Abstract
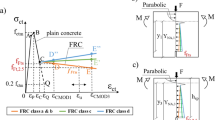
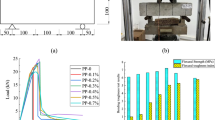
Quasi-brittleness is an important factor affecting the size effect of concrete, and the addition of steel fiber can effectively change this effect in concrete. The size effect on the fracture energy of steel fiber reinforced high-strength concrete was investigated in this paper. A total of 156 concrete single-edge notched beams (SENB) of various span-to-depth ratios, crack-to-depth ratios and steel fiber contents were tested to study the size effect of fracture energy of the high-strength concrete added steel fibers. The parameters of fracture in the boundary effect model (BEM) and size effect law (SEL) were deeply analyzed. The results show that the addition of steel fiber will generate significant influence on the parameter values obtained from both BEM and SEL. Based on the BEM, the relationship among Gf (experimental test fracture energy), gf (local fracture energy), and GF (fracture energy unaffected by specimen boundary) could be obtained. Thus, a method for analyzing the influence of steel fiber on GF was proposed using small-size SENB specimens at laboratory. In addition, based on the SEL, the impact of size effect on the fracture energy was effectively mitigated by the addition of steel fibers in high-strength concrete to a certain extent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Initial crack length for notched specimens
- A :
-
The angular coefficient of the regression line
- A lig :
-
The area of the crack ligament
- \(a_l^*\) :
-
Boundary influence length
- B :
-
Width of the single-edge notched beam
- c f :
-
The effective length of FPZ
- E C :
-
Elasticity modulus of concrete
- f c :
-
Compressive strength of concrete
- f t :
-
Tensile strength of concrete
- FPZ:
-
Fracture process zone with crack bridging stress
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- G f :
-
Experimental fracture energy
- g f :
-
Local fracture energy in the fracture process zone
- G F :
-
Fracture energy unaffected by specimen boundary
- G f :
-
Initial fracture energy
- K IC :
-
Fracture toughness of concrete
- L :
-
Length of the single-edge notched beam
- L ch :
-
Characteristic length
- m :
-
The relative width of the scatter band
- m 1 :
-
The mass of the notched specimen
- m 2 :
-
The mass of the loading device acting on the specimen
- P :
-
Ultimate load in the test recommended by RILEM
- P m :
-
Corrected ultimate load
- S :
-
Span of the specimen in the test
- SENB:
-
Single-edge notched beams
- SFC:
-
Steel fiber content
- W :
-
Depth of the single-edge notched beam
- W 0 :
-
The area enclosed by the load-deflection curve
- w A :
-
The variation coefficient of the slope
- w C :
-
The variation coefficient of the intercept
- α 0 :
-
Crack length-to-depth ratios =a/W
- δ 0 :
-
Maximum deflection of the specimen in the test
- σ N :
-
Nominal strength of the specimen in the test
References
Bažant ZP, Kazemi MT (1990) Determination of fracture energy, process zone length and brittleness number from size effect, with application to rock and concrete. International Journal of Fracture 44:111–131, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00047063
Beigi MH, Berenjian J, Omran OL, Nik AS, Nikbin IM (2013) An experimental survey on combined effects of fibers and nanosilica on the mechanical, rheological, and durability properties of self-compacting concrete. Materials & Design 50(50):1019–1029, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.046
Duan K, Hu XZ, Wittmann FH (2003) Boundary effect on concrete fracture and non-constant fracture energy distribution. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 70(16):2257–2268, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0013-7944(02)00223-0
Duan K, Hu XZ, Wittmann FH (2006) Scaling of quasi-brittle fracture: Boundary and size effect. Mechanics of Materials 38(1–2):128–141, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2005.05.016
Ghasemi M, Ghasemi MR, Mousavi SR (2019) Studying the fracture parameters and size effect of steel fiber-reinforced self-compacting concrete. Construction & Building Materials 201(20):447–460, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.172
Holschemacher K, Mueller T, Ribakov Y (2010) Effect of steel fibres on mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. Materials & Design 31(5): 2604–2615, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.11.025
Hoover CG, Bažant ZP (2013) Comprehensive concrete fracture tests: Size effects of Types 1 & 2, crack length effect and postpeak. Engineering Fracture Mechanic 110(2):281–289, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2013.08.008
Hu XZ, Duan K (2004) Influence of fracture process zone height on fracture energy of concrete. Cement and Concrete Research 34(8): 1321–1330, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.12.027
Hu XZ, Duan K (2007) Size effect: Influence of proximity of fracture process zone to specimen boundary. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 74(7):1093–1100, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2006.12.009
Kazemi MT, Fazileh F, Ebrahiminezhad MA (2007) Cohesive crack model and fracture energy of steel-fiber-reinforced-concrete notched cylindrical specimens. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 19(10):884–890, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0899-1561(2007)19:10(884)
Le JL, Bažant ZP, Bazant MZ (2011) Unified nano-mechanics based probabilistic theory of quasibrittle and brittle structures: I. Strength, static crack growth, lifetime and scaling. Journal of the Mechanics & Physics of Solids 59(7):1291–1321, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2011.03.002
Lepech M, Li VC (2003) Preliminary findings on size effect in ECC structural members in flexure. Brittle Matrix Composites 7 2003: 57–66, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857093103.57
Lin YK, Karadelis JN (2019) Interfacial fracture toughness of composite concrete beams. Construction & Building Materials 213:413–423, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.066
Mamun M, Bindiganavile V (2014) Specimen size effects and dynamic fracture toughness of cement-based foams. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 26(1):143–151, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0000784
Şahin Y, Köksal F (2011) The influences of matrix and steel fibre tensile strengths on the fracture energy of high-strength concrete. Construction & Building Materials 25(4):1801–1806, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.11.084
Shah SP (1990) Size-effect method for determining fracture energy and process zone size of concrete. Materials & Structures 23(6):461–465, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02472030
Teng S, Liu Y, Lim TYD (2014) Determination of fracture energy of ultra-high-strength concrete. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 131: 602–615, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2014.09.017
Wang JJ, Tao MX, Nie X (2017) Fracture energy-based model for average crack spacing of reinforced concrete considering size effect and concrete strength variation. Construction & Building Materials 148:398–410, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.082
Wittmann FH (2002) Crack formation and fracture energy of normal and high strength concrete. Sadhana 27(4):413–423, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02706991
Won JP, Hong BT, Choi TJ, Lee SJ, Kang JW (2012) Flexural behaviour of amorphous micro-steel fibre-reinforced cement composites. Composite Structures 94(4):1443–1449, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.11.031
Xu P, Ma JY, Zhang MX, Ding YH, Meng LQ (2018) Fracture energy analysis of concrete considering the boundary effect of single-edge notched beams. Advances in Civil Engineering 2018:1–16, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3067236
Yoo DY, Banthia N, Kang ST, Yoon YS (2016) Size effect in ultra-high-performance concrete beams. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 157:86–106, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.02.009
Yoo DY, Yoon YS, Banthia N (2015) Predicting the post-cracking behavior of normal- and high-strength steel-fiber-reinforced concrete beams. Construction & Building Materials 93:477–485, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.06.006
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from the Key Science and Technology Program of Henan Province, China (No. 202102310253), National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1904188) and the Science and Technology Project of Henan Provincial Department of Transportation, China (No. 2019J-2-13), are gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, P., Ma, J., Ding, Y. et al. Influences of Steel Fiber Content on Size Effect of the Fracture Energy of High-Strength Concrete. KSCE J Civ Eng 25, 948–959 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-0141-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-0141-7