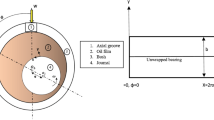
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to propose magnetorheological fluid-lubricated rubber stern bearing test ring, to study the effects of temperature, magnetic field strength and eccentricity ratio on lubrication performance. The Reynolds equation considering effects of eccentricity ratio, temperature and magnetic field strength is adopted and solved by finite difference method and successive over-relaxation method to calculate pressure distribution and friction coefficient with real bearing shapes and boundary conditions. Bearing capacity can be improved and friction coefficient can be reduced by decreasing temperature, increasing magnetic field strength and increasing eccentricity ratio. The paper’s results may provide important design theoretical and experimental guidelines support for rubber stern bearing in this kind of magnetorheological fluids-lubricated.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cruze D, Hemalatha G, Jebadurai SVS et al (2018) A review on the magnetorheological fluid, damper and its applications for seismic mitigation. Civ Eng J 4(12):3058–3074
Aruna MN, Rahman MR, Joladarashi S et al (2020) Investigation of sedimentation, rheological, and damping force characteristics of carbonyl iron magnetorheological fluid with/without additives. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42:228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02322-5
Rabinow J (1948) The magnetic fluid clutch. Electr Eng 67(12):1308–1315. https://doi.org/10.1109/EE.1948.6444497
Rabinow J (1951) Magnetic Fluid Torque and Force Transmitting Device. U.S. Patent, US78342647A, http://www.freepatentsonline.com/2575360.html
Milecki A, Hauke M (2012) Application of magnetorheological fluid in industrial shock absorbers. Mech Syst Signal Process 28:528–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.11.008
Lim ST, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2005) Magnetorheological characterization of carbonyl iron-organoclay suspensions. IEEE Trans Magn 41(10):3745–3747. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979205029985
Jang IB, Kim HB, Lee JY, You JL, Choi HJ (2005) Role of organic coating on carbonyl iron suspended particles in magnetorheological fluids. J Appl Phys 97(10):24–27. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1853835
Rodríguez-López J, Elvira MD ,Espinosa LF (2012) Magnetorheological fluid characterization using ultrasound measurements. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering, vol 42, no. 1, p 2032. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/42/1/012032
Zhang X, Li W, Gong XL (2008) Study on magnetorheological shear thickening fluid. In: IOP conference series”, smart materials and structures, vol 17 no. 1, p. 015051. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/17/1/015051
Zite JL, Ahmadkhanlou F, Neelakantan VA ,Washington GN (2006) A magnetorheological fluid based orthopedic active knee brace. In: Proceedings of SPIE 6171, smart structures and materials 2006: industrial and commercial applications of smart structures technologies, 61710H. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.658693
Papell SS (1965) Low viscosity magnetic fluid obtained by the olloidal suspension of magnetic particles. US Patent 3,215,572.
McTague JP (1969) Magnetoviscosity of magnetic colloids. J Chem Phys 51:133. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1671697
Odenbach S (2000) Magnetoviscous effects in ferrofluids. Appl. Heol. 10:178–184
Odenbach S (2004) Recent progress in magnetic fluid research. J Phys Condens Matter 16(32):1135–1150
Jacob R (1951) Magnetic fluid torque and force transmitting evice. US Patent 2,575,360.
Carlson JD, Chrzan MJ (1994) Magnetorheological fluid ampers. US Patent 5,277,281.
Huang J, Zhang JQ, Yang Y, Wei YQ (2002) Analysis and esign of a cylindrical magneto-rheological fluid brake. J Mater Process Technol 129:559–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00634-9
Baranwal D, Deshmukh TS (2012) MR-Fluid technology nd its application—a review. Int J Emerg Technol Adv Eng 2(12):563–569
Wang J, Meng G (2001) Magnetorheological fluid devices: principles, characteristics and applications in mechanical engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part L J Mater Des Appl 215(3):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1243/1464420011545012
De Vicente J, Klingenberg D, Hidalgo-Alvarez R (2011) Magnetorheological fluids: a review. Soft Matter 7(8):3701–3710. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0sm01221a
Bahar A, Pozo F, Acho L, Rodellar J, Barbat A (2010) Parameter identification of large-scale magnetorheological dampers in a benchmark building. Comput. Struct. 8(3):198–206. https://doi.org/10.23919/ECC.2009.7074451
Sarkar C, Hirani H (2017) Experimental studies on magnetorheological brake containing plane, holed and slotted discs. Ind Lubr Tribol 69(2):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-12-2015-0205
Lijesh KP, Deepak K, Harish H (2017) Synthesis and field dependent shear stress evaluation of stable MR fluid for brake application. Ind Lubr Tribol 69(14):282–294. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-03-2016-0061
Liu C, Hu JA (2019) Magnetorheological hydrostatic guideway system for machining vibration control. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41:12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1525-6
Lv F, Jiao C, Zou D, Ta N, Zhushi R (2019) Analysis of misaligned water-lubricated polymer bearing with axial grooves. Ind Lubr Tribol 71(3):411–419. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-08-2018-0320
Zhao ZM, Zhang R (2020) Theoretical and experimental analysis of a water-lubricated rubber journal bearing with a large aspet ratio. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-10-2019-0400
Hesselbach J, Abel-keilhack C (2003) Active hydrostatic bearing with magnetorheological fluid. J Appl Phys 93(10):8441–8443. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1555850
Urreta H, Leicht Z, Sanchez A, Agirre A, Kuzhir P, Magnac G (2010) Hydrodynamic bearing lubricated with magnetic fluids. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 21(15):1491–1499. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/149/1/012113
Lampaert Stefan GE, van Ostayen RAJ (2020) Lubrication theory for Bingham plastics. Tribol Int 147:106–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106160
Abbaspur A, Norouzi M, Akbarzadeh P, Vaziri SA (2020) Analysis of nonlinear viscoelastic lubrication using Giesekus constitutive equation. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650120944280
Tichy J (1991) Hydrodynamic lubrication theory for the Bingham plastic flow model. J Rheol 35(4):477–496. https://doi.org/10.1122/1.550231
Gertzos KP, Nikolakopoulos PG, Papadopoulos CA (2008) CFD analysis of journal bearing hydrodynamic lubrication by Bingham lubricant. Tribol Int 41(12):1190–1204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.03.002
Bompos DA, Nikolakopoulos PG (2016) Rotordynamicanalysis of a shaft using magnetorheological and nanomagne-torheological fluid journal bearings. Tribol Trans 59(1):108–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2015.1050137
Babin A, Fetisov A, Tyurin V (2020) Numerical modelling of fluid-film bearing lubricated with magnetorheological fluid. In: Radionov A, Kravchenko O, Guzeev V, Rozhdestvenskiy Y (eds) Proceedings of the 5th international conference on industrial engineering (ICIE 2019). ICIE 2019. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22041-9_136
Bhat AK; Vaz N; Kumar Y; Rolvin DS; Kumar P (2019) Comparative study of journal bearing performance with ferrofluid and MR fluid as lubricant. In: AIP conference proceedings, vol 2080, p. 040008. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5092926
Rao BN, Sekhar AS (2019) Analysis of magneto rheological fluid journal bearing. Appl Mech Mater 895:152–157. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.895.152
Kt S, Sharma SC (2019) A simulation study on the behavior of magnetorheological fluid on Herringbone-grooved hybrid slot-entry bearing. Tribol Trans 62(6):1099–1118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2019.1649775
Lampaert SGE, Quinci F, van Ostayen Ron AJ (2020) Rheological texture in a journal bearing with magnetorheological fluids. J Magn Magn Mater 499:166218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166218
Urreta H, Aguirre G, Kuzhir P, Lopez DL, Luis N (2019) Actively lubricated hybrid journal bearings based on magnetic fluids for high-precision spindles of machine tools. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 30(15):2257–2271. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X19862358
Sahu K, Sharma SC (2019) Magneto-rheological fluid slot-entry journal bearing considering thermal effects. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 30(18–19):2831–2852. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X19873401
Lampaert SGE, Van Ostayen RAJ (2019) Experimental results on a hydrostatic bearing lubricated with a magnetorheological fluid. Curr Appl Phys 19(12):1441–1448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2019.09.004
Laukiavich C, Braun MJ, Chandy A (2014) A comparison between the performance of ferro-and magnetorheological fluids in a hydrodynamic bearing. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part J J Eng Tribol 228(6):649–666. https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650114523753
Genç S, Phulé Pradeep P (2002) Rheological properties of magnetorheological fluids. Smart Mater Struct 11(1):140. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/11/1/316
Su B, Huang L, Huang W, Wang X (2016) The load carrying capacity of textured sliding bearings with elastic deformation. Tribol Int 109:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.11.030
Liu SB (2012) On boundary conditions in lubrication with one dimensional analytical solutions. Tribol Int 48:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.11.021
Ai XL, Cheng HS, Zheng LQ (1993) A transient model for micro-elastohy dro dynamic lubrication with three-dimensional irregularities. ASME J Tribol 115:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2920961
MIL-DTL-17901C(SH) (2005) Bearing components, bonded synthetic rubber, water lubricated. USA: department of defense. https://www.techstreet.com/standards/mil-mil-dtl-17901c?product_id=1442696. Accessed 7 Jan 2021
Acknowledgements
The authors give sincere thanks to the editors and the reviewers for their patient work and constructive suggestions. This work is supported by the Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 20192BBEL50028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Daniel Onofre de Almeida Cruz.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Long, Z. & Yang, X. Lubrication performance of magnetorheological fluid-lubricated rubber stern bearing test ring. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 43, 56 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02796-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02796-3