Abstract
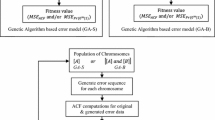
This paper proposes the use of evolutionary algorithms (EAs) to estimate the physical parameters of the generalized \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) mobile fading channel model. The estimation of parameters is a fundamental step that allows for the statistical model to adjust to the real experimental data. The The maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) method that is traditionally used for estimating parameters of the \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) channel uses nonlinear numerical methods. In some cases, the use of nonlinear numerical methods may lead the MLE to make physically unacceptable estimations, or even to not be able to obtain a result. Our proposal is to innovate the existing EAs by incorporating an adaptive approach, a new mutation strategy and an adequate fitness function for the estimation of \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) parameters. Experimental results are presented to confirm that parameters estimated by the EAs (genetic algorithms, differential evolution algorithms, and differential evolution algorithms with an adaptive guiding mechanism) are all physically acceptable. These experiments show that the EAs outperform MLE estimation results.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobayashi, H., Mark, B., & Turin, W. (2012). Probability, Random Processes, and Statistical Analysis: Applications to Communications. Signal Processing, Queueing Theory and Mathematical Finance: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511977770.
Xuefeng, Y. X., & Cheng, (2016). Propagation channel characterization, parameter estimation and modeling for wireless communications. New Yor: Wiley-IEEE Press.
Panic, S., Stefanovic, M., Anastasov, J., & Spalevic, P. (2013). Fading and interference mitigation in wireless communications. Boca Raton: CRC Press (Verlag).
Rappaport, T. (2001). Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall PTR.
Pätzold, M. (2012). Mobile radio channels (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Simon, M., & Alouini, M. (2000). Digital communications over fading channels: A unified approach to performance analysis. New York: Wiley.
Leon-Garcia, A. (2008). Probability, statistics, and random processes for electrical engineering (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Abd-Elfattah, A. (2010). Goodness of fit test for the generalized rayleigh distribution with unknown parameters. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation.
Fraidenraich, G., & Yacoub, M. (2006). The \(\alpha -\eta -\mu \) and \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) fading distributions. In: IEEE (ed) IEEE Ninth International Symposium on Spread Spectrum Techniques and Applications, pp 16 – 20, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISSSTA.2006.311725.
Batista, F. P., Souza, R. A. A., & Ribeiro, A.M.O. (2016). Maximum likelihood estimator for the \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) fading environment. In: IEEE (ed) 2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, IEEE, pp 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/WCNC.2016.7564734.
Cogliatti, R., & Souza, R.A.A. (2013). A near-100% efficient algorithm for generating \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) and \(\alpha -\eta -\mu \) variates. In: IEEE (ed) Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), 2013 IEEE 78th, pp 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1109/VTCFall.2013.6692042.
Souza, R., Ribeiro, A., & Guimarães, D. (2015). On the efficiente generation of \(\alpha - \kappa -\mu \) and \(\alpha - \eta -\mu \) white samples with applications. International Journal of Antennaas and Propagation, 2015, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/873890.
Moualeu, J. M., da Costa, D. B., Hamouda, W., Dias, U. S., & de Souza, R. A. A. (2019). Performance analysis of digital communication systems over \(\alpha \) - \(\kappa \) - \(\mu \) fading channels. IEEE Communications Letters, 23(1), 192–195. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2878218.
Kalia, S., Joshi, A., & Agrawal, A. (2019). Performance analysis of spatial modulation over generalized \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) fading distribution. Physical Communication, 35, 100696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2019.04.010.
Salahat, E., & Yang, N. (2018). Modeling recharge time of radio frequency energy harvesters in \(\alpha -\eta -\mu \) and \({\alpha }\,{-}\,{\kappa } \,{-}\,{\mu }\) fading channels. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), pp 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCW.2018.8403574.
Yacoub, M. (2016). The \(\alpha -\eta -\kappa -\mu \) fading model. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 64(8),
Ribeiro, A.M.O. (2013). Contribuições à caracterização estatística do canal de radio móvel e estimação de para̧metros por máxima verossimilhança. Phd dissertation, Universidade Estadual de Campinas.
Das, S., Mullick, S. S., & Suganthan, P. (2016). Recent advances in differential evolution—An updated survey. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 27, 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2016.01.004.
Das, S., & Suganthan, P. N. (2011). Differential evolution: a survey of the state-of-the-art. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2010.2059031.
Cai, Y., Shao, C., Zhou, Y., Fu, S., Zhang, H., & Tian, H. (2019). Differential evolution with adaptive guiding mechanism based on heuristic rules. IEEE Access, 7, 58023–58040. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914963.
Eiben, A., & Smith, J. (2015). Introduction to evolutionary computing (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-44874-8.
Almeida, C. F. M., & Kagan, N. (2011). Aplicação de algoritmos genéticos e teoria dos conjuntos fuzzy no dimensionamento de sistemas de monitoração para redes de transmissão de energia elétrica. Revista Controle & Automação, 21(4), 363–378. http://www.scielo.br/pdf/ca/v21n4/a04v21n4.pdf.
Fasolo, S. A., Lemos, C. P., Cardoso, A. S. V., & Araújo, L. C. (2018). Simulador para sinais com desvanecimento rápido para o modelo \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \). In ENCOM 2018 - VIII Conferȩncia Nacional em Comunicações, Redes e Segurança da Informação.
Rennó, V., Souza, R., & Yacoub, M. (2018). On the generation of \(\alpha -\eta -\kappa -\mu \) samples with applications. In 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), IEEE.
Gentle, J. E. (2003). Randon number generation and Monte Carlo Methods (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Yacoub, M. (2007a). The \(\kappa -\mu \) distribution and the \(\eta -\mu \) distribuition. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 49(1),
Yacoub, M. (2007b). The \(\alpha -\mu \) distribution: A physical fading model for the stacy distribution. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 56(1),
Baricz, Á. (2010). Generalized Bessel Functions of the First Kind. Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer. https://books.google.com.br/books?id=Xc5qCQAAQBAJ.
Fernandes, G., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., Carvalho, L. F., Al-Muhtadi, J. F., & Proença, M. L. (2019). A comprehensive survey on network anomaly detection. Telecommunication Systems, 70, 447–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-018-0475-8.
Al-Dabbagh, R. D., Neri, F., Idris, N., & Baba, M. S. (2018). Algorithmic design issues in adaptive differential evolution schemes: Review and taxonomy. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 43, 284–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.03.008.
Awad, N. H., Ali, M. Z., Mallipeddi, R., & Suganthan, P. N. (2019). An efficient differential evolution algorithm for stochastic opf based active-reactive power dispatch problem considering renewable generators. Applied Soft Computing, 76, 445–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.12.025.
Abduljabbar, D., Hashim, S., & Sallehuddin, R. (2020). Nature-inspired optimization algorithms for community detection in complex networks: A review and future trends. Telecommunication Systems, 74, 225–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-019-00636-x.
Sivanandam, S., & Deepa, S. N. (2008). Introduction to genetic algorithms. Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73190-0.
Liang, Y., & Leung, K. S. (2011). Genetic algorithm with adaptive elitist-population strategies for multimodal function optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 11(2), 2017–2034. 10.1016/j.asoc.2010.06.017, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494610001535, the Impact of Soft Computing for the Progress of Artificial Intelligence.
Gämperle, R., Müller, S., & Koumoutsakos, P. (2002). A parameter study for differential evolution. Advances in intelligent systems, fuzzy systems, evolutionary computation 10.
Cai, Y., Zhao, M., Liao, J., Wang, T., Tian, H., & Chen, Y. (2017). Neighborhood guided differential evolution. Soft Computing, 21(16), 4769–4812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2088-z.
Ali, M., & Törn, A. (2004). Population set-based global optimization algorithms: some modifications and numerical studies. Computers & Operations Research, 31(10), 1703–1725. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-0548(03)00116-3.
Wu, X., Jain, L., Graña, M., Duro, R. J., d’Anjou, A., & Wang, P. P. (Eds.). (2005). Information Processing with Evolutionary Algorithms From Industrial Applications to Academic Speculations. Springer, London,. https://doi.org/10.1007/b138854.
Thirumalai, C. S., Manickam, V., & Balaji, R. (2017). Data analysis using box and whisker plot for lung cancer. In IEEE (ed) International Conference on Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies [i-PACT2017], https://doi.org/10.1109/IPACT.2017.8245071.
Selvin, S. (2019). The Joy of Statistics: A treasury of elementary statistical tools and their applications. Oxford: Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198833444.001.0001.
Ronkkonen, J., Kukkonen, S., & Price, K. V. (2005). Real-parameter optimization with differential evolution. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 1, 506–513. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2005.1554725.
Li, Y., Wang, S., & Yang, B. (2020). An improved differential evolution algorithm with dual mutation strategies collaboration. Expert Systems with Applications, 153, 113451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113451.
Krzywinski, M., & Altman, N. (2014). Visualizing samples with box plots. Nat Methods, 11, 119–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2813.
Lobo, F. G., Goldberg, D. E., & Pelikan, M. (2000). Time complexity of genetic algorithms on exponentially scaled problems. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco, CA, USA, GECCO’00, p 151-158.
Acknowledgements
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemos, C.P., Veiga, A.C.P. & Fasolo, S.A. Estimation of \(\alpha -\kappa -\mu \) mobile fading channel parameters using evolutionary algorithms. Telecommun Syst 77, 189–211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00743-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00743-0