Abstract
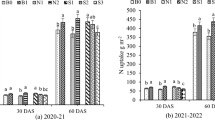
Straw and plastic mulching have been widely used in northwest China because of their ability to improve water use efficiency and increase grain yields. However, the dynamic changes of soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) under continuous straw and plastic mulching is rarely mentioned. A field experiment was conducted over four consecutive wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)-maize (Zea mays L.) rotation cycles in Northwest China to determine dynamic changes in soil C and N under three treatments: CK (traditional non-mulched), PM (transparent plastic mulching), and SM (straw mulching). Over the four wheat–maize cycles, soil organic carbon (SOC) in SM increased by 18% in the 0–0.2 m soil layer, while in PM SOC decreased by 15%, and in CK SOC changed little. Total N under CK and SM remained basically unchanged over time, but declined over time under PM. The overall microbial biomass carbon (MBC) and nitrogen (MBN) under SM increased by 32% and 17%, respectively, after four rotation cycles compared with significant decreases of 29% and 22% under PM and little change under CK. SM reduced soil temperature and increased soil water content, while PM increased both ST and water relation to the CK. Both SM and PM treatments increased grain yield and reduced nitrate N leaching. In the long run, straw mulching can improve SOC, MBC, MBN, and wheat–maize yield, and should be the recommended mulching practice for sustainable wheat–maize production in dryland areas in response to the potential challenges of climate change to dryland agriculture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakht J, Shafi M, Jan MT, Shah Z (2009) Influence of crop residue management, cropping system and N fertilizer on soil N and C dynamics and sustainable wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production. Soil Till Res 104:233–240
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Bu LD, Liu JL, Zhu L, Luo SS, Chen XP, Li SQ, Hill RL, Zhao Y (2013) The effects of mulching on maize growth, yield and water use in a semi-arid region. Agric Water Manag 123:71–78
Chen AQ, Fu B, Lu Y, Duan ZY, Hu WL (2015a) Exogenous organic materials applied to paddy field improving soil microbial biomass C, N and dissolved organic C. N Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 31:160–167 ((in Chinese))
Chen YL, Liu T, Tian XH, Wang XF, Li M, Wang SX, Wang ZH (2015b) Effects of plastic film combined with straw mulch on grain yield and water use efficiency of winter wheat in Loess Plateau. Field Crops Res 172:53–58
Chhatarpal S, Shashank T, Vijai KG, Jay SS (2018) The effect of rice husk biochar on soil nutrient status, microbial biomass and paddy productivity of nutrient poor agriculture soils. CATENA 171:485–493
Coppens F, Garnier P, De Gryze S, Merckx R, Recous S (2006) Soil moisture, carbon and nitrogen dynamics following incorporation and surface application of labelled crop residues in soil columns. Eur J Soil Sci 57:894–905
Ding DY, Zhao Y, Feng H, Hill RL, Chu XS, Zhang TB, He JQ (2018) Soil water utilization with plastic mulching for a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric Water Manag 201:246–257
Dong W, Hu C, Chen S, Zhang Y (2009) Plough and residue management effects on soil carbon and CO2 emission in a wheat-corn double-cropping system. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 83:27–37
Dong QG, Yang YC, Yu K, Feng H (2018) Effects of straw mulching and plastic film mulching on improving soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions, crop yield and water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau, China. Agric Water Manag 201:133–143
Du Z, Angers DA, Ren T, Zhang Q, Li G (2017) The effect of no-till on organic C storage in Chinese soils should not be over emphasized: a meta-analysis. Agric Ecosyst Environ 236:1–11
Eswaran H, Van den Berg E, Reich P (1993) Organic carbon in soils of the word. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:192–194
Fan M, Lu S, Jiang R, Six J, Zhang F (2012) Long-term non-flooded mulching cultivation influences rice productivity and soil organic carbon. Soil Use Manag 28:544–550
Fu X, Wang J, Zhang Q, Ge XR (2018) Effects of straw and plastic film mulching on soil nitrogen fractions and corn yield in the Weibei rainfed highland. Acta Ecol Sin 38:6912–6920 ((in Chinese))
Gao YJ, Li Y, Zhang JC, Liu WG, Dang ZP, Cao WX, Qiang Q (2009) Effects of mulch, N fertilizer, and plant density on wheat yield, wheat nitrogen uptake, and residual soil nitrate in a dryland area of China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 85:109–121
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296
Gu XB, Li YN, Du YD (2017) Biodegradable film mulching improves soil temperature, moisture and seed yield of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Soil Till Res 171:42–50
Hu YJ, Ma PH, Zhang BB, Hill RL, Wu S, Dong QG, Chen GJ (2019) Exploring optimal soil mulching for the wheat-maize cropping system in sub-humid drought-prone regions in China. Agric Water Manag 219:59–71
Huo L, Pang HC, Zhao YG, Wang J, Lu C, Li YY (2017) Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching improves soil organic carbon fractions in an arid saline soil from Northwest China. Soil Till Res 165:286–293
Jackson LE, Calderon FJ, Steenwerth KL, Scow KM, Rolston DE (2003) Responses of soil microbial processes and community structure to tillage events and implications for soil quality. Geoderma 114:305–317
Joergensen RG, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1990) Survival of the microbial biomass at elevated temperatures. Soil Biol Biochem 22:1129–1136
Kar G, Kumar A (2007) Effects of irrigation and straw mulch on water use and tuber yield of potato in eastern India. Agric Water Manag 94:109–116
Lal R (2003) Global potential of soil C sequestration to mitigate the greenhouse effect. Plant Sci 22:151–184
Lal R (2004) Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change. Geoderma 123:1–22
Li FM, Song QH, Jemba PK, Shi YC (2004) Dynamics of soil microbial biomass C and soil fertility in cropland mulched with plastic film in a semiarid agro-ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1893–1902
Li R, Hou XQ, Jia ZK, Han QF, Ren XL, Yang BP (2013) Effects on soil temperature, moisture, and maize yield of cultivation with ridge and furrow mulching in the rainfed area of the Loess Plateau, China. Agric Water Manag 116:101–109
Li S, Zhang SR, Pu YL, Li YL, Xu XX, Jia YX, Deng OP, Gong GS (2016) Dynamics of soil labile organic carbon fractions and C-cycle enzyme activities under straw mulch in Chengdu Plain. Soil Till Res 155:78–86
Liu G, Jiang N, Zhang L, Liu Z (1996) Soil physical and chemical analysis and description of soil profiles, vol 24. China Standard Methods Press, Beijing, p 266
Magill AH, Aber JD (2000) Dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen relationships in forest litter as affected by nitrogen deposition. Soil Biol Biochem 32:603–613
Mebius LJ (1960) A rapid method for the determination of organic carbon in soil. Anal Chim Acta 22:120–124
Mo F, Wang JY, Zhou H, Luo CL, Zhang XF, Li XY, Li FM, Xiong LB, Kavagi L, Nguluu SN, Xiong YC (2017) Ridge–furrow plastic-mulching with balanced fertilization in rainfed maize (Zea mays L.): An adaptive management in east African Plateau. Agric For Meteorol 236:100–112
Qin W, Hu CS, Oenema O (2015) Soil mulching significantly enhances yields and water and nitrogen use efficiencies of maize and wheat: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 5:16210
Qiu SJ, Gao HJ, Zhu P, Hou YP, Zhao SC, Rong XM, Zhang YP, He P, Christie P, Zhou W (2016) Changes in soil carbon and nitrogen pools in a Mollisol after long-term fallow or application of chemical fertilizers, straw or manures. Soil Till Res 163:255–265
Rosenzweig ST, Fonte SJ, Schipanski ME (2018) Intensifying rotations increases soil carbon, fungi, and aggregation in semi-arid agroecosystems. Agric Ecosyst Environ 258:14–22
Tan ZX, Lal R (2005) Carbon sequestration potential estimates with changes in land use and tillage practice in Ohio, USA. Agric Ecosyst Environ 111:140–152
Taylor JP, Wilson B, Mills MS, Burns RG (2002) Comparison of microbial numbers and enzymatic activities in surface soils and subsoils using various techniques. Soil Biol Biochem 34:387–401
Tu C, Ristaino JB, Hu SJ (2006) Soil microbial biomass and activity in organic tomato farming systems: Effects of organic inputs and straw mulching. Soil Biol Biochem 38:247–255
Van Gestel M, Ladd JN, Amato M (1991) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization from two soils of contrasting texture and microaggregate stability: influence of sequential fumigation, drying and storage. Soil Biol Biochem 23:313–322
Vance ED, Brooks PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Wang H, Wang CB, Zhao XM, Wang FL (2015) Mulching increases water-use efficiency of peach production on the rainfed semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Agric Water Manag 154:20–28
Wang XJ, Jia ZK, Liang LY, Zhao YF, Yang BP, Ding RX, Wang JP, Nie JF (2018) Changes in soil characteristics and maize yield under straw returning system in dryland farming. Field Crop Res 218:11–17
Wu J, Joergensen RG, Pommerening B, Chaussod R, Brookes PC (1990) Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction: an automated procedure. Soil Biol Biochem 22:1167–1169
Xiao X, Zhu W, Xiao L, Deng YP, Zhao YW, Wang JF (2013) Suitable water and nitrogen treatment improves soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activities of paddy field. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 29:91–98 ((in Chinese))
Yadav GS, Das A, Lal R, Batu S, Datta M, Meena RS, Patil SB, Singh R (2019) Impact of no-till and mulching on soil carbon sequestration under rice (Oryza sativa L.)-rapeseed (Brassica campestris L. var. rapeseed) cropping system in hilly agro-ecosystem of the Eastern Himalayas. India Agric Ecosyst Environ 275:81–92
Yin H, Xiao J, Li Y, Chen Z, Cheng X, Zhao C, Liu Q (2013) Warming effects on root morphological and physiological traits: the potential consequences on soil C dynamics as altered root exudation. Agric For Meteorol 180:287–296
Yuan HZ, Liu SL, Razavi BS, Zhran M, Wang JR, Zhu ZK, Wu JS, Ge TD (2019) Differentiated response of plant and microbial C:N: P stoichiometries to phosphorus application in phosphorus-limited paddy soil. Eur J Soil Biol 95:103122
Zhang SL, Lovdahl L, Grip H, Tong YN, Yang XY, Wang QJ (2009) Effects of mulching and catch cropping on soil temperature, soil moisture and wheat yield on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Till Res 102:78–86
Zhang P, Chen XL, Wei T, Yang Z, Jia ZK, Yang BP, Han QF, Ren XL (2016) Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Till Res 160:65–72
Zhao H, Jian S, Xu XL, Qin XJ (2017) Stoichiometry of soil microbial biomass carbon and microbial biomass nitrogen in China’s temperate and alpine grasslands. Eur J Soil Biol 83:1–8
Zhou LM, Jin SL, Liu CA, Xiong YC, Si JT, Li XG, Gan YT, Li FM (2012) Ridge-furrow and plastic-mulching tillage enhances maize-soil interactions: opportunities and challenges in a semiarid agroecosystem. Field Crop Res 126:181–188
Zhou LM, Zhang F, Liu CA (2015) Improved yield by harvesting water with ridges and subgrooves using buried and surface plastic mulchs in a semiarid area of China. Soil Till Res 150:21–29
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Key Project of Science and Technology Service Network Initiative (STS) in CAS and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51879224) and Shaanxi Natural Science Basic Research Project (2018JM4007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Sun, B., Wu, S. et al. Soil carbon and nitrogen of wheat–maize rotation system under continuous straw and plastic mulch. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 119, 181–193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-020-10114-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-020-10114-5