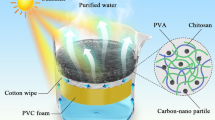
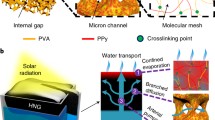
Abstract
Efficient light absorption and trapping are of vital importance for the solar water evaporation by hydrogel-based photothermal conversion materials. Conventional strategies are focused on the development of the composition and structure of the hydrogel's internal network. In our point of view, the importance of the surface structure of hydrogel has usually been underestimated or ignored. Here inspired by the excellent absorbance and water transportation ability of biological surface structure, the hierarchical structured hydrogel evaporators (HSEs) increased the light absorption, trapping, water transportation and water-air interface, which is the beneficial photothermal conversion and water evaporation. The HSEs showed a rapid evaporation rate of 1.77 kg·m-2·h-1 at about 92% energy efficiency under one sun (1 kW·m-2). Furthermore, the superhydrophilic window device was used in this work to collect the condensed water, which avoids the light-blocking caused by the water mist formed by the small droplets and the problem of the droplets stick on the device dropping back to the bulk water. Integrated with the excellent photothermal conversion hydrogel and superhydrophilic window equipment, this work provides efficient evaporation and desalination of hydrogel-based solar evaporators in practical large-scale applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis, N. S.; Research opportunities to advance solar energy utilization. Science, 2016, 351, aad1920.
Kraemer, D.; Poudel, B.; Feng, H. P.; Caylor, J. C.; Yu, B.; Yan, X.; Ma, Y., Wang, X. W.; Wang, D. Z.; Muto, A. et al. High-performance flat-panel solar thermoelectric generators with high thermal concentration. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 532–538.
Tao, P.; Ni, G.; Song C. Y.; Shang, W.; Wu, J. B.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Deng, T. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation. Nat. Energy, 2018, 3, 1031–1041.
Chen, C. J.; Kuang, Y. D.; Hu, L. B.; Challenges and opportunities for solar evaporation. Joule, 2019, 3, 683–718.
Zhou, L.; Li, X. Q.; Ni, G. W.;; Zhu, S. N.; Zhu, J. The revival of thermal utilization from the Sun: Interfacial solar vapor generation. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 562–578.
Gao, M. M.; Zhu, L. L.; Peh, C. K.; Ho, G. W.; Solar absorber material and system designs for photothermal water vaporization towards clean water and energy production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 841–864.
Brongersma, M. L.; Halas, N. J.; Nordlander, P. Plasmon-induced hot carrier science and technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 25–34.
Wu, S. H.; Xiong, G. P.;; Yang, H. C.; Gong, B. Y.; Tian, Y. K.;; Xu, C. X.; Wang, Y., Fisher, T.; Yan, J. H.; Cen, K. F.; et al. Multifunctional solar waterways: Plasma-enabled self-cleaning nanoarchitectures for energy-efficient desalination. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901286.
Liang, J.; Liu, H. Z.; Yu, J. Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, J. Plasmon-enhanced solar vapor generation. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8, 771–786.
Liu, H. W.; Chen, C. J.; Wen, H.; Guo, R. X.; Williams, N. A.; Wang, B. D.; Chen, F. J.; Hu, L. B.; Narrow bandgap semiconductor decorated wood membrane for high-efficiency solar-assisted water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18839–18846.
Cheng, H. Y.; Liu, X. H.; Zhang, L. X.; Hou, B. F.; Yu, F., Shi, Z. X.; Wang, X. B.; Self-floating Bi2S3/poly (vinylidene fluoride) composites on polyurethane sponges for efficient solar water purification. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2019, 203, 110127.
Yi, L. C.; Ci, S. Q.; Luo, S. L.; Shao, P.; Hou, Y., Wen, Z. H.; Scalable and low-cost synthesis of black amorphous Al-Ti-O nanostructure for high-efficient photothermal desalination. Nana Energy 2017, 41, 600–608.
Zhu, L. L.; Gao, M. M.; Peh, C. K.; N; Wang, X. Q.; Ho, G. W.; Self-contained monolithic carbon sponges for solar-driven interfacial water evaporation distillation and electricity generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702149.
Zhang, P. P.; Li, J.; Lv, L. X.; Zhao, Y., Qu, L. T.; Vertically aligned graphene sheets membrane for highly efficient solar thermal generation of clean water. ACS Nana 2017, 11, 5087–5093.
Fu, Y., Wang, G., Mei, T.; Li, J. H.; Wang, J. Y.; Wang, X. B.; Accessible graphene aerogel for efficiently harvesting solar energy. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4665–4671.
Zhang, L. B.; Tang, B.; Wu, J. B.; Li, R. Y.; Wang, P. Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4889–4894.
Wang, Z.; Yan, Y. T.; Shen, X. P.; Jin, C. D.; Sun, Q. F.; Li, H. Q.; A wood-polypyrrole composite as a photothermal conversion device for solar evaporation enhancement. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20706–20712.
Wang, X.; Liu, Q. C.; Wu, S. Y.; Xu, B. X.; Xu, H. X.; Multilayer polypyrrole nanosheets with self-organized surface structures for flexible and efficient solar-thermal energy conversion. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807716.
Xiao, P.; Gu, J. C.; Zhang, C., Liang, F., Ni, Y., He, J.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, J. Y.; Kuo, S. W.; Chen, T. A scalable, low-cost and robust photo-thermal fabric with tunable and programmable 2D/3D structures towards environmentally adaptable liquid/solid-medium water extraction. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104002.
Xu, N., Hu, X. Z.; Xu, W. C.; Li, X. C.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, S. N.; Zhu, J. Mushrooms as efficient solar steam-generation devices. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606762.
Wang, C. B.; Wang, J. L.; Li, Z. T.; Xu, K. Y.; Lei, T., Wang, W. K.; Superhydrophilic porous carbon foam as a self-desalting monolithic solar steam generation device with high energy efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9528–9535.
Xie, Y. H.; Li, W. J.; Huang, H. W.; Dong, D. X.; Zhang, X. Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y., Lu, X. Bio-based Radish@PDA/PEG sandwich composite with high efficiency solar thermal energy storage. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8448–8457.
Zhang, Z. H.; Chen, Z. Y.; Sun, L. Y.; Zhang, X. X.; Zhao, Y. J.; Bio-inspired angle-independent structural color films with anisotropic colloidal crystal array domains. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1579–1584.
Rong, Q. F.; Lei, W. W.; Liu, M. J.; Conductive hydrogels as smart materials for flexible electronic devices. Chem. -Eur. J. 2018, 24, 16930–16943.
Yuk, H.; Lu, B. Y.; Zhao, X. H.; Hydrogel bioelectronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1642–1667.
Proctor, C. M.; Chan, C. Y.; Porcarelli, L.; Udabe, E.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; del Agua, I.; Mecerreyes, D.; Malliaras, G. G. Ionic hydrogel for accelerated dopamine delivery via retrodialysis. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 7080–7084.
Zhao, F., Zhou, X. Y.; Shi, Y., Qian, X.; Alexander, M.; Zhao, X. P.; Mendez, S.; Yang, R. G.; Qu, L. T.; Yu, G. H.; Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 489–495.
Zhou, X. Y.; Zhao, F., Guo, Y. H.; Rosenberger, B.; Yu, G. H.; Architecting highly hydratable polymer networks to tune the water state for solar water purification. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw5484.
Zhao, L. Y.; Wang, P. S.; Tian, J.; Wang, J. H.; Li, L.; Xu, L. Q.; Wang, Y., Fei, X.; Li, Y. A novel composite hydrogel for solar evaporation enhancement at air-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 153–160.
Gao, M. M.; Peh, C. K.; Phan, H. T.; Zhu, L. L.; Ho, G. W.; Solar absorber gel: Localized macro-nano heat channeling for efficient plasmonic Au nanoflowers photothermic vaporization and triboelectric generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800711.
Kim, J. B.; Kim, P.; Pegard, N. C.; Oh, S. J.; Kagan, C. R.; Fleischer, J. W.; Stone, H. A.; Loo, Y. L.; Wrinkles and deep folds as photonic structures in photovoltaics. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 327–332.
Dotan, H., Kfir, O.; Sharlin, E.; Blank, O.; Gross, M.; Dumchin, I.; Ankonina, G., Rothschild, A. Resonant light trapping in ultrathin films for water splitting. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 158–164.
Tadepalli, S.; Slocik, J. M.; Gupta, M. K.; Naik, R. R.;; Singamaneni, S. Bio-optics and bio-inspired optical materials. Chem. Rev. 2017, 777, 12705–12763.
Tao, P.; Shang, W.; Song, C. Y.; Shen, Q. C.; Zhang, F. Y.; Luo, Z.; Yi, N., Zhang, D.; Deng, T. Bioinspired engineering of thermal materials. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 428–463.
Qian, X. S.; Zhao, Y. S.; Alsaid, Y., Wang, X.; Hua, M. T.; Galy, T., Gopalakrishna, H., Yang, Y. Y.; Cui, J.S.; Liu, N. et al. Artificial phototropism for omnidirectional tracking and harvesting of light. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1048–1055.
Chen, H. W.; Zhang, P. F.; Zhang, L. W.; Liu, H. L.; Jiang, Y., Zhang, D. Y.; Han, Z. W.; Jiang, L. Continuous directional water transport on the peristome surface of Nepenthes alata. Nature, 2016, 532, 85–89.
Ishii, D.; Horiguchi, H., Hirai, Y., Yabu, H., Matsuo, Y., Ijiro, K., Tsujii, K., Shimozawa, T., Hariyama, T., Shimomura, M. Water transport mechanism through open capillaries analyzed by direct surface modifications on biological surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3024.
Lei, W. W.; Qi, S. H.; Rong, Q. F.; Huang, J.; Xu, Y. C.; Fang, R. C.; Liu, K. S.; Jiang, L., Liu, M. J.; Diffusion-freezing-induced microphase separation for constructing large-area multiscale structures on hydrogel surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808217.
Mansur, H. S.; Orefice, R. L.; Mansur, A. A. P. Characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels and PVA-derived hybrids by small-angle X-ray scattering and FTIR spectroscopy. Polymer 2004, 45, 7193–7202.
Gomez, H., Ram, M. K.; Alvi, F., Villalba, P.; Stefanakos, E.; Kumar, A. Graphene-conducting polymer nanocomposite as novel electrode for supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2011, 796, 4102–4108.
Liu, T. Q.; Jiao, C., Peng, X.; Chen, Y. N.; Chen, Y. Y.; He, C. C.; Liu, R. G.; Wang, H. L.; Super-strong and tough poly(vinyl alcohol)/ poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels reinforced by hydrogen bonding. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 8105–8114.
Liu, M. J.; Wang, S. T.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036.
Guo, Y. H; Lu, H. Y.; Zhao, F., Zhou, X. Y.; Shi, W.; Yu, G.H. Biomass-derived hybrid hydrogel evaporators for cost-effective solar water purification. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907061.
Surwade, S. P.; Smirnov, S. N.; Vlassiouk, I. V.; Unocic, R. R.; Veith, G. M.;; Dai, S.; Mahurin, S. M.; Water desalination using nanoporous single-layer graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 459–464.
Yang, J.; Zhang, Z. Z.; Xu, X. H.; Zhu, X. T.; Men, X. H.; Zhou, X. Y Superhydrophilic-superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2834–2837.
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Cunming Yu and Dr. Xiao Xiao for providing COMSLO simulation. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (No. 21725401), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFA0207800), the 111 project (B14009), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2020_3162_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Hierarchical structures hydrogel evaporator and superhydrophilic water collect device for efficient solar steam evaporation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, W., Khan, S., Chen, L. et al. Hierarchical structures hydrogel evaporator and superhydrophilic water collect device for efficient solar steam evaporation. Nano Res. 14, 1135–1140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3162-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-3162-5