Abstract
The importance of the dry reforming of methane (DRM) lies in its capability to upgrade two greenhouse gases (CH4 and CO2) into synthesis gas (CO and H2), which is one of the main building block for synthesizing hydrocarbons. However, the Ni-based catalysts for DRM reaction usually have a major catalytic stability drawback. This works aims to assess the catalytic activity and stability of two Ni-based catalysts obtained from hydrotalcite (HT) precursors (i.e., NiAl-HT and NiMgAl-HT). The precursors, calcined (-c), reduced (-R) and spent samples were characterized by a series of techniques to gain insight into the influence of MgO over Ni-based catalyst in the drying reforming of methane. An in-situ ageing cycle process to speed up the deactivation of hydrotalcite-derived catalysts showed that the NiMgAl-HTc-R catalyst displayed a higher activity and resistance to coke formation (stability) than NiAl-HTc-R because of the introduction of Mg into hydrotalcite structure in the catalyst precursor. The presence of this element enhances several factors involved in the stability of Ni-based catalysts for the DRM process such as the reducibility and textural features of the catalysts, size and dispersion of Ni0 nanoparticles and also maintains a good compromise between the acid and base properties of the solid catalysts.
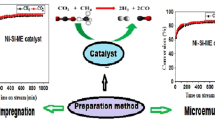
Graphic Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HT:
-
Material type hydrotalcite
- HTc:
-
After calcination
- HTc-R:
-
After reduction
References
Lavoie J-M (2014) Review on dry reforming of methane, a potentially more environmentally-friendly approach to the increasing natural gas exploitation. Front Chem 2:1–17
le Saché E, Santos JL, Smith TJ, Centeno MA, Arellano-Garcia H, Odriozola JA, Reina TR (2018) Multicomponent Ni-CeO2 nanocatalysts for syngas production from CO2/CH4 mixtures. J CO2 Util 25:68–78
Stroud T, Smith TJ, Le Saché E, Santos JL, Centeno MA, Arellano-Garcia H, Odriozola JA, Reina TR (2018) Chemical CO2 recycling via dry and bi reforming of methane using Ni-Sn/Al2O3 and Ni-Sn/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts. Appl Catal B 224:125–135
Pereñiguez R, Gonzalez-delaCruz VM, Caballero A, Holgado JP (2012) LaNiO3 as a precursor of Ni/La2O3 for CO2 reforming of CH4: effect of the presence of an amorphous NiO phase. Appl Catal B 123–124:324–332
Hu J, Yu F, Lu Y (2012) Application of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis in biomass to liquid conversion. Catalysts 2:303–326
Dębek R, Motak M, Grzybek T, Galvez M, Da Costa P (2017) A short review on the catalytic activity of hydrotalcite-derived materials for dry reforming of methane. Catalysts 7:32
Halliche D, Cherifi O, Auroux A (2002) Etude De L’acidité De Zéolithes Y Modifiées Par Différents Cations. Application à la réaction de reformage sec du méthane. J Therm Anal Calorim 68:997–1002
Gonzalez-Delacruz VM, Pereñiguez R, Ternero F, Holgado JP, Caballero A (2011) Modifying the size of nickel metallic particles by H2/CO treatment in Ni/ZrO2 methane dry reforming catalysts. ACS Catal 1:82–88
Schwengber CA, da Silva FA, Schaffner RA, Fernandes-Machado NRC, Ferracin RJ, Bach VR, Alves HJ (2016) Methane dry reforming using Ni/Al2O3 catalysts: evaluation of the effects of temperature, space velocity and reaction time. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3688–3695
Wang J, Fan G, Li F (2012) Carbon-supported Ni catalysts with enhanced metal dispersion and catalytic performance for hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene. RSC Adv 2:9976
Bradford MCJ, Vannice MA (1999) CO2 reforming of CH4. Catal Rev 41:1–42
San-José-Alonso D, Juan-Juan J, Illán-Gómez MJ, Román-Martínez MC (2009) Ni, Co and bimetallic Ni–Co catalysts for the dry reforming of methane. Appl Catal A 371:54–59
Zhang X, Zhang L, Peng H, You X, Peng C, Xu X, Liu W, Fang X, Wang Z, Zhang N, Wang X (2018) Nickel nanoparticles embedded in mesopores of AlSBA-15 with a perfect peasecod-like structure: a catalyst with superior sintering resistance and hydrothermal stability for methane dry reforming. Appl Catal B 224:488–499
Liu W, Li L, Zhang X, Wang Z, Wang X, Peng H (2018) Design of Ni-ZrO2@SiO2 catalyst with ultra-high sintering and coking resistance for dry reforming of methane to prepare syngas. J CO2 Util 27:297–307
Peng H, Zhang X, Han X, You X, Lin S, Chen H, Liu W, Wang X, Zhang N, Wang Z, Wu P, Zhu H, Dai S (2019) Catalysts in coronas: a surface spatial confinement strategy for high-performance catalysts in methane dry reforming. ACS Catal 9:9072–9080
Nazemi MK, Sheibani S, Rashchi F, Gonzalez-DelaCruz VM, Caballero A (2012) Preparation of nanostructured nickel aluminate spinel powder from spent NiO/Al2O3 catalyst by mechano-chemical synthesis. Adv Powder Technol 23:833–838
Cavani F, Trifirò F, Vaccari A (1991) Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: preparation, properties and applications. Catal Today 11:173–301
Roelofs JCAA, van Bokhoven JA, van Dillen AJ, Geus JW, de Jong KP (2002) The thermal decomposition of Mg–Al hydrotalcites: effects of interlayer anions and characteristics of the final structure. Chem Eur J 8:5571–5579
Dębek R, Motak M, Galvez ME, Da Costa P, Grzybek T (2017) Catalytic activity of hydrotalcite-derived catalysts in the dry reforming of methane: on the effect of Ce promotion and feed gas composition. React Kinet Mech Catal 121:185–208
Usman M, Wan Daud WMA, Abbas HF (2015) Dry reforming of methane: influence of process parameters—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 45:710–744
Dębek R, Zubek K, Motak M, Galvez ME, Da Costa P, Grzybek T (2015) Ni–Al hydrotalcite-like material as the catalyst precursors for the dry reforming of methane at low temperature. C R Chim 18:1205–1210
Abdelsadek Z, Sehailia M, Halliche D, Gonzalez-Delacruz VM, Holgado JP, Bachari K, Caballero A, Cherifi O (2016) In-situ hydrogasification/regeneration of NiAl-hydrotalcite derived catalyst in the reaction of CO 2 reforming of methane: a versatile approach to catalyst recycling. J CO2 Util 14:98–105
Nawfal M, Gennequin C, Labaki M, Nsouli B, Aboukaïs A, Abi-Aad E (2015) Hydrogen production by methane steam reforming over Ru supported on Ni–Mg–Al mixed oxides prepared via hydrotalcite route. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:1269–1277
Park JE, Koo KY, Jung UH, Lee JH, Roh H-S, Yoon WL (2015) Syngas production by combined steam and CO2 reforming of coke oven gas over highly sinter-stable La-promoted Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:13909–13917
Tsyganok AI, Tsunoda T, Hamakawa S, Suzuki K, Takehira K, Hayakawa T (2003) Dry reforming of methane over catalysts derived from nickel-containing Mg–Al layered double hydroxides. J Catal 213:191–203
González AR, Asencios YJO, Assaf EM, Assaf JM (2013) Dry reforming of methane on Ni–Mg–Al nano-spheroid oxide catalysts prepared by the sol–gel method from hydrotalcite-like precursors. Appl Surf Sci 280:876–887
Düdder H, Kähler K, Krause B, Mette K, Kühl S, Behrens M, Scherer V, Muhler M (2014) The role of carbonaceous deposits in the activity and stability of Ni-based catalysts applied in the dry reforming of methane. Catal Sci Technol 4:3317–3328
Abdelssadek Z, Bachari K, Saadi A, Cherifi O, Halliche D (2013) Study of the catalytic activity of calcined hydrotalcites for Friedel–Crafts reactions. Res Chem Intermed 41:1757–1764
Monshi A, Foroughi MR, Monshi MR (2012) Modified Scherrer equation to estimate more accurately nano-crystallite size using XRD. World J Nano Sci Eng 02:154–160
Muniz FTL, Miranda MAR, Morilla dos Santos C, Sasaki JM (2016) The Scherrer equation and the dynamical theory of X-ray diffraction. Acta Crystallogr Sect A Found Adv 72:385–390
Casenave S, Martinez H, Guimon C, Auroux A, Hulea V, Cordoneanu A, Dumitriu E (2001) Acid–base properties of Mg–Ni–Al mixed oxides using LDH as precursors. Thermochim Acta 379:85–93
Rivera JA, Fetter G, Jiménez Y, Xochipa MM, Bosch P (2007) Nickel distribution in (Ni, Mg)/Al-layered double hydroxides. Appl Catal A 316:207–211
Rodrigues ACC, Henriques CA, Monteiro JLF (2003) Influence of Ni content on physico-chemical characteristics of Ni, Mg, Al-hydrotalcite like compounds. Mater Res 6:563–568
Forano C, Hibino T, Leroux F, Taviot-Guého C (2006). Chapter 13.1: layered double hydroxides. In: Bergaya F, Theng BKG, Lagaly G (eds) Handbook of clay science, vol. 1. Elsevier, pp, 1021–1095
Martínez-Lozano G, Hesiquio-Garduño M, Zeifert B, Salmones J (2007) Structural and microstructural characterization of Co-hydrotalcite-like compounds by X-ray diffraction. J Alloys Compd 434–435:816–819
Reichle WT, Kang SY, Everhardt DS (1986) The nature of the thermal decomposition of a catalytically active anionic clay mineral. J Catal 101:352–359
Rey F, Fornés V, Rojo JM (1992) Thermal decomposition of hydrotalcites. An infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 88:2233–2238
Fornasari G, Gazzano M, Matteuzzi D, Trifirò F, Vaccari A (1995) Structure and reactivity of high-surface-area Ni/Mg/Al mixed oxides. Appl Clay Sci 10:69–82
Tichit D, Medina F, Coq B, Dutartre R (1997) Activation under oxidizing and reducing atmospheres of Ni-containing layered double hydroxides. Appl Catal A 159:241–258
Li Y, Lu G, Ma J (2014) Highly active and stable nano NiO–MgO catalyst encapsulated by silica with a core–shell structure for CO2 methanation. RSC Adv 4:17420–17428
Guil-Lopez R, Navarro RM, Ismail AA, Al-Sayari SA, Fierro JLG (2015) Influence of Ni environment on the reactivity of Ni–Mg–Al catalysts for the acetone steam reforming reaction. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:5289–5296
Pérez-Ramı́rez J, Mul G, Moulijn JA (2001) In situ Fourier transform infrared and laser Raman spectroscopic study of the thermal decomposition of Co–Al and Ni–Al hydrotalcites. Vib Spectrosc 27:75–88
Aramendía MA, Borau V, Jiménez C, Marinas JM, Ruiz JR, Urbano FJ (2002) Comparative study of Mg/M(III) (M=Al, Ga, In) layered double hydroxides obtained by coprecipitation and the sol–gel method. J Solid State Chem 168:156–161
Wu G, Wang X, Chen B, Li J, Zhao N, Wei W, Sun Y (2007) Fluorine-modified mesoporous Mg–Al mixed oxides: Mild and stable base catalysts for O-methylation of phenol with dimethyl carbonate. Appl Catal A 329:106–111
Crivello M, Pérez C, Fernández J, Eimer G, Herrero E, Casuscelli S, Rodríguez-Castellón E (2007) Synthesis and characterization of Cr/Cu/Mg mixed oxides obtained from hydrotalcite-type compounds and their application in the dehydrogenation of isoamylic alcohol. Appl Catal A 317:11–19
de Sousa HSA, da Silva AN, Castro AJR, Campos A, Filho JM, Oliveira AC (2012) Mesoporous catalysts for dry reforming of methane: Correlation between structure and deactivation behaviour of Ni-containing catalysts. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:12281–12291
Ferreira OP, Alves OL, Gouveia DX, Souza Filho AG, de Paiva JAC, Filho JM (2004) Thermal decomposition and structural reconstruction effect on Mg–Fe-based hydrotalcite compounds. J Solid State Chem 177:3058–3069
Perez-Lopez OW, Senger A, Marcilio NR, Lansarin MA (2006) Effect of composition and thermal pretreatment on properties of Ni–Mg–Al catalysts for CO2 reforming of methane. Appl Catal A 303:234–244
Guil-López R, La Parola V, Peña MA, Fierro JLG (2012) Evolution of the Ni-active centres into ex hydrotalcite oxide catalysts during the COx-free hydrogen production by methane decomposition. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:7042–7055
González-Cortés SL, Aray I, Rodulfo-Baechler SMA, Lugo CA, Del Castillo HL, Loaiza-Gil A, Imbert FE, Figueroa H, Pernía W, Rodríguez A, Delgado O, Casanova R, Mendialdua J, Rueda F (2007) On the structure and surface properties of NiO/MgO–La2O3 catalyst: influence of the support composition and preparation method. J Mater Sci 42:6532–6540
Tsyganok AI, Inaba M, Tsunoda T, Hamakawa S, Suzuki K, Hayakawa T (2003) Dry reforming of methane over supported noble metals: a novel approach to preparing catalysts. Catal Commun 4:493–498
Huang YJ, Schwarz JA, Diehl JR, Baltrus JP (1988) Effect of catalyst preparation on catalytic activity: V. Chemical structures on nickel/alumina catalysts. Appl Catal 36:163–175
Molina R, Poncelet G (1998) α-Alumina-supported nickel catalysts prepared from nickel acetylacetonate: a TPR study. J Catal 173:257–267
Bhattacharyya A, Chang VW, Schumacher DJ (1998) CO2 reforming of methane to syngas: I: evaluation of hydrotalcite clay-derived catalysts. Appl Clay Sci 13:317–328
Hou Z, Yashima T (2004) Meso-porous Ni/Mg/Al catalysts for methane reforming with CO2. Appl Catal A 261:205–209
Dębek R, Motak M, Duraczyska D, Launay F, Galvez ME, Grzybek T, Da Costa P (2016) Methane dry reforming over hydrotalcite-derived Ni–Mg–Al mixed oxides: the influence of Ni content on catalytic activity, selectivity and stability. Catal Sci Technol 6:6705–6715
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the General Directorate for Scientific Research and Technological Development (DGRSDT) of the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and the Spanish Ministry of Science for funding and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelsadek, Z., Holgado, J.P., Halliche, D. et al. Examination of the Deactivation Cycle of NiAl- and NiMgAl-Hydrotalcite Derived Catalysts in the Dry Reforming of Methane. Catal Lett 151, 2696–2715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03513-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03513-4