Abstract
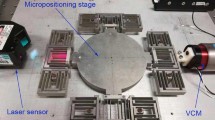
In this paper, a novel electromagnetic micropositioner is designed from an orthogonal 3-P(4S) parallel mechanism through the substitution method and modular design techniques. Preliminary prototype experiments show that the micropositioner possesses an excellent decoupling performance. Thus an independent control strategy is carried out for the motion control of the micropositioner. An RBF neural networks based adaptive backstepping terminal sliding mode controller is designed according to the nonlinearity characteristics of the actuator. Parameters of the system are identified with a genetic algorithm. Finally, the performances of the micropositioner and the developed control strategy are verified. Experimental results demonstrate that satisfactory performances can be achieved.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M, Wu QX, Cui RX (2013) Terminal sliding mode tracking control for a class of SISO uncertain nonlinear systems. ISA Trans 52(2):198–206
Clark L, Shirinzadeh B, Tian Y, Yao B (2016) Development of a passive compliant mechanism for measurement of micro/nanoscale planar 3-DOF motions. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 21(3):1222–1232
Dan W, Rui F (2016) Design and nonlinear analysis of a 6-DOF compliant parallel manipulator with spatial beam flexure hinges. Precision Eng 45:365–373
Ding BX, Yang ZX, Li YM (2020) Design of flexure-based modular architecture micro-positioning stage. Microsyst Technol 26(4):2893–2901
Du Z, Shi R, Dong W (2014) A piezo-actuated high-precision flexible parallel pointing mechanism: conceptual design, development, and experiments. IEEE Trans Rob 30(1):131–137
Hajhashemi MS, Barazandeh F, Nazari Nejad S, Nadafi DBR (2011) Design and microfabrication of a constant-force microgripper. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C 225(11):2739–2748
Joo T, Yang GL, Chen IM (2015) Compliant manipulators. Handbook of manufacturing engineering and technology. Springer-Verlag London Ltd, London, pp 2229–2300
Kenton BJ, Leang KK (2012) Design and control of a three-axis serial-kinematic high-bandwidth nanopositioner. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 17(2):356–369
Kozuka H, Arata J, Okuda K, Onaga A, Ohno M, Sano A, Fujimoto H (2012) A bio-inspired compliant parallel mechanism for high-precision robots. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Saint Paul, MN, USA, pp 3122–3127
Li CX, Gu GY, Yang MJ, Zhu LM (2013) Design, analysis and testing of a parallel-kinematic high-bandwidth XY nanopositioning stage. Rev Sci Instrum 84(12):125111.1–13
Li T, Shi C, Ren H (2018) A high-sensitivity tactile sensor array based on fiber bragg grating sensing for tissue palpation in minimally invasive surgery. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 23(5):2306–2315
Li CS, Gu X, Xiao X, Lim CM, Ren H (2019a) Flexible robot with variable stiffness in transoral surgery. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 25(1):1–10
Li JP, Huang H, Morita T (2019b) Stepping piezoelectric actuators with large working stroke for nano-positioning systems: A review. Sens Actuat A 292:39–51
Lin C, Zheng S, Li P, Shen Z, Wang S (2019) Positioning error analysis and control of a piezo-driven 6-DOF micro-positioner. Micromachines (Basel) 10(8):542.1–20
Ling MX, Cao JY, Li QS, Zhuang J (2018) Design, pseudostatic model, and PVDF-based motion sensing of a piezo-actuated XYZ flexure manipulator. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 23(6):2837–2848
Liu J, Gong Z, Tang K, Lu Z, Ru C, Luo J, Xie S, Sun Y (2014) Locating end-effector tips in robotic micromanipulation. IEEE Trans Rob 30(1):125–130
Man Z, Yu XH (1996) Terminal sliding mode control of MIMO linear systems. In: Proceedings of 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Kobe, Japan, pp 4619–4624
Mayyas M, Mamidala I (2020) Prosthetic finger based on fully compliant mechanism for multi-scale grasping. Microsyst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05045-8
Nguyen DN, Ho NL, Dao TP, Le Chau N (2019) Multi-objective optimization design for a sand crab-inspired compliant microgripper. Microsyst Technol 25(10):3991–4009
Pinskier J, Shirinzadeh B, Clark L, Qin YD (2018) Development of a 4-DOF haptic micromanipulator utilizing a hybrid parallel-serial flexure mechanism. Mechatronics 50:55–68
Wang F, Shi B, Tian Y, Huo Z, Zhao X, Zhang D (2019) Design of a novel dual-axis micromanipulator with an asymmetric compliant structure. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 24(2):656–665
Xiao X, Li YM (2016) Development of an electromagnetic actuated microdisplacement module. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 21(3):1252–1261
Xiao X, Li YM (2017) Development and visual servo control of an electromagnetic actuated micromanipulation system. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Macau, China, pp 326–331
Xiao X, Li YM, Xiao SL (2017) Development of a novel large stroke 2-DOF micromanipulator for micro/nano manipulation. Microsyst Technol 23(7):2993–3003
Yang M, Zhang C, Yang GL, Dong W (2019) Optimal design and tracking control of a superelastic flexure hinge based 3-PRR compliant parallel manipulator. IEEE Access 7:174236–174247
Zhu Z, To S, Zhu WL, Li YM, Huang P (2018) Optimum design of a piezo-actuated triaxial compliant mechanism for nanocutting. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 65(8):6362–6371
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Key R&D program of China with Grant No. 2019YFB1312400, National Natural Science Foundation of China (51575544), Hong Kong RGC TRS grant T42-409/18-R, Huxiang High Level Talent Project of Hunan Province (2019RS1066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Xi, R., Li, Y. et al. Design and control of a novel electromagnetic actuated 3-DoFs micropositioner. Microsyst Technol 27, 3763–3772 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05163-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-05163-3