Abstract
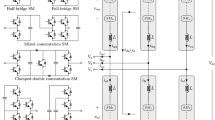
A digital pulse width modulation architecture (DPWM) along with digital proportional integral derivative (PID) controller to control the DC-DC converter is presented in this paper. Difference between the actual output voltage and the reference voltage is calculated as error value. The look up table is created for PID controller to store the duty cycle ratio and the error value of power converters. Multipliers used in conventional algorithms are replaced by look up tables in the proposed work that enable the compact and low power implementation of digital controllers. DPWM architecture is developed with gray logic against the binary logic used in traditional DPWM architectures. Usage of gray counter also leads to low power consumption in the DPWM architecture. The proposed architecture is designed using Verilog hardware language and realized using field programmable gate array. PWM signals with varying duty cycle percentage can be derived from the proposed architecture. The generated PWM signal can control the switching condition of power converter to regulate the output voltage. Duty cycle percentage ranging from 16 to 96% can be developed with the proposed architecture. Simulation and experimental results of the architecture validate the proposed architecture. PWM signal with maximum operating frequency of 59.49 MHz and 60.22 MHz for SPARTAN 3A and SPARTAN 3E respectively can be generated with the proposed architecture.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv, L., Chang, C., Zhou, Z., & Yuan, Y. (2015). An FPGA-based modified adaptive PID controller for DC/DC buck converters. Journal of Power Electronics, 15(2), 346–355.
Huang, W., & Qahouq, J. A. A. (2013). Tuning of a digital proportional-integral compensator for DC-DC power converter. In 2013 twenty-eighth annual IEEE applied power electronics conference and exposition (APEC) (pp. 270–275). IEEE.
Cheng, Y., Yang, C., Wen, G., & He, Y. (2017). Adaptive saturated finite-time control algorithm for buck type DC-DC converter systems. International Journal of Adaptive Control, 31(10), 1428–1436.
Abhilash, K., & Vinay, P. (2016). Advance control techniques for DC-DC buck converter in improvement of performance. International Journal on Emerging Technologies., 7(1), 101–106.
Qahouq, J. A. A., & Arikatla, V. (2012). Online closed-loop autotuning digital controller for switching power converters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(5), 1747–1758.
Cuoghi, S., Ntogramatzidis, L., Padula, F., & Grandi, G. (2019). Direct digital design of PIDF controllers with ComPlex zeros for DC-DC buck converters. Energies, 12(1), 36.
Joseph Anthony, P., Anandhi, T.-S., & Sivakumaran, T.-S. (2016). Implementation of FPGA based DPWM-Digital PI closed loop controller for voltage regulation. Indian Journal of Science and Technology., 9(38), 1–9.
Kartik, S. (2018). Design and assessment of digital PID and Fuzzy controller for DC-DC converter. International Journal of Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology., 6(3), 1289–1301.
Reshma, B. R., & Mathew, A. S. (2015). Gain scheduling implementation in DC/DC buck converter using PID controller. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), 4(07), 1063–1067.
Sujata, V., Singh, S.-K., & Rao, A.-G. (2013). Overview of control techniques for DC/DC converters. Research Journal of Engineering Sciences, 2, 18–21.
Subramanian, V., & Renga Raja, T. S. (2014). Time domain based Digital PWM controller for DC-DC converter. Automatika, 55(4), 434–445.
Arnab, G., & Subrata, B. (2017). Study of complex dynamics of DC-DC buck converter. International Journal of Power Electronics, 8(4), 323–348.
Dwivedi, A., & Tiwari, A. N. (2017). Analysis of three-phase PWM rectifiers using hysteresis current control techniques: a survey. International Journal of Power Electronics, 8(4), 349–377.
Varsha, K.-K., & Savitha, P.-R. (2019). FPGA Implementation of High-Speed Digital Pulse Width Modulator Technique for DC-DC Converter. Indian Journal of Science and Technology., 12(29), 1–6.
Badgujar, K. R., Salunkhe, P. A., & Patil, T. M. (2016). Generation of a high-resolution pulse width modulated wave using FPGA. International Journal of Computer Science and Network, 5(5), 741–745.
Fernández, D., Madrenas, J., & Alarcón, E. (2013). An asynchronous finite-state-machine-based buck-boost converter for on-chip adaptive power supply. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 74(1), 227–238.
Altinoz, O. T., & Erdem, H. (2015). Particle swarm optimisation-based PID controller tuning for static power converters. International Journal of Power Electronics, 7(1–2), 16–35.
Sedaghati, F., & Haghmaram, R. (2020). A modular DC-DC converter with zero voltage switching capability. International Journal of Power Electronics, 11(1), 56–73.
Sadek, U., Sarjaš, A., Svečko, R., & Chowdhury, A. (2015). FPGA-based control of a DC-DC boost converter. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 48(10), 22–27.
Khiavi, A. M., Sobhi, J., Koozehkanani, Z. D., & Kangarlu, M. F. (2017). FPGA-based reconfigurable PWM generator for power electronic converter applications. Journal of Control, Automation and Electrical Systems, 28(4), 516–531.
Oladimeji, I., Nor, Z. Y., & Nordin, S. (2016). State space modelling and digital controller design for DC-DC converter. Telecommunication, Computing, Electronics and Control., 14(2), 497–506.
Nitish, D., & Aruna, P. (2018). FPGA implemntation of reconfigurable finite state machine with input multiplexing architecture using Hungarian Method. International Journal of Reconfigurable Computing., 2018, 1–15.
Lakka, M., Koutroulis, E., & Dollas, A. (2014). Devlopment of FPGA based SPWM generator for high switching DC/AC invertres. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 29(1), 356–365.
Lupon, E., Busquets-Monge, S., & Nicolas-Apruzzese, J. (2014). FPGA implementation of a PWM for a three-phase DC–AC multilevel active-clamped converter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 10(2), 1296–1306.
Curkovic, M., Jezernik, K., & Horvat, R. (2013). FPGA-based predictive sliding mode controller of a three-phase inverter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(2), 637–644.
Sepulveda, C. A., Munoz, J. A., Espinoza, J. R., Figueroa, M. E., & Baier, C. R. (2013). FPGA v/s DSP performance comparison for a VSC-based STATCOM control application. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(3), 1351–1360.
Navarro, D., Lucia Gil, O., Barragan, L., Urriza, I., & Jimenez, O. (2013). High-level synthesis for accelerating the FPGA implementation of computationally-demanding control algorithms for power converters. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(3), 1371–1379.
Vyncke, T. J., Thielemans, S., & Melkebeek, J. A. (2013). Finite-set model-based predictive control for flying-capacitor converters: Cost function design and efficient FPGA implementation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 9(2), 1113–1121.
Kim, J. G., So, J., & Yoon, K. S. (2019). A CMOS PFM buck converter employing a digitally programmable voltage level-shifting technique. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 98, 321–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1369-0.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the Management, Director, Principal and Head of the Department of Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College for the extended support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radhika, V., Srinivasan, K., Sharmila, B.B. et al. Design of digital pulse width modulator architecture with digital PID controller for DC-DC converter using FPGA. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 107, 299–307 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01794-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01794-8