podocyte expression of α-galactosidase A in normal human kidneys is weak to absent (Christensen et al. 2007), renal and glomerular involvement is common in Fabry patients and constitutes a key contributor to the morbidity and mortality. In contrast, mouse models of Fabry disease fail to exhibit glomerular pathology (Ohshima et al. 1997), despite the comparable prevalence of glycosphingolipid storage per renal cell type including podocytes, and interstitial cells, vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells, as well as the tubular cells of the distal tubules and loop of Henle (Kantola 2019). Gb3 accumulations significantly differ between humans and mice in mesangial (higher in humans) and in proximal tubular cells (higher in mice) (Valbuena et al. 2011). Another interesting finding concerning glomerular cell-type-specific differences in lysosomal dependency is the fact that in Fabry patient’s enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) with α-galactosidase A efficiently clears Gb3 accumulation in glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells, however, to a far lesser extent in podocytes (Thurberg et al. 2002). Human podocytes take up recombinant α-galactosidase A during ERT through the endocytic receptors MPR, sortilin, and megalin (Prabakaran et al. 2011) (of note: megalin expression in human podocyte is debated (Kerjaschki and Farquhar 1983)). The endocytosis activity for lysosomal acid hydrolases such as α-galactosidase A (Christensen et al. 2007) and arylsulfatase B (Hendrickx et al. 2020) seems, however, to be weaker in podocytes than in other (renal) cell types such as proximal tubular cells (Christensen et al. 2007). Nonetheless, podocyte injury and loss correlate with Gb3 accumulation (Najafian et al. 2020), suggesting that podocytes are especially sensitive to Gb3. Pathomechanistically, globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3), which also accumulates in Fabry disease (Gold et al. 2013), promotes Notch1-mediated inflammatory and fibrogenic responses in podocytes that may contribute to Fabry nephropathy (Sanchez-Nino et al. 2015) among others.
SCARB2 mutations
One further example for species-related differences can be seen in humans with mutations in SCARB2, which encodes for LIMP2. Patients present with action myoclonus renal failure (AMRF) accompanied by storage in the brain but not in the kidney. Renal failure and proteinuria in humans with AMRF is thought to relate to hypertrophy and hyperplasia of podocytes in the early phase of injury and severe focal glomerulosclerosis with glomerular collapse as an endpoint (Berkovic et al. 2008). Limp2-deficient mice on the other hand present with obstruction of the ureteric pelvic junction, deafness and a peripheral demyelinating neuropathy and exhibit slight proteinuria with the occurrence of mesangial expansion, thickening of the glomerular basement membrane and foot process effacement, however, without the development of FSGS-like lesions (Berkovic et al. 2008; Desmond et al. 2011; Gamp et al. 2003).
Farber disease
A recent publication demonstrated that mice with a podocyte-specific deficiency of lysosomal acid ceramidase, exhibited podocyte injury due to the accumulation of ceramide and nephrotic syndrome (Li et al. 2020a). The related human genetic mutations leading to deficiency of lysosomal acid ceramidase lead to Farber disease, which is characterized by subcutaneous nodules, joint pain, and voice hoarseness. Patients also present with enlarged liver and spleen and with neurologic and respiratory complications. In this rare LSD, ceramidase activity has not been recognized in the kidney (Yu et al. 2018), but one case reports ceramide accumulation in the kidney (Samuelsson and Zetterstrom 1971). No description of ceramide accumulation in podocytes or nephrotic syndrome exist to date.
Gaucher disease
In the most common LSD, Gaucher disease, glomerular involvement is (again, as typical for LSD) extremely rare. However, seldom cases of glomerular glucocerebroside (Gaucher bodies) accumulation are described, mainly in glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells and are thought to be indicative of the phagocytic potential and of the deficiency of glucocerebroside-cleaving enzyme in these cells (Chander et al. 1979). Gaucher disease arises from an autosomal recessive deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase (encoded by the GBA gene) resulting in a decreased lysosomal degradation of the sphingolipid glucocerebroside, which is a normal intermediate in the degradation of membrane compounds (Peters et al. 1977). Numerous mutations in the GBA gene have been associated with Gaucher disease whose hallmark are the Gaucher cells, lipid-laden macrophages with lysosomal glucocerebroside deposits (reviewed in (Boer et al. 2020)). Why glomerular cells, especially podocytes are so rarely affected in Gaucher disease, is not known, as more and more studies demonstrate the importance of a balanced lipid metabolism, especially of sphingolipids for podocytes (reviewed in (Merscher and Fornoni 2014)). Sphingolipids are involved in the formation of lipid rafts in podocytes and are essential for the maintenance of a functional slit diaphragm in the glomerulus. To different degrees, sphingolipids not only accumulate in glomerular cells in Gaucher disease but also in other LSDs such as Tay-Sachs, Sandhoff, Fabry, hereditary inclusion body myopathy 2, Niemann-Pick, and nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type (Merscher and Fornoni 2014).
Lysosomes in nonhereditary glomerular diseases
Our knowledge about a direct involvement of lysosomes to glomerular cell pathology in nonhereditary diseases is scarce. The typical morphologic alterations of increased lysosomal size and amount, which suggest an affected lysosomal function have been described in many contexts. However, whether the cause of increased lysosomal size/amount is an underlying direct lysosomal disturbance(s) or merely a compensatory upregulation of lysosomes to maintain cellular homeostasis remains largely unknown. Most research attention in glomerular injury has been given to autophagy. Autophagy is directly coupled to lysosomal function as one arm of the endocytic pathway but does not necessarily mirror lysosomal function in glomerular cells per se, as autophagy can be altered in a lysosome-independent way, i.e., in the case of failure to form autophagosomes (Hartleben et al. 2014). Therefore, this review will focus on those findings that directly examine lysosomal function in the context of glomerular cell injury. Many excellent reviews exist, which discuss the importance of autophagy and mTOR in podocyte (and to a lesser extent for glomerular) physiology and pathophysiology (Cui et al. 2020; Cybulsky 2017; Lenoir et al. 2016).
Sphingolipid accumulation, which frequently is related to disturbed lysosomal lipid metabolism, occurs in glomerular diseases of nongenetic origin (Merscher and Fornoni 2014). However, what factors trigger these lipid accumulations remains unclear and the cause is seldomly traced back to (a) lysosome-dependent pathomechanism(s). Similarly to the proteasomal degradation system, lysosomal proteins and activities are induced in glomerular injury in humans and rodents, however, frequently secondary after the induction of the proteasomal system (Beeken et al. 2014), suggesting a potentially compensatory effect for an underlying proteasomal impairment. Of note, not all lipid accumulating glomerulonephritis forms exhibit a regulation of lysosomes. In human pathology, one example is minimal change disease, where no transcriptional regulation of lysosomal membrane proteins or acid hydrolases occurs, contrasting patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis or diabetic nephropathy, where these transcripts are enhanced (Beeken et al. 2014). Despite this differential regulation of lysosomal proteins, all three glomerulonephritis forms exhibit abnormal lipid accumulation (Merscher and Fornoni 2014). Similar observations were made in different rat models of glomerular disease, where puromycin aminonucleosid-induced glomerulonephritis does not result in a transcriptional regulation of lysosomal membrane proteins or acid hydrolases in glomeruli, whereas in the passive Heymann nephritis model of membranous nephropathy such a regulation occurs. Therefore, lysosomal induction does not appear to be a universal reaction to glomerular injury and the factors resulting in / or preventing an induction of lysosomal biosynthesis need to be unraveled for the specific disease entities. Not surprising, a functioning lysosomal system is required for the attenuation of glomerular injury, as shown in the exacerbation of glomerular injury following the induction of antibody-mediated podocyte injury in Limp2-deficient mice (Beeken et al. 2014).
Specific glomerular diseases
A direct link to lysosomal impairment and glomerular cell injury has been reported in patients with primary podocyte diseases such as membranous nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and in secondary glomerular injuries in the setting of diabetes and ANCA-vasculitis. These will be highlighted in a disease-specific manner in the following sections and in Fig. 4c–f. Other glomerular injuries such as IgA nephritis, membranoproliferative GN are likely to exhibit alterations in lysosomal function; however, no data to such observations are published to the best of our knowledge.
Membranous nephropathy (Fig. 4c)
Membranous nephropathy is an autoimmune-mediated form of podocyte injury, where autoantibodies bind to the podocyte foot process expressed antigens PLA2R1 (Beck et al. 2009) and THSD7A (Tomas et al. 2014) and induce injury (Meyer-Schwesinger, C., Huber, T.B. 2020; Tomas et al. 2016) culminating in nephrotic syndrome. Morphologic hallmarks of MN are a thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, the subepithelial deposition of immune deposits and complement, and foot process effacement. The mechanisms that initiate podocyte injury after autoantibody binding to foot process antigens remain obscure. Complement deposition (Beck 2017) and mechanical or antigen-related effects are discussed (Herwig et al. 2019). Downstream of these initiating events, catabolic pathways are induced in human and rodent MN (Beeken et al. 2014; Meyer-Schwesinger et al. 2009). An impairment of the proteasomal system is thought to relate to podocyte hypertrophy (Lohmann et al. 2014) and injury in MN (Meyer-Schwesinger et al. 2011). An upregulation of lysosomal proteins, especially of Limp2-expressing lysosomes (Rood et al. 2015), and cathepsin D (Wu et al. 2011) is prominent in MN. In light of the fact that signs of lysosomal impairment such as accumulation of lipids and of undegraded storage material in lysosomes are not described in human MN, lysosomal induction might represent a compensatory mechanism for proteasomal impairment (Beeken et al. 2014). Further, lysosomal acid hydrolases were suggested to be involved in the slow degradation of the deposited IgG in MN (Singh 1992). Interestingly, a recent publication by Liu et al. suggests a role for lysosomal dysfunction as the basis of impaired autophagy in MN (Liu et al. 2017). In this study, lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) was detected in cultured human podocytes exposed to sublytic complement C5b-9 membrane attack complex (Liu et al. 2017). Since oxidative stress is prominent in MN (Exner et al. 1996; Neale et al. 1994), the LMP observed in cultured podocytes exposed to sublytic C5b-9 could be the sequel of reactive oxygen species mediating lysosomal injury. It will be of interest to see, if LMP occurs in human MN and whether it accounts for podocyte injury.
Diabetic nephropathy (Fig. 4d)
Another glomerular injury form, in which oxidative stress is prominent and could induce LMP in glomerular cells is diabetic nephropathy (DN), the most common cause of end-stage renal disease. Glomerular changes in DN include thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, mesangial expansion, proteinuria and fibrosis. All three glomerular cell types are affected in DN, and podocyte damage and loss contribute to the impairment of renal function. Studies showing the importance of mTOR signaling (and thereby autophagy and lysosomal function) in DN are numerous and reviewed in (Li et al. 2020b). Lysosomal protein transcripts are upregulated in glomeruli of patients with DN (Beeken et al. 2014). Lysosomes exert a protective role in DN due to their end-position within the endocytic pathway responsible for the degradation of cargo delivered by autophagosomes. The injury of glomerular cell types in DN is driven by advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) in podocytes (Zhou et al. 2012). On the one side, ROS represent one of the factors inducing autophagy in DN (Ma et al. 2013), which is considered cytoprotective. On the other side, podocytes exposed to AGEs show enhanced oxidative stress, which then triggers lysosomal membrane permeabilization and hence, secondary impairment of autophagy (Liu et al. 2019). The finding that cathepsin L knockout mice are protected from glomerular damage in diabetes (Garsen et al. 2016) supports the concept of LMP as a main trigger to glomerular cell injury in DN. Cathepsin L is one of the acid hydrolases leaking from injured lysosomes in LMP and promotes the proteolysis of proteins essential for foot process morphology, namely CD2AP, synaptopodin (Yaddanapudi et al. 2011), and dynamin (Sever et al. 2007). Besides LMP as a mechanism by which lysosomes drive glomerular cell injury in DN, a decreased interaction of lysosomes with MVBs was suggested to induce lysosome exocytosis of extracellular vesicles containing pro-inflammatory IL-1β (Hong et al. 2019), thereby triggering an inflammatory response. Further, altered lysosome-dependent lipid metabolism contributes to glomerular cell injury in DN. In diabetic mice, lysosomal acid ceramidase, which converts ceramide to sphingosine, is reduced (Choi et al. 2018) and pharmacologic enhancement of lysosomal acid ceramidase activity ameliorates glomerular endothelial cell and podocyte injury (Choi et al. 2018). This could represent a relevant mechanism of human glomerular cell injury, as DN patients exhibit enhanced urinary ceramide content (Morita et al. 2020). Of note: Other metabolic conditions are associated with increased ceramide levels due to decreased lysosomal acid ceramidase levels or activity, such as obesity and hyperhomocysteinemic nephropathy, directly linking metabolism to altered lysosomal function and glomerular cell injury (Li et al. 2020b).
Crescentic glomerulonephritis (Fig. 4e)
Lysosomes have reached fame in nephrology with the discovery that antibodies to a bacterial antigen can cross-react to a previously characterized antineutrophil cytoplasmic antigen (ANCA), namely LAMP2 (Kain et al. 1995) to cause pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis (Kain et al. 2008). Mechanistically, these autoantibodies activate neutrophils and damage human microvascular endothelium in vitro and cause pauci-immune focal necrotizing glomerulonephritis in rats. This pathogenicity of LAMP2 autoantibodies is thought to arise (1) from autoantibody binding to LAMP2 at the plasma membrane and at the limiting membrane of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and proteinase 3 (PR3) containing lysosomes in neutrophils (Kettritz 2012) and (2) from binding to a structurally related membrane protein at the surface of glomerular and renal microvascular endothelial cells (Kain et al. 2008, 1995). LAMP2, as other lysosomal membrane proteins, is found at low levels at the plasma membrane of cells, a fact most likely attributed to a MPR-independent targeting pathway of lysosomal membrane proteins to lysosomes (Carlsson et al. 1988). The involvement of anti-LAMP2 autoantibodies remains controversial in crescentic glomerulonephritis because of the absence of confirmatory data from other groups regarding their high prevalence and their pathogenicity (Kettritz 2012; Roth et al. 2012).
Besides the abovementioned potential involvement of autoantibodies to LAMP2 in the pathogenesis of crescentic GN, a study performed in Limp2-deficient mice highlights a pro-inflammatory involvement of lysosomes in the anti-glomerular basement membrane model of crescentic GN, as Limp2-deficient mice exhibit a decreased renal infiltration of macrophages and T cells (Lee et al. 2014). This could relate to a blockage of the lysosomal involvement in driving inflammation through lysosomal exocytosis and inflammasome activation.
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (Fig. 4f)
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a generic term for a histological injury pattern defined by segmental glomerular consolidation into a scar that affects some but not all glomeruli with a wide range of etiological interpretations. FSGS describes both a disease characterized by primary podocyte injury (primary FSGS) and a lesion that occurs secondarily in any type of chronic kidney disease (secondary FSGS) (Fogo 2015). Besides the direct involvement of LIMP2 mutations to genetic FSGS, the studies underlining lysosomal involvement in secondary FSGS are rare. An upregulation of lysosomal protein transcripts is seen in glomeruli of patients with FSGS (Beeken et al. 2014); however, the prominent upregulation of LIMP2 observed in MN patients is absent in FSGS (Rood et al. 2015). Nonetheless, the connection between metabolism–lysosomal dysfunction–glomerular injury discussed in the setting of DN is most likely to also contribute to the development of secondary FSGS. Studies of the increased susceptibility of African Americans to FSGS have implicated variants of apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) (Genovese et al. 2013) to lysosomal dysfunction in podocytes. As a secreted protein, APOL1 can induce lysosomal membrane depolarization and a continuous chloride influx, representing the mechanism by which APOL1 promotes lysis of trypanosomes and imparts resistance to trypanosomiasis (Perez-Morga et al. 2005). Experimental expression of the APOL1 risk alleles in a podocyte-specific manner is causal for podocyte foot process effacement, proteinuria, and glomerulosclerosis (Beckerman et al. 2017). The risk-variant APOL1 alleles interfere with endosomal trafficking and block autophagic flux, ultimately leading to inflammatory-mediated podocyte death and glomerular scarring (Beckerman et al. 2017). Pointing to a mechanistic involvement of lysosomes in this setting is the fact that inhibition of chloride channels and of the interaction of APOL1 with lysosomes attenuates lysosomal swelling and APOL1 variant-induced podocyte injury (Lan et al. 2014).
Closing remarks
Lysosomes represent the endpoint of numerous vesicle trafficking pathways including the endocytic, phagocytic, and autophagic pathways and physiologically and pathophysiologically represent a cellular node for catabolism and signaling. The lessons we learn from existing investigations on the effect of lysosomal storage disorders and of nongenetic lysosomal disorders on glomerular cell types leave many questions open and stress the urgent need for future basic research. Glomerular cell-type-specific research should focus on (1) lysosomal enzyme targeting mechanisms (endocytosis) to lysosomes; on (2) the distribution of lysosome types; on (3) the dependence on protein and lipid metabolism; on (4) the susceptibility to accumulating macromolecules; and on (5) the stress response mechanisms activated in specific subsets of lysosomal disorders. These investigations are extremely challenging due to the rare nature of LSDs, the difficulty to phenocopy human lysosomal disorders in rodents, the lack of experimental techniques that go beyond the localization and morphology of lysosomes and allow an assessment of lysosomal functionality in archived tissue, and the fact that glomerular cell types and cellular degradation systems are most likely to interact in their quest to keep glomeruli free from macromolecule accumulations. Human-relevant research should be the focus of future investigations, as the profound differences in the cellular metabolism of lipids and proteins between rodents and humans renders knowledge transfer from bench-to-bed challenging. A deeper knowledge in these fundamental processes will pave the way to a better understanding of the clinical heterogeneity lysosomal dysfunction exerts in glomerular cell-types, a prerequisite for the development of specific and efficient therapeutic targeting strategies. It is to be expected that new therapeutic strategies beyond mTOR inhibitors are forthcoming, which specifically target different components of lysosomal function such as the activity of specific lysosomal acid hydrolases, lysosomal Ca2+ channels, or which stabilize lysosomes to prevent lysosomal membrane permeabilization.
References
Abe A, Gregory S, Lee L, Killen PD, Brady RO, Kulkarni A, Shayman JA et al (2000) Reduction of globotriaosylceramide in Fabry disease mice by substrate deprivation. J Clin Invest 105:1563–1571
Alroy J, Sabnis S, Kopp JB (2002) Renal pathology in Fabry disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13(Suppl 2):S134-138
Arantes RM, Andrews NW (2006) A role for synaptotagmin VII-regulated exocytosis of lysosomes in neurite outgrowth from primary sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci 26:4630–4637
Bainton DF (1981) The discovery of lysosomes. J Cell Biol 91:66s–76s
Baixauli F, Lopez-Otin C, Mittelbrunn M et al (2014) Exosomes and autophagy: Coordinated mechanisms for the maintenance of cellular fitness. Front Immunol 5:403
Ballabio A, Bonifacino JS (2020) Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:101–118
Bargal R, Avidan N, Ben-Asher E, Olender Z, Zeigler M, Frumkin A, Raas-Rothschild A, Glusman G, Lancet D, Bach G (2000) Identification of the gene causing mucolipidosis type IV. Nat Genet 26:118–123
Bassi MT, Manzoni M, Monti E, Pizzo MT, Ballabio A, Borsani G (2000) Cloning of the gene encoding a novel integral membrane protein, mucolipidin-and identification of the two major founder mutations causing mucolipidosis type IV. Am J Hum Genet 67:1110–1120
Beck LH Jr (2017) PLA2R and THSD7A: Disparate paths to the same disease? J Am Soc Nephrol 28:2579–2589
Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, Beck DM, Powell DW, Cummins TD, Klein JB, Salant DJ et al (2009) M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 361:11–21
Beckerman P, Bi-Karchin J, Park AS, Qiu C, Dummer PD, Soomro I, Boustany-Kari CM, Pullen SS, Miner JH, Hu CA et al (2017) Transgenic expression of human APOL1 risk variants in podocytes induces kidney disease in mice. Nat Med 23:429–438
Beeken M, Lindenmeyer MT, Blattner SM, Radon V, Oh J, Meyer TN, Hildebrand D, Schluter H, Reinicke AT, Knop JH et al (2014) Alterations in the ubiquitin proteasome system in persistent but not reversible proteinuric diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2511–2525
Berkovic SF, Dibbens LM, Oshlack A, Silver JD, Katerelos M, Vears DF, Lullmann-Rauch R, Blanz J, Zhang KW, Stankovich J et al (2008) Array-based gene discovery with three unrelated subjects shows SCARB2/LIMP-2 deficiency causes myoclonus epilepsy and glomerulosclerosis. Am J Hum Genet 82:673–684
Bifsha P, Landry K, Ashmarina L, Durand S, Seyrantepe V, Trudel S, Quiniou C, Chemtob S, Xu Y, Gravel RA et al (2007) Altered gene expression in cells from patients with lysosomal storage disorders suggests impairment of the ubiquitin pathway. Cell Death Differ 14:511–523
Blott EJ, Griffiths GM (2002) Secretory lysosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:122–131
Boer DEC, van Smeden J, Bouwstra JA, Aerts J et al (2020) Glucocerebrosidase: Functions in and beyond the lysosome. J Clin Med 9.
Briere J, Calman F, Lageron A, Hinglais N, Emerit J and Bernard J (1976) [Adult Niemann-Pick disease: a 26 years follow-up. Report of a case with isolated visceral involvement, excess of tissue sphingomyelin, and deficient sphingomyelinase activity (author's transl)]. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol Blood Cells 16:185-202
Brinkkoetter PT, Bork T, Salou S, Liang W, Mizi A, Ozel C, Koehler S, Hagmann HH, Ising C, Kuczkowski A et al (2019) Anaerobic glycolysis maintains the glomerular filtration barrier independent of mitochondrial metabolism and dynamics. Cell Rep 27(1551–1566):e1555
Brocker C, Engelbrecht-Vandre S, Ungermann C et al (2010) Multisubunit tethering complexes and their role in membrane fusion. Curr Biol 20:R943-952
Buratta S, Tancini B, Sagini K, Delo F, Chiaradia E, Urbanelli L, Emiliani C (2020) Lysosomal exocytosis, exosome release and secretory autophagy: The autophagic- and endo-lysosomal systems go extracellular. Int J Mol Sci 21.
Caimi L, Tettamanti G, Berra B, Omodeo Sale F, Borrone C, Gatti R, Durand P, Martin JJ (1982) Mucolipidosis IV, a sialolipidosis due to ganglioside sialidase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 5:218–224
Calcraft PJ, Ruas M, Pan Z, Cheng X, Arredouani A, Hao X, Tang J, Rietdorf K, Teboul L, Chuang KT et al (2009) NAADP mobilizes calcium from acidic organelles through two-pore channels. Nature 459:596–600
Caler EV, Chakrabarti S, Fowler KT, Rao S, Andrews NW et al (2001) The Exocytosis-regulatory protein synaptotagmin VII mediates cell invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med 193:1097–1104
Carlsson SR, Roth J, Piller F, Fukuda M et al (1988) Isolation and characterization of human lysosomal membrane glycoproteins, h-lamp-1 and h-lamp-2. Major sialoglycoproteins carrying polylactosaminoglycan. J Biol Chem 263:18911–18919
Chander PN, Nurse HM, Pirani CL et al (1979) Renal involvement in adult Gaucher’s disease after splenectomy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 103:440–445
Chang TY, Chang CC, Ohgami N, Yamauchi Y et al (2006) Cholesterol sensing, trafficking, and esterification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:129–157
Chauhan S, Kumar S, Jain A, Ponpuak M, Mudd MH, Kimura T, Choi SW, Peters R, Mandell M, Bruun JA et al (2016) TRIMs and Galectins globally cooperate and TRIM16 and galectin-3 co-direct autophagy in endomembrane damage homeostasis. Dev Cell 39:13–27
Chen J, Chen MX, Fogo AB, Harris RC, Chen JK et al (2013) mVps34 deletion in podocytes causes glomerulosclerosis by disrupting intracellular vesicle trafficking. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:198–207
Chen W, Yang S, Shi H, Guan W, Dong Y, Wang Y, Wang L (2011) Histological studies of renal biopsy in a boy with nephrosialidosis. Ultrastruct Pathol 35:168–171
Chen Y, Yu L (2017) Recent progress in autophagic lysosome reformation. Traffic 18:358–361
Choi SR, Lim JH, Kim MY, Kim EN, Kim Y, Choi BS, Kim YS, Kim HW, Lim KM, Kim MJ et al (2018) Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon decreased ceramide, and lipotoxicity, and ameliorated diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism 85:348–360
Christensen EI, Zhou Q, Sorensen SS, Rasmussen AK, Jacobsen C, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Nielsen R et al (2007) Distribution of alpha-galactosidase A in normal human kidney and renal accumulation and distribution of recombinant alpha-galactosidase A in Fabry mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:698–706
Clarke, L.A. (1993). Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. In GeneReviews((R)), M.P. Adam, H.H. Ardinger, R.A. Pagon, S.E. Wallace, L.J.H. Bean, K. Stephens, and A. Amemiya, eds. (Seattle (WA)).
Cox TM, Cachon-Gonzalez MB (2012) The cellular pathology of lysosomal diseases. J Pathol 226:241–254
Cui J, Bai X, Chen X et al (2020) Autophagy and glomerular diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 1207:481–486
Cybulsky AV (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress, the unfolded protein response and autophagy in kidney diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol 13:681–696
Czibener C, Sherer NM, Becker SM, Pypaert M, Hui E, Chapman ER, Mothes W, Andrews NW et al (2006) Ca2+ and synaptotagmin VII-dependent delivery of lysosomal membrane to nascent phagosomes. J Cell Biol 174:997–1007
de Castro MA, Bunt G, Wouters FS et al (2016) Cathepsin B launches an apoptotic exit effort upon cell death-associated disruption of lysosomes. Cell Death Discov 2:16012
de Duve C (2005) The lysosome turns fifty. Nat Cell Biol 7:847–849
De Duve C, Pressman BC, Gianetto R, Wattiaux R, Appelmans F et al (1955) Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J 60:604–617
Devi ARR, Gopikrishna M, Ratheesh R, Savithri G, Swarnalata G, Bashyam M (2006) Farber lipogranulomatosis: clinical and molecular genetic analysis reveals a novel mutation in an Indian family. J Hum Genet 51:811–814
Dell’Angelica EC, Mullins C, Caplan S, Bonifacino JS et al (2000) Lysosome-related organelles. FASEB J 14:1265–1278
Desmond MJ, Lee D, Fraser SA, Katerelos M, Gleich K, Martinello P, Li YQ, Thomas MC, Michelucci R, Cole AJ et al (2011) Tubular proteinuria in mice and humans lacking the intrinsic lysosomal protein SCARB2/Limp-2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300:F1437-1447
Dimke H, Maezawa Y, Quaggin SE et al (2015) Crosstalk in glomerular injury and repair. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 24:231–238
Duvel K, Yecies JL, Menon S, Raman P, Lipovsky AI, Souza AL, Triantafellow E, Ma Q, Gorski R, Cleaver S et al (2010) Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell 39:171–183
Exner M, Susani M, Witztum JL, Hovorka A, Curtiss LK, Spitzauer S, Kerjaschki D et al (1996) Lipoproteins accumulate in immune deposits and are modified by lipid peroxidation in passive Heymann nephritis. Am J Pathol 149:1313–1320
Fader CM, Sanchez D, Furlan M, Colombo MI et al (2008) Induction of autophagy promotes fusion of multivesicular bodies with autophagic vacuoles in k562 cells. Traffic 9:230–250
Fogo AB (2015) Causes and pathogenesis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Rev Nephrol 11:76–87
Gamp AC, Tanaka Y, Lullmann-Rauch R, Wittke D, D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP, Moser T, Maier H, Hartmann D, Reiss K et al (2003) LIMP-2/LGP85 deficiency causes ureteric pelvic junction obstruction, deafness and peripheral neuropathy in mice. Hum Mol Genet 12:631–646
Garsen M, Rops AL, Dijkman H, Willemsen B, van Kuppevelt TH, Russel FG, Rabelink TJ, Berden JH, Reinheckel T, van der Vlag J et al (2016) Cathepsin L is crucial for the development of early experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 90:1012–1022
Genovese G, Friedman DJ, Pollak MR et al (2013) APOL1 variants and kidney disease in people of recent African ancestry. Nat Rev Nephrol 9:240–244
Ghosh P, Dahms NM, Kornfeld S et al (2003) Mannose 6-phosphate receptors: New twists in the tale. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:202–212
Giardino L, Armelloni S, Corbelli A, Mattinzoli D, Zennaro C, Guerrot D, Tourrel F, Ikehata M, Li M, Berra S et al (2009) Podocyte glutamatergic signaling contributes to the function of the glomerular filtration barrier. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1929–1940
Gold H, Mirzaian M, Dekker N, Joao Ferraz M, Lugtenburg J, Codee JD, van der Marel GA, Overkleeft HS, Linthorst GE, Groener JE et al (2013) Quantification of globotriaosylsphingosine in plasma and urine of fabry patients by stable isotope ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 59:547–556
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2015) A century of cholesterol and coronaries: From plaques to genes to statins. Cell 161:161–172
Gomez-Guerrero C, Suzuki Y, Egido J et al (2002) The identification of IgA receptors in human mesangial cells: In the search for “Eldorado.” Kidney Int 62:715–717
Graves AR, Curran PK, Smith CL, Mindell JA et al (2008) The Cl-/H+ antiporter ClC-7 is the primary chloride permeation pathway in lysosomes. Nature 453:788–792
Griffiths G, Hoflack B, Simons K, Mellman I, Kornfeld S et al (1988) The mannose 6-phosphate receptor and the biogenesis of lysosomes. Cell 52:329–341
Hao R, Nanduri P, Rao Y, Panichelli RS, Ito A, Yoshida M, Yao TP et al (2013) Proteasomes activate aggresome disassembly and clearance by producing unanchored ubiquitin chains. Mol Cell 51:819–828
Hartleben B, Godel M, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Liu S, Ulrich T, Kobler S, Wiech T, Grahammer F, Arnold SJ, Lindenmeyer MT et al (2010) Autophagy influences glomerular disease susceptibility and maintains podocyte homeostasis in aging mice. J Clin Invest 120:1084–1096
Hartleben B, Wanner N, Huber TB et al (2014) Autophagy in glomerular health and disease. Semin Nephrol 34:42–52
Hendrickx G, Danyukova T, Baranowsky A, Rolvien T, Angermann A, Schweizer M, Keller J, Schroder J, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Muschol N et al (2020) Enzyme replacement therapy in mice lacking arylsulfatase B targets bone-remodeling cells, but not chondrocytes. Hum Mol Genet 29:803–816
Herb M, Gluschko A, Schramm M et al (2020) LC3-associated phagocytosis - the highway to hell for phagocytosed microbes. Semin Cell Dev Biol 101:68–76
Herman PK, Emr SD (1990) Characterization of VPS34, a gene required for vacuolar protein sorting and vacuole segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 10:6742–6754
Herwig J, Skuza S, Sachs W, Sachs M, Failla AV, Rune G, Meyer TN, Fester L, Meyer-Schwesinger C et al (2019) Thrombospondin type 1 domain-containing 7A localizes to the slit diaphragm and stabilizes membrane dynamics of fully differentiated podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol 30:824–839
Heybrock S, Kanerva K, Meng Y, Ing C, Liang A, Xiong ZJ, Weng X, Ah Kim Y, Collins R, Trimble W et al (2019) Lysosomal integral membrane protein-2 (LIMP-2/SCARB2) is involved in lysosomal cholesterol export. Nat Commun 10:3521
Hjerpe R, Bett JS, Keuss MJ, Solovyova A, McWilliams TG, Johnson C, Sahu I, Varghese J, Wood N, Wightman M et al (2016) UBQLN2 mediates autophagy-independent protein aggregate clearance by the proteasome. Cell 166:935–949
Hong J, Bhat OM, Li G, Dempsey SK, Zhang Q, Ritter JK, Li W, Li PL et al (2019) Lysosomal regulation of extracellular vesicle excretion during d-ribose-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in podocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1866:849–860
Hong W, Lev S (2014) Tethering the assembly of SNARE complexes. Trends Cell Biol 24:35–43
Huotari J, Helenius A (2011) Endosome maturation. EMBO J 30:3481–3500
Infante RE, Wang ML, Radhakrishnan A, Kwon HJ, Brown MS, Goldstein JL et al (2008) NPC2 facilitates bidirectional transfer of cholesterol between NPC1 and lipid bilayers, a step in cholesterol egress from lysosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:15287–15292
Itakura E, Kishi C, Inoue K, Mizushima N et al (2008) Beclin 1 forms two distinct phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes with mammalian Atg14 and UVRAG. Mol Biol Cell 19:5360–5372
Jaiswal JK, Andrews NW, Simon SM et al (2002) Membrane proximal lysosomes are the major vesicles responsible for calcium-dependent exocytosis in nonsecretory cells. J Cell Biol 159:625–635
Jegga AG, Schneider L, Ouyang X, Zhang J et al (2011) Systems biology of the autophagy-lysosomal pathway. Autophagy 7:477–489
Kain R, Exner M, Brandes R, Ziebermayr R, Cunningham D, Alderson CA, Davidovits A, Raab I, Jahn R, Ashour O et al (2008) Molecular mimicry in pauci-immune focal necrotizing glomerulonephritis. Nat Med 14:1088–1096
Kain R, Matsui K, Exner M, Binder S, Schaffner G, Sommer EM, Kerjaschki D et al (1995) A novel class of autoantigens of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis: The lysosomal membrane glycoprotein h-lamp-2 in neutrophil granulocytes and a related membrane protein in glomerular endothelial cells. J Exp Med 181:585–597
Kantola IM (2019) Renal involvement in Fabry disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34:1435–1437
Kerjaschki D, Farquhar MG (1983) Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med 157:667–686
Kerr DA, Memoli VA, Cathey SS, Harris BT et al (2011) Mucolipidosis type III alpha/beta: The first characterization of this rare disease by autopsy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135:503–510
Kettritz R (2012) How anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies activate neutrophils. Clin Exp Immunol 169:220–228
Klionsky DJ, Emr SD (2000) Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science 290:1717–1721
Kobayashi H, Takahashi-Fujigasaki J, Fukuda T, Sakurai K, Shimada Y, Nomura K, Ariga M, Ohashi T, Eto Y, Otomo T et al (2011) Pathology of the first autopsy case diagnosed as mucolipidosis type III alpha/beta suggesting autophagic dysfunction. Mol Genet Metab 102:170–175
Kollmann K, Pohl S, Marschner K, Encarnacao M, Sakwa I, Tiede S, Poorthuis BJ, Lubke T, Muller-Loennies S, Storch S et al (2010) Mannose phosphorylation in health and disease. Eur J Cell Biol 89:117–123
Kolter T, Sandhoff K (2005) Principles of lysosomal membrane digestion: Stimulation of sphingolipid degradation by sphingolipid activator proteins and anionic lysosomal lipids. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:81–103
Kuemmel TA, Thiele J, Schroeder R, Stoffel W (1997) Pathology of visceral organs and bone marrow in an acid sphingomyelinase deficient knock-out mouse line, mimicking human Niemann-Pick disease type A. A light and electron microscopic study. Pathol Res Pract 193:663–671
Kurz T, Eaton JW, Brunk UT et al (2011) The role of lysosomes in iron metabolism and recycling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1686–1697
Kurz T, Terman A, Gustafsson B, Brunk UT et al (2008) Lysosomes in iron metabolism, ageing and apoptosis. Histochem Cell Biol 129:389–406
Lamason RL, Mohideen MA, Mest JR, Wong AC, Norton HL, Aros MC, Jurynec MJ, Mao X, Humphreville VR, Humbert JE et al (2005) SLC24A5, a putative cation exchanger, affects pigmentation in zebrafish and humans. Science 310:1782–1786
Lan X, Jhaveri A, Cheng K, Wen H, Saleem MA, Mathieson PW, Mikulak J, Aviram S, Malhotra A, Skorecki K et al (2014) APOL1 risk variants enhance podocyte necrosis through compromising lysosomal membrane permeability. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 307:F326-336
Langman CB (2019) Oh cystinosin: Let me count the ways! Kidney Int 96:275–277
Lawrence RE, Zoncu R (2019) The lysosome as a cellular centre for signalling, metabolism and quality control. Nat Cell Biol 21:133–142
Lee DH, Gan PY, Katerelos M, Fraser SA, Gleich K, Holdsworth SR, Power DA et al (2014) Absence of the lysosomal protein Limp-2 attenuates renal injury in crescentic glomerulonephritis. Immunol Cell Biol 92:400–408
Lee J, Ye Y (2018) The roles of endo-lysosomes in unconventional protein secretion. Cells 7.
Lemyre E, Russo P, Melancon SB, Gagne R, Potier M, Lambert M (1999) Clinical spectrum of infantile free sialic acid storage disease. Am J Med Genet 82:385–391
Lenoir O, Tharaux PL, Huber TB et al (2016) Autophagy in kidney disease and aging: Lessons from rodent models. Kidney Int 90:950–964
Li G, Kidd J, Kaspar C, Dempsey S, Bhat OM, Camus S, Ritter JK, Gehr TWB, Gulbins E, Li PL et al (2020) Podocytopathy and nephrotic syndrome in mice with podocyte-specific deletion of the Asah1 gene: Role of ceramide accumulation in glomeruli. Am J Pathol 190:1211–1223
Li G, Kidd J, Li PL (2020b) Podocyte lysosome dysfunction in chronic glomerular diseases. Int J Mol Sci 21.
Li J, Pfeffer SR (2016) Lysosomal membrane glycoproteins bind cholesterol and contribute to lysosomal cholesterol export. Elife 5.
Li L, Friedrichsen HJ, Andrews S, Picaud S, Volpon L, Ngeow K, Berridge G, Fischer R, Borden KLB, Filippakopoulos P et al (2018) A TFEB nuclear export signal integrates amino acid supply and glucose availability. Nat Commun 9:2685
Li P, Gu M, Xu H et al (2019) Lysosomal ion channels as decoders of cellular signals. Trends Biochem Sci 44:110–124
Li Y, Xu M, Ding X, Yan C, Song Z, Chen L, Huang X, Wang X, Jian Y, Tang G et al (2016) Protein kinase C controls lysosome biogenesis independently of mTORC1. Nat Cell Biol 18:1065–1077
Liu WJ, Gan Y, Huang WF, Wu HL, Zhang XQ, Zheng HJ, Liu HF et al (2019) Lysosome restoration to activate podocyte autophagy: A new therapeutic strategy for diabetic kidney disease. Cell Death Dis 10:806
Liu WJ, Li ZH, Chen XC, Zhao XL, Zhong Z, Yang C, Wu HL, An N, Li WY, Liu HF et al (2017) Blockage of the lysosome-dependent autophagic pathway contributes to complement membrane attack complex-induced podocyte injury in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Sci Rep 7:8643
Lloyd-Evans E, Waller-Evans H, Peterneva K, Platt FM et al (2010) Endolysosomal calcium regulation and disease. Biochem Soc Trans 38:1458–1464
Lohmann F, Sachs M, Meyer TN, Sievert H, Lindenmeyer MT, Wiech T, Cohen CD, Balabanov S, Stahl RA, Meyer-Schwesinger C et al (2014) UCH-L1 induces podocyte hypertrophy in membranous nephropathy by protein accumulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:945–958
Lopez JJ, Jardin I, Bobe R, Pariente JA, Enouf J, Salido GM, Rosado JA et al (2008) STIM1 regulates acidic Ca2+ store refilling by interaction with SERCA3 in human platelets. Biochem Pharmacol 75:2157–2164
Lovett DH, Ryan JL, Kashgarian M, Sterzel RB et al (1982) Lysosomal enzymes in glomerular cells of the rat. Am J Pathol 107:161–166
Lubke T, Lobel P, Sleat DE et al (2009) Proteomics of the lysosome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:625–635
Ma T, Zhu J, Chen X, Zha D, Singhal PC, Ding G et al (2013) High glucose induces autophagy in podocytes. Exp Cell Res 319:779–789
Maejima I, Takahashi A, Omori H, Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Saitoh T, Yamamoto A, Hamasaki M, Noda T, Isaka Y et al (2013) Autophagy sequesters damaged lysosomes to control lysosomal biogenesis and kidney injury. EMBO J 32:2336–2347
Maroofian R, Schuele I, Najafi M, Bakey Z, Rad A, Antony D, Habibi H, Schmidts M (2018) Parental Whole-Exome Sequencing Enables Sialidosis Type II Diagnosis due to an NEU1 Missense Mutation as an Underlying Cause of Nephrotic Syndrome in the Child. Kidney Int Rep 3:1454–1463
Marques ARA, Saftig P (2019) Lysosomal storage disorders - challenges, concepts and avenues for therapy: Beyond rare diseases. J Cell Sci 132.
Martina JA, Puertollano R (2018) Protein phosphatase 2A stimulates activation of TFEB and TFE3 transcription factors in response to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 293:12525–12534
Mattocks M, Bagovich M, De Rosa M, Bond S, Binnington B, Rasaiah VI, Medin J, Lingwood C et al (2006) Treatment of neutral glycosphingolipid lysosomal storage diseases via inhibition of the ABC drug transporter, MDR1. Cyclosporin A can lower serum and liver globotriaosyl ceramide levels in the Fabry mouse model. FEBS J 273:2064–2075
McNeil PL, Kirchhausen T (2005) An emergency response team for membrane repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:499–505
Medina DL, Di Paola S, Peluso I, Armani A, De Stefani D, Venditti R, Montefusco S, Scotto-Rosato A, Prezioso C, Forrester A et al (2015) Lysosomal calcium signalling regulates autophagy through calcineurin and TFEB. Nat Cell Biol 17:288–299
Merscher S, Fornoni A (2014) Podocyte pathology and nephropathy - sphingolipids in glomerular diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 5:127
Meyer-Schwesinger C (2019) The ubiquitin proteasome system in kidney physiology and disease Nat Rev Nephrol.
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Huber TB (2020) Glomerular cell biology and podocytopathies. In Brenner + Rector's The Kidney, pp. 115–132.
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Meyer TN, Munster S, Klug P, Saleem M, Helmchen U, Stahl RA et al (2009) A new role for the neuronal ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1) in podocyte process formation and podocyte injury in human glomerulopathies. J Pathol 217:452–464
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Meyer TN, Sievert H, Hoxha E, Sachs M, Klupp EM, Munster S, Balabanov S, Carrier L, Helmchen U et al (2011) Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-l1 activity induces polyubiquitin accumulation in podocytes and increases proteinuria in rat membranous nephropathy. Am J Pathol 178:2044–2057
Meyer-Schwesinger C, Tomas NM, Dehde S, Seifert L, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Wiech T, Koch-Nolte F, Huber TB, Zahner G et al (2020) A novel mouse model of phospholipase A2 receptor 1-associated membranous nephropathy mimics podocyte injury in patients. Kidney Int 97:913–919
Miller F, Palade GE (1964) Lytic activities in renal protein absorption droplets. An electron microscopical cytochemical study. J Cell Biol 23:519–552
Mindell JA (2012) Lysosomal acidification mechanisms. Annu Rev Physiol 74:69–86
Miyaji T, Echigo N, Hiasa M, Senoh S, Omote H, Moriyama Y (2008) Identification of a vesicular aspartate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11720–11724
Moore D, Connock MJ, Wraith E, Lavery C (2008) The prevalence of and survival in Mucopolysaccharidosis I: Hurler, Hurler-Scheie and Scheie syndromes in the UK. Orphanet J Rare Dis 3:24
Morgan AJ, Platt FM, Lloyd-Evans E, Galione A et al (2011) Molecular mechanisms of endolysosomal Ca2+ signalling in health and disease. Biochem J 439:349–374
Morita Y, Kurano M, Sakai E, Nishikawa T, Nishikawa M, Sawabe M, Aoki J, Yatomi Y et al (2020) Analysis of urinary sphingolipids using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Investig 11:441–449
Maroteaux P, Humbel R, Strecker G, Michalski JC, Mande R (1978) A new type of sialidosis with kidney disease: nephrosialidosis. I. Clinical, radiological and nosological study. Arch Fr Pediatr 35:819–829
Najafian B, Tondel C, Svarstad E, Gubler MC, Oliveira JP, Mauer M et al (2020) Accumulation of globotriaosylceramide in podocytes in Fabry nephropathy is associated with progressive podocyte loss. J Am Soc Nephrol 31:865–875
Neale TJ, Ojha PP, Exner M, Poczewski H, Ruger B, Witztum JL, Davis P, Kerjaschki D et al (1994) Proteinuria in passive Heymann nephritis is associated with lipid peroxidation and formation of adducts on type IV collagen. J Clin Invest 94:1577–1584
Ohshima T, Murray GJ, Swaim WD, Longenecker G, Quirk JM, Cardarelli CO, Sugimoto Y, Pastan I, Gottesman MM, Brady RO et al (1997) alpha-Galactosidase A deficient mice: A model of Fabry disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:2540–2544
Palmieri M, Impey S, Kang H, di Ronza A, Pelz C, Sardiello M, Ballabio A et al (2011) Characterization of the CLEAR network reveals an integrated control of cellular clearance pathways. Hum Mol Genet 20:3852–3866
Papadopoulos C, Meyer H (2017) Detection and clearance of damaged lysosomes by the endo-lysosomal damage response and lysophagy. Curr Biol 27:R1330–R1341
Pavenstadt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M et al (2003) Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev 83:253–307
Perez-Morga D, Vanhollebeke B, Paturiaux-Hanocq F, Nolan DP, Lins L, Homble F, Vanhamme L, Tebabi P, Pays A, Poelvoorde P et al (2005) Apolipoprotein L-I promotes trypanosome lysis by forming pores in lysosomal membranes. Science 309:469–472
Peters SP, Lee RE, Glew RH et al (1977) Gaucher’s disease, a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 56:425–442
Prabakaran T, Nielsen R, Larsen JV, Sorensen SS, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Saleem MA, Petersen CM, Verroust PJ, Christensen EI et al (2011) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of alpha-galactosidase A in human podocytes in Fabry disease. PLoS ONE 6:e25065
Pryor PR, Luzio JP (2009) Delivery of endocytosed membrane proteins to the lysosome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:615–624
Raben N, Puertollano R (2016) TFEB and TFE3: Linking lysosomes to cellular adaptation to stress. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 32:255–278
Rastaldi MP, Armelloni S, Berra S, Li M, Pesaresi M, Poczewski H, Langer B, Kerjaschki D, Henger A, Blattner SM et al (2003) Glomerular podocytes possess the synaptic vesicle molecule Rab3A and its specific effector rabphilin-3a. Am J Pathol 163:889–899
Ravikumar B, Sarkar S, Davies JE, Futter M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Green-Thompson ZW, Jimenez-Sanchez M, Korolchuk VI, Lichtenberg M, Luo S et al (2010) Regulation of mammalian autophagy in physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 90:1383–1435
Reczek D, Schwake M, Schroder J, Hughes H, Blanz J, Jin X, Brondyk W, Van Patten S, Edmunds T, Saftig P et al (2007) LIMP-2 is a receptor for lysosomal mannose-6-phosphate-independent targeting of beta-glucocerebrosidase. Cell 131:770–783
Reddy A, Caler EV, Andrews NW et al (2001) Plasma membrane repair is mediated by Ca(2+)-regulated exocytosis of lysosomes. Cell 106:157–169
Rinschen MM, Schroeter CB, Koehler S, Ising C, Schermer B, Kann M, Benzing T, Brinkkoetter PT et al (2016) Quantitative deep mapping of the cultured podocyte proteome uncovers shifts in proteostatic mechanisms during differentiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 311:C404-417
Rood IM, Merchant ML, Wilkey DW, Zhang T, Zabrouskov V, van der Vlag J, Dijkman HB, Willemsen BK, Wetzels JF, Klein JB et al (2015) Increased expression of lysosome membrane protein 2 in glomeruli of patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Proteomics 15:3722–3730
Roth AJ, Brown MC, Smith RN, Badhwar AK, Parente O, Chung H, Bunch DO, McGregor JG, Hogan SL, Hu Y et al (2012) Anti-LAMP-2 antibodies are not prevalent in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:545–555
Roth KS, Chan JC, Ghatak NR, Mamunes P, Miller WW, O’Brien JS et al (1988) Acid alpha-neuraminidase deficiency: A nephropathic phenotype? Clin Genet 34:185–194
Sachs W, Sachs M, Kruger E, Zielinski S, Kretz O, Huber TB, Baranowsky A, Westermann LM, Voltolini Velho R, Ludwig NF et al (2020) Distinct modes of balancing glomerular cell proteostasis in mucolipidosis type II and III prevent proteinuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 31:1796–1814
Saftig P, Klumperman J (2009) Lysosome biogenesis and lysosomal membrane proteins: Trafficking meets function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:623–635
Saftig P, Puertollano R (2020) How Lysosomes Sense, Integrate, and Cope with Stress. Trends Biochem Sci.
Saftig P, Schroder B, Blanz J (2010) Lysosomal membrane proteins: Life between acid and neutral conditions. Biochem Soc Trans 38:1420–1423
Samie MA, Xu H (2014) Lysosomal exocytosis and lipid storage disorders. J Lipid Res 55:995–1009
Samuelsson K, Zetterstrom R (1971) Ceramides in a patient with lipogranulomatosis (Farber’s disease) with chronic course. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 27:393–405
Sandhoff K, Andreae U, Jatzkewitz H (1968) Deficient hexozaminidase activity in an exceptional case of Tay-Sachs disease with additional storage of kidney globoside in visceral organs. Life Sci 7:283–288
Sanchez-Nino MD, Carpio D, Sanz AB, Ruiz-Ortega M, Mezzano S, Ortiz A et al (2015) Lyso-Gb3 activates Notch1 in human podocytes. Hum Mol Genet 24:5720–5732
Sardiello M, Palmieri M, di Ronza A, Medina DL, Valenza M, Gennarino VA, Di Malta C, Donaudy F, Embrione V, Polishchuk RS et al (2009) A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science 325:473–477
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM (2017) mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 169:361–371
Schlondorff D (1987) The glomerular mesangial cell: An expanding role for a specialized pericyte. FASEB J 1:272–281
Schoneberg J, Lee IH, Iwasa JH, Hurley JH et al (2017) Reverse-topology membrane scission by the ESCRT proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:5–17
Schroeter CB, Koehler S, Kann M, Schermer B, Benzing T, Brinkkoetter PT, Rinschen MM et al (2018) Protein half-life determines expression of proteostatic networks in podocyte differentiation. FASEB J 32:4696–4713
Schwake M, Schroder B, Saftig P et al (2013) Lysosomal membrane proteins and their central role in physiology. Traffic 14:739–748
Settembre C, Di Malta C, Polito VA, Garcia Arencibia M, Vetrini F, Erdin S, Erdin SU, Huynh T, Medina D, Colella P et al (2011) TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis. Science 332:1429–1433
Sever S, Altintas MM, Nankoe SR, Moller CC, Ko D, Wei C, Henderson J, del Re EC, Hsing L, Erickson A et al (2007) Proteolytic processing of dynamin by cytoplasmic cathepsin L is a mechanism for proteinuric kidney disease. J Clin Invest 117:2095–2104
Singh AK (1992) Proteolytic machinery of glomerular epithelial cells against IgG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186:639–644
Skotland T, Sandvig K, Llorente A et al (2017) Lipids in exosomes: Current knowledge and the way forward. Prog Lipid Res 66:30–41
Skowyra ML, Schlesinger PH, Naismith TV, Hanson PI et al (2018) Triggered recruitment of ESCRT machinery promotes endolysosomal repair. Science 360
Sperl W, Gruber W, Quatacker J, Monnens L, Thoenes W, Fink FM, Paschke E et al (1990) Nephrosis in two siblings with infantile sialic acid storage disease. Eur J Pediatr 149:477–482
Stuart LM, Ezekowitz RA (2005) Phagocytosis: Elegant complexity. Immunity 22:539–550
Tang X, Hinohara T, Kato S, Watanabe K, Tsutsumi Y et al (1995) I-cell disease: Report of an autopsy case. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 20:109–120
Tatematsu M, Imaida K, Ito N, Togari H, Suzuki Y, Ogiu T (1981) Sandhoff disease. Acta Pathol Jpn 31:503–512
Taugner R, Whalley A, Angermuller S, Buhrle CP, Hackenthal E et al (1985) Are the renin-containing granules of juxtaglomerular epithelioid cells modified lysosomes? Cell Tissue Res 239:575–587
Taylor J, Thorner P, Geary DF, Baumal R, Balfe JW et al (1986) Nephrotic syndrome and hypertension in two children with Hurler syndrome. J Pediatr 108:726–729
Thelen AM, Zoncu R (2017) Emerging roles for the lysosome in lipid metabolism. Trends Cell Biol 27:833–850
Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F, Atkin-Smith GK et al (2018) Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles 7:1535750
Thurberg BL, Rennke H, Colvin RB, Dikman S, Gordon RE, Collins AB, Desnick RJ, O’Callaghan M et al (2002) Globotriaosylceramide accumulation in the Fabry kidney is cleared from multiple cell types after enzyme replacement therapy. Kidney Int 62:1933–1946
Thurston TL, Wandel MP, von Muhlinen N, Foeglein A, Randow F et al (2012) Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion. Nature 482:414–418
Tomas NM, Beck LH Jr, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Seitz-Polski B, Ma H, Zahner G, Dolla G, Hoxha E, Helmchen U, Dabert-Gay AS et al (2014) Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med 371:2277–2287
Tomas NM, Hoxha E, Reinicke AT, Fester L, Helmchen U, Gerth J, Bachmann F, Budde K, Koch-Nolte F, Zahner G et al (2016) Autoantibodies against thrombospondin type 1 domain-containing 7A induce membranous nephropathy. J Clin Invest 126:2519–2532
Tylki-Szymanska A, Lugowska A, Czartoryska B (1996) Neuraminidase deficiency presenting as a nephrosialidosis: the first case detected in Poland. Acta Paediatr Jpn 38:529–532
Tuysuz B, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Canpolat N, Koparir A, Yilmaz S, Kilicaslan I, Gulez B, Bilguvar K, Gunel M et al (2016) Renal involvement in patients with mucolipidosis IIIalpha/beta: Causal relation or co-occurrence? Am J Med Genet A 170A:1187–1195
Tylki-Szymanska A, Lugowska A, Czartoryska B (1996) Neuraminidase deficiency presenting as a nephrosialidosis: the first case detected in Poland. Acta Paediatr Jpn 38:529–532
Vaes G (1968) On the mechanisms of bone resorption. The action of parathyroid hormone on the excretion and synthesis of lysosomal enzymes and on the extracellular release of acid by bone cells. J Cell Biol 39:676–697
Valbuena C, Oliveira JP, Carneiro F, Relvas S, Ganhao M, Sa-Miranda MC, Rodrigues LG et al (2011) Kidney histologic alterations in alpha-galactosidase-deficient mice. Virchows Arch 458:477–486
Velho RV, De Pace R, Klunder S, Di Lorenzo G, Schweizer M, Braulke T, Pohl S et al (2017) Site-1 protease and lysosomal homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1864:2162–2168
Wang F, Gomez-Sintes R, Boya P et al (2018) Lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cell death. Traffic 19:918–931
Wu CC, Chen JS, Huang CF, Chen CC, Lu KC, Chu P, Sytwu HK, Lin YF et al (2011) Approaching biomarkers of membranous nephropathy from a murine model to human disease. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:581928
Xiong J, Zhu MX (2016) Regulation of lysosomal ion homeostasis by channels and transporters. Sci China Life Sci 59:777–791
Yaddanapudi S, Altintas MM, Kistler AD, Fernandez I, Moller CC, Wei C, Peev V, Flesche JB, Forst AL, Li J et al (2011) CD2AP in mouse and human podocytes controls a proteolytic program that regulates cytoskeletal structure and cellular survival. J Clin Invest 121:3965–3980
Yokota S, Tsuji H, Kato K et al (1985) Immunocytochemical localization of cathepsin D in lysosomes of cortical collecting tubule cells of the rat kidney. J Histochem Cytochem 33:191–200
Yu FPS, Amintas S, Levade T, Medin JA et al (2018) Acid ceramidase deficiency: Farber disease and SMA-PME. Orphanet J Rare Dis 13:121
Yu L, McPhee CK, Zheng L, Mardones GA, Rong Y, Peng J, Mi N, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Wan F et al (2010) Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature 465:942–946
Zhang F, Jin S, Yi F, Li PL et al (2009) TRP-ML1 functions as a lysosomal NAADP-sensitive Ca2+ release channel in coronary arterial myocytes. J Cell Mol Med 13:3174–3185
Zhao Y, Ren J, Padilla-Parra S, Fry EE, Stuart DI et al (2014) Lysosome sorting of beta-glucocerebrosidase by LIMP-2 is targeted by the mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Nat Commun 5:4321
Zhou LL, Cao W, Xie C, Tian J, Zhou Z, Zhou Q, Zhu P, Li A, Liu Y, Miyata T et al (2012) The receptor of advanced glycation end products plays a central role in advanced oxidation protein products-induced podocyte apoptosis. Kidney Int 82:759–770
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft CRC1192, project B3 and ME2108/10-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer-Schwesinger, C. Lysosome function in glomerular health and disease. Cell Tissue Res 385, 371–392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03375-7