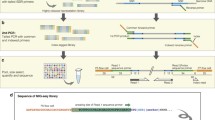
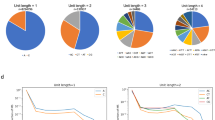
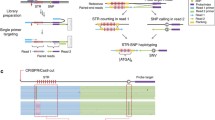
Abstract
Although genetic techniques are moving toward collecting massive amounts of genome-wide data through genome-scans, microsatellite markers (µsats) still provide a simple and cost-effective method for key applications such as parentage analyses, pedigree tracking, assessing likelihoods of disease conditions and DNA fingerprinting, among others. Newer laboratory protocols using high throughput sequencing platforms can now generate µsat data more efficiently than ever before. Yet, there is a dearth of easy to use, interactive software reliably converting raw sequencing data into individual-based multi-locus µsat genotypes suitable for typical downstream analyses. We describe the development and application of NGS-µsat, an R-based software workflow capable of converting raw µsat sequence data produced using next-generation sequencing platforms into multi-locus genotypes. Because the algorithm identifies repeat motifs, it does not rely on identifying and removing extraneous sequence fragments from sequenced reads to score loci. Accordingly, the software scores ‘true’ µsat repeats and provides an accurate, and clean picture of locus information without the typical assessment ambiguity based on fragment lengths. In comparative analyses, results show that NGS-µsat leads to cleaner, more reliable genotypes that are more repeatable than those made by scoring the same data using other software based on fragment lengths. This increased reliability/reproducibility of generated data may expand the use of high throughput sequencing-based techniques to routine DNA profiling, DNA fingerprinting and parentage/pedigree analyses and revitalise the application of µsats more broadly.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw fasta files and scores for all individuals used in this study are stored and accessible through LabArchives at the following https://doi.org/10.25833/g5gp-1703.
Availability and requirements
Project home page: https://github.com/denisroy1/NGS-usat.
Operating system(s): Platform independent.
Programming language: R.
Other requirements: Bioconductor, XQuartz.
License: GNU General Public License v 3.0.
References
Borchers HW (2018) Practical numerical math functions in RR. Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Bradbury IR et al (2018) Genotyping-by-sequencing of genome-wide microsatellite loci reveals fine-scale harvest composition in a coastal Atlantic salmon fishery. Evol Appl 11:918–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.12606
Cao MD, Balasubramanian S, Boden M (2015) Sequencing technologies and tools for short tandem repeat variation detection. Brief Bioinform 16:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbu001
Cao MD et al (2014) Inferring short tandem repeat variation from paired-end short reads. Nucleic Acids Res 42:e16. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1313
Christie MR, Tennessen JA, Blouin MS (2013) Bayesian parentage analysis with systematic accountability of genotyping error, missing data and false matching. Bioinformatics 29:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt039
Cole JR et al (2014) Ribosomal Database Project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D633–D642. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1244
Dashnow H, Tan S, Das D, Easteal S, Oshlack A (2015) Genotyping microsatellites in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform 16:A5
De Barba M, Miquel C, Lobreaux S, Quenette PY, Swenson JE, Taberlet P (2017) High-throughput microsatellite genotyping in ecology: improved accuracy, efficiency, standardization and success with low-quantity and degraded DNA. Mol Ecol Resour 17:492–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12594
Elphinstone MS, Hinten GN, Anderson MJ, Nock CJ (2003) An inexpensive and high-throughput procedure to extract and purify total genomic DNA for population studies. Mol Ecol Notes 3:317–320. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1471-8286.2003.00397.X
Evrard C, Tachon G, Randrian V, Karayan-Tapon L, Tougeron D (2019) Microsatellite instability: diagnosis, heterogeneity, discordance, and clinical impact in colorectal cancer. Cancers 11:1567
Fernandez-Silva I et al (2013) Microsatellites for next-generation ecologists: a post-sequencing bioinformatics pipeline. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055990
Gymrek M, Golan D, Rosset S, Erlich Y (2012) lobSTR: a short tandem repeat profiler for personal genomes. Genome Res 22:1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.135780.111
Haasl RJ, Payseur BA (2011) Multi-locus inference of population structure: a comparison between single nucleotide polymorphisms and microsatellites. Heredity 106:158–171. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2010.21
Highnam G, Franck C, Martin A, Stephens C, Puthige A, Mittelman D (2013) Accurate human microsatellite genotypes from high-throughput resequencing data using informed error profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e32. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks981
Huber W et al (2015) Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat Methods 12:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/Nmeth.3252
Kalinowski ST, Taper ML, Marshall TC (2007) Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol Ecol 16:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03089.x
Narum SR, Buerkle CA, Davey JW, Miller MR, Hohenlohe PA (2013) Genotyping-by-sequencing in ecological and conservation genomics. Mol Ecol 22:2841–2847. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12350
Olsen GJ et al (1992) The Ribosomal Database Project. Nucleic Acids Res 20:2199–2200. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2199
Pagès H, Aboyoun P, Gentleman R, DebRoy s (2014) Biostrings: efficient manipulation of biological stringsR. Package version 2.34.0
Pasqualotto AC, Denning DW, Anderson MJ (2007) A cautionary tale: lack of consistency in allele sizes between two laboratories for a published multilocus microsatellite typing system. J Clin Microbiol 45:522–528. https://doi.org/10.1128/Jcm.02136-06
Pemberton JM (2008) Wild pedigrees: the way forward. Proc R Soc B 275:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2007.1531
Petit RJ, Deguilloux M-F, Chat J, Grivet D, Garnier-Géré P, Vendramin GG (2005) Standardizing for microsatellite length in comparisons of genetic diversity. Mol Ecol 14:885–890. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02446.x
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J Theor Biol 13:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(66)90013-0
Pimentel JSM et al (2018) High-throughput sequencing strategy for microsatellite genotyping using Neotropical fish as a model. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00073
Putman AI, Carbone I (2014) Challenges in analysis and interpretation of microsatellite data for population genetic studies. Ecol Evol 4:4399–4428. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1305
Roy D, Paterson IG, Hurlbut TR, Ruzzante DE (2010) Development and design of five multi-locus microsatellite PCR panels for population genetic surveys of white hake (Urophycis tenuis) in the Northwest Atlantic. Conserv Genet Resour 2:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-009-9140-6
Sarhanova P, Pfanzelt S, Brandt R, Himmelbach A, Blattner FR (2018) SSR-seq: genotyping of microsatellites using next-generation sequencing reveals higher level of polymorphism as compared to traditional fragment size scoring. Ecol Evol 8:10817–10833. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.4533
Vartia S et al (2016) A novel method of microsatellite genotyping-by-sequencing using individual combinatorial barcoding. R Soc Open Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.150565
Zhan L et al (2017) MEGASAT: automated inference of microsatellite genotypes from sequence data. Mol Ecol Resour 17:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12561
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Shawna Semple (University of Waterloo) for help testing code, Kyle Wellband (IBIS Université Laval) for help in logic based peak searches, Hans W. Borchers (CRAN Senior Developer) for pracma code, and Yellow Island Aquaculture (YIAL) for experimentation facilities and salmon resources. Wild fish were seined by the Quinsam River Hatchery and collected under Permit No. 12279 issued by Fisheries and Oceans Canada.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council Operating Grant 814014 awarded to DDH. The work supported the development of the sequencing protocols and stipends for some students/researchers involved for code development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DH, DR and SL developed the concept and protocols for experimentation. SL performed experimentations and prepared DNA libraries for sequencing. DR and SL developed the software and drafted the manuscript. DR, SL and CJV scored the data and ran the various analyses. RW revised the manuscript and provided input for µsat literature review. All authors revised and wrote the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest in this work.
Ethical approval
The use of Chinook salmon in this research adhered to the ethical treatment of animals as mandated by the Animal Care Committee at the University of Windsor and in accordance with the Canadian Council for Animal Care.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, D., Lehnert, S.J., Venney, C.J. et al. NGS-μsat: bioinformatics framework supporting high throughput microsatellite genotyping from next generation sequencing platforms. Conservation Genet Resour 13, 161–173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-020-01186-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-020-01186-0