Abstract
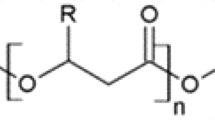
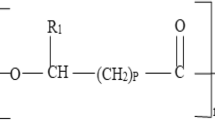
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are bio-polyesters of hydroxyalkanoates that accumulate intracellularly in case of prokaryotes, as cytoplasmic granules, under carbon rich and paucity of nitrogen, phosphorous, sulphur and oxygen where it can serve as carbon and energy source under nutrient limiting condition and/or environmental stress conditions. In adverse growth conditions, many bacteria have ability to store nutrients in form of PHA granules using their specific metabolic pathways during stationary growth phase, in the presence of high levels of carbon containing nutrient sources. Bacterial PHAs have generated attention as an alternative to petroleum derived synthetic plastics. It possesses the characteristic physico-chemical properties comparable to the synthetic plastics. These properties of PHAs can be improved by blending of PHAs with other natural polymer like starch, cellulose and semisynthetic polymers like poly lactic acids and polycaprolactones. Being eco-friendly, biodegradable and biocompatible; major PHAs such as, Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) have found numerous vital applications in pharmaceutical, biomedical, textile, cosmetic, agricultural, treatment of waste water and have been successfully employed for Food packaging industries. This review provides a comprehensive knowledge about the world of PHAs covering its major aspects, namely its chemical nature and structure, biosynthesis, various methods of screening of potential PHA producing bacteria along with properties, several techniques used for its recovery and further characterization.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacquel N, Lo CW, Wu HS, Wei YH, Wang SS (2007) Solubility of polyhydroxyalkanoates by experiment and thermodynamic correlations. AIChE J 53(10):2704–2714
Muthusamy MS, Pramasivam S (2017) Bioplastics–an eco-friendly alternative to petrochemical plastics. Curr World Environ 14(1):49
Slaninova E, Sedlacek P, Mravec F, Mullerova L, Samek O, Koller M, Hesko O, Kucera D, Marova I, Obruca S (2018) Light scattering on PHA granules protects bacterial cells against the harmful effects of UV radiation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(4):1923–1931
Shah K (2014) Original research article optimization and production of Polyhydroxybutarate (PHB) by Bacillus subtilis G1S1from soil. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 3(5):377–387
Ostle AG, Holt J (1982) Nile blue a as a fluorescent stain for poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate. Appl Environ Microbiol 44(1):238–241
Spiekermann P, Rehm BH, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbüchel A (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171(2):73–80
Manju J, Prabakaran P (2015) Comparative study on screening methods of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) producing bacteria’s isolated from root nodules of selected leguminous plants. Int J Eng Sci Invent 4(11):23–28
Bhuwal AK, Singh G, Aggarwal NK, Goyal V, Yadav A (2013) Isolation and screening of polyhydroxyalkanoates producing bacteria from pulp, paper, and cardboard industry wastes. Int J Biomat 2013:1–10
Muhammadi S, Afzal M, Hameed S (2015) Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates-eco-friendly next generation plastic: production, biocompatibility, biodegradation, physical properties and applications. Green Chem Lett Rev 8(3–4):56–77
Sheu D-S, Wang Y-T, Lee C-Y (2000) Rapid detection of polyhydroxyalkanoate-accumulating bacteria isolated from the environment by colony PCR. Microbiology 146(8):2019–2025
Sujatha K, Mahalakshmi A, Shenbagarathai R (2005) A study on accumulation of PHB in native Pseudomonas isolates LDC-5 and LDC-25. Indian J Biotechnol 4(2):216–221
Ciesielski S, Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A, Pokoj T, Klimiuk E (2006) Molecular detection and diversity of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates-producing bacteria enriched from activated sludge. J Appl Microbiol 101(1):190–199
Hong K, Sun S, Tian W, Chen G, Huang W (1999) A rapid method for detecting bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates in intact cells by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51(4):523–526
Chandrashekharaiah P (2005) Isolation, screening and selection of efficient poly-Β-Hydroxybutyrate (Phb) synthesizing Bacteria. Master’s Thesis, Dharwad University Of Agricultural Sciences, Karnataka, India
Keshavarz T, Roy I (2010) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: bioplastics with a green agenda. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(3):321–326
Yu J (2007) Microbial production of bioplastics from renewable resources. In: Yang S-T (ed) Bioprocessing for value-added products from renewable resources. Elsevier, Dublin, pp 585–610
Tan G-YA, Chen C-L, Li L, Ge L, Wang L, Razaad IMN, Li Y, Zhao L, Mo Y, Wang J-Y (2014) Start a research on biopolymer polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): a review. Polymers 6(3):706–754
Raza ZA, Riaz S, Banat IM (2018) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: properties and chemical modification approaches for their functionalization. Biotechnol Prog 34(1):29–41
Verlinden RA, Hill DJ, Kenward M, Williams CD, Radecka I (2007) Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Appl Microbiol 102(6):1437–1449
Prados E, Maicas S (2016) Bacterial production of hydroxyalkanoates (PHA). Univ J Microbiol Res 4(1):23–30
Divya G, Archana T, Manzano R (2013) Polyhydroxy alkanoates—a sustainable alternative to petro-based plastics. J Pet Environ Biotechnol 4(143):1–8
Kim HW, Chung MG, Rhee YH (2007) Biosynthesis, modification, and biodegradation of bacterial medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Microbiol 45(2):87–97
Saharan B, Ankita SD (2012) Bioplastics-for sustainable development: a review. Int J Microbial Res Technol 1:11–23
Grumezescu AM, Butu A (2017) AMH AMG (ed) Food packaging and preservation, vol 9. Academic Press, San Diego, p 588
Ong SY, Chee JY, Sudesh K (2017) Degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): a review. J Siberian Fed Univ 10(2):211–225
Kumaravel S, Hema R, Lakshmi R (2010) Production of polyhydroxybutyrate (bioplastic) and its biodegradation by Pseudomonas lemoignei and Aspergillus Niger. J Chem 7(S1):S536–S542
Singh Saharan B, Grewal A, Kumar P (2014) Biotechnological production of polyhydroxyalkanoates: a review on trends and latest developments. Chinese J Biol 2014
Singh AK, Mallick N (2017) Advances in cyanobacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates production. FEMS Microbiol Lett 364(20)
Matias F, Bonatto D, Padilla G, Rodrigues MFDA, Henriques JAP (2009) Polyhydroxyalkanoates production by actinobacteria isolated from soil. Can J Microbiol 55(7):790–800
Han J, Hou J, Liu H, Cai S, Feng B, Zhou J, Xiang H (2010) Wide distribution among halophilic archaea of a novel polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase subtype with homology to bacterial type III synthases. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(23):7811–7819
Safak S, Mercan N, Aslim B, Beyatli Y (2002) A study on the production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate by some eukaryotic microorganisms. Turk Electr J Biotechnol 1:11–17
Reddy C, Ghai R, Kalia VC (2003) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: an overview. Bioresour Technol 87(2):137–146
Haddadi M, Asadolahi R, Negahdari B (2019) The bioextraction of bioplastics with focus on polyhydroxybutyrate: a review. Int J Environ Sci Technol (Tehran):1–14
Hasan D, Rezani S, Shohreh T, Saeid M (2015) Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), intracellular pathways and properties. Curr World Environ 1(10):644–649
Zinn M, Witholt B, Egli T (2001) Occurrence, synthesis and medical application of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate. Adv Drug Del Rev 53(1):5–21
Aldor IS, Keasling JD (2003) Process design for microbial plastic factories: metabolic engineering of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14(5):475–483
Rivera-Terceros P, Tito-Claros E, Torrico S, Carballo S, Van-Thuoc D, Quillaguamán J (2015) Production of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) by Halomonas boliviensis in an air-lift reactor. J Biol Res Thessaloniki 22(1):1–9
Gamal RF, Abdelhady HM, Khodair TA, El-Tayeb TS, Hassan EA, Aboutaleb KA (2013) Semi-scale production of PHAs from waste frying oil by Pseudomonas fluorescens S48. Braz J Microbiol 44(2):539–549
Gross RA, DeMello C, Lenz RW, Brandl H, Fuller RC (1989) The biosynthesis and characterization of poly (β-hydroxyalkanoates) produced by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Macromolecules 22(3):1106–1115
Getachew A, Woldesenbet F (2016) Production of biodegradable plastic by polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) accumulating bacteria using low cost agricultural waste material. BMC Res Notes 9(1):509
Sharma M, Harish K (2015) Isolation and culture conditions optimization for PHB production by Pseudochrobactrum asaccharolyticum. IJSR 4:1895–1901
Godbole S (2016) Methods for identification, quantification and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoates-a review. Int J Bioassays 5(4):2016
Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1990) Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 54(4):450–472
Karr DB, Waters JK, Emerich DW (1983) Analysis of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids by ion-exclusion high-pressure liquid chromatography and UV detection. Appl Environ Microbiol 46(6):1339–1344
Grubelnik A, Wiesli L, Furrer P, Rentsch D, Hany R, Meyer VR (2008) A simple HPLC-MS method for the quantitative determination of the composition of bacterial medium chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Sep Sci 31(10):1739–1744
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty R (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6(1):29–37
Girdhar M, Sharma A, Mohan A (2014) Enhancement of commercial production of polymeric PHB material from bacterial strains through mutagenic strategies. Biosci Biotechnol Res ASIA 11(3):1591–1599
Madkour MH, Heinrich D, Alghamdi MA, Shabbaj II, Steinbüchel A (2013) PHA recovery from biomass. Biomacromolecules 14(9):2963–2972
Jacquel N, Lo C-W, Wei Y-H, Wu H-S, Wang SS (2008) Isolation and purification of bacterial poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates). Biochem Eng J 39(1):15–27
Koller M, Niebelschütz H, Braunegg G (2013) Strategies for recovery and purification of poly [(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates](PHA) biopolyesters from surrounding biomass. Eng Life Sci 13(6):549–562
Horowitz DM, Brennan EM (2002) Method of decolorizing or deodorizing polyhydroxyalkanoates from biomass with ozone. 6,368,836,
El-Hadi A, Schnabel R, Straube E, Müller G, Henning S (2002) Correlation between degree of crystallinity, morphology, glass temperature, mechanical properties and biodegradation of poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) PHAs and their blends. Polym Test 21(6):665–674
Ojumu T, Yu J, Solomon B (2004) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates, a bacterial biodegradable polymers. Afr J Biotechnol 3(1):18–24
Poirier Y, Nawrath C, Somerville C (1995) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates, a family of biodegradable plastics and elastomers, in bacteria and plants. Biotechnology (N Y) 13(2):142
Brandi H, Bachofen R, Mayer J, Wintermantel E (1995) Degradation and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Can J Microbiol 41(13):143–153
Mergaert J, Webb A, Anderson C, Wouters A, Swings J (1993) Microbial degradation of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(10):3233–3238
Lee SY (1996) Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol Bioeng 49(1):1–14
Philip S, Keshavarz T, Roy I (2007) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: biodegradable polymers with a range of applications. J Chem Technol Biotechnol Int Res Process Environ Clean Technol 82(3):233–247
Jendrossek D, Handrick R (2002) Microbial degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Annu Rev Microbiol 56(1):403–432
Jendrossek D, Schirmer A, Schlegel H (1996) Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46(5–6):451–463
Saito Y, Doi Y (1994) Microbial synthesis and properties of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) in Comamonas acidovorans. Int J Biol Macromol 16(2):99–104
Kumar S, Thakur K (2017) Bioplastics-classification, production and their potential food applications. J Hill Agric 8(2):118–129
Volova T, Gladyshev M, Trusova MY, Zhila N (2006) Degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates and the composition of microbial destructors under natural conditions. Microbiology 75(5):593–598
Shrivastav A, Kim H-Y, Kim Y-R (2013) Advances in the applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles for novel drug delivery system. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–12
Brigham CJ, Sinskey AJ (2012) Applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates in the medical industry. Int J Biotechnol Wellness Indust 1(1):52–60
Mathuriya AS, Yakhmi J (2017) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: biodegradable plastics and their applications. Handbook of Ecomaterials:1–29
Kavitha G, Rengasamy R, Inbakandan D (2018) Polyhydroxybutyrate production from marine source and its application. Int J Biol Macromol 111:102–108
Koller M (2018) Biodegradable and biocompatible polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): auspicious microbial macromolecules for pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications. Molecules 23(2):362
Chen G-Q, Zhang J (2018) Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates as medical implant biomaterials. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(1):1–18
Bugnicourt E, Cinelli P, Lazzeri A, Alvarez VA (2014) Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): review of synthesis, characteristics, processing and potential applications in packaging. Express Polym Lett 8(11):791–808
Poltronieri P, Kumar P (2017) Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) in industrial applications. Handbook of Ecomaterials:1–30
Yeo JCC, Muiruri JK, Thitsartarn W, Li Z, He C (2018) Recent advances in the development of biodegradable PHB-based toughening materials: approaches, advantages and applications. Mater Sci Eng C 92:1092–1116
Zhang M, Thomas NL (2010) Preparation and properties of polyhydroxybutyrate blended with different types of starch. J Appl Polym Sci 116(2):688–694
Lim J, Chong MSK, Teo EY, Chen GQ, Chan JK, Teoh SH (2013) Biocompatibility studies and characterization of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)/polycaprolactone blends. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 101(5):752–761
Khosravi-Darani K, Bucci D (2015) Application of poly (hydroxyalkanoate) in food packaging: improvements by nanotechnology. Chem Biochem Eng Q 29(2):275–285
Gassner F, Owen A (1996) Some properties of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)–poly (3-hydroxyvalerate) blends. Polym Int 39(3):215–219
Li Z, Yang J, Loh XJ (2016) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: opening doors for a sustainable future. NPG Asia Mat 8(4):e265
Chiono V, Ciardelli G, Vozzi G, Sotgiu MG, Vinci B, Domenici C, Giusti P (2008) Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/poly (ϵ-caprolactone) blends for tissue engineering applications in the form of hollow fibers. J Biomed Mat Res Part A Off J Soc Biomat, Jpn Soc Biomat, Aus Soc Biomat Korean Soc Biomat 85(4):938–953
Yadav A, Mangaraj S, Singh R, Kumar N, Arora S (2018) Biopolymers as packaging material in food and allied industry. Int J Chem Stud 6(2):2411–2418
Tripathi AD, Raj Joshi T, Kumar Srivastava S, Darani KK, Khade S, Srivastava J (2019) Effect of nutritional supplements on bio-plastics (PHB) production utilizing sugar refinery waste with potential application in food packaging. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 49(6):567–577
Liu L (2006) Bioplastics in food packaging: innovative technologies for biodegradable packaging. San Jose State Univ Pack Eng 13:1348–1368
Peelman N, Ragaert P, De Meulenaer B, Adons D, Peeters R, Cardon L, Van Impe F, Devlieghere F (2013) Application of bioplastics for food packaging. Trends Food Sci Technol 32(2):128–141
Ravindran R, Jaiswal AK (2016) Exploitation of food industry waste for high-value products. Trends Biotechnol 34(1):58–69
Nielsen C, Rahman A, Rehman AU, Walsh MK, Miller CD (2017) Food waste conversion to microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microb Biotechnol 10(6):1338–1352
Zhang J, Shishatskaya EI, Volova TG, da Silva LF, Chen G-Q (2018) Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) for therapeutic applications. Mater Sci Eng C 86:144–150
Nigmatullin R, Thomas P, Lukasiewicz B, Puthussery H, Roy I (2015) Polyhydroxyalkanoates, a family of natural polymers, and their applications in drug delivery. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90(7):1209–1221
Wu Q, Wang Y, Chen G-Q (2009) Medical application of microbial biopolyesters polyhydroxyalkanoates. Artif Cells, Blood Substitutes, Biotechnol 37(1):1–12
Mukheem A, Hossain M, Shahabuddin S, Muthoosamy K, Manickam S, Sudesh K, Saidur R, Sridewi N, Campus NM (2018) Bioplastic Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): recent advances in modification and medical applications
Okun MS, Boothby LA, Bartfield RB, Doering PL (2001) GHB: an important pharmacologic and clinical update. J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(2):167–175
Utsunomia C, Ren Q, Zinn M (2020) Poly (4-Hydroxybutyrate): current state and perspectives. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:257
Masood F (2016) Polymeric nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery system for cancer therapy. Mater Sci Eng C 60:569–578
Shrivastav A, Kim H-Y, Kim Y-R (2013) Advances in the applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles for novel drug delivery system. Biomed Res Int 2013
Li Z, Loh XJ (2015) Water soluble polyhydroxyalkanoates: future materials for therapeutic applications. Chem Soc Rev 44(10):2865–2879
Wang J, Chu L (2016) Biological nitrate removal from water and wastewater by solid-phase denitrification process. Biotechnol Adv 34(6):1103–1112
Hiraishi A, Khan S (2003) Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates for denitrification in water and wastewater treatment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61(2):103–109
Liu F, Li J, Zhang X (2019) Bioplastic production from wastewater sludge and application. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019. vol 1. IOP Publishing, p 012071
Coats ER, Loge FJ, Wolcott MP, Englund K, McDonald AG (2007) Synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates in municipal wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res 79(12):2396–2403
Basset N, Katsou E, Frison N, Malamis S, Dosta J, Fatone F (2016) Integrating the selection of PHA storing biomass and nitrogen removal via nitrite in the main wastewater treatment line. Bioresour Technol 200:820–829
Lam W, Wang Y, Chan PL, Chan SW, Tsang YF, Chua H, Yu PHF (2017) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) using sludge from different wastewater treatment processes and the potential for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Environ Technol 38(13–14):1779–1791
Grancarić AM, Jerković I, Tarbuk A (2013) Bioplastics in textiles. Polimeri 34(1):9
Chen G-Q (2009) A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio-and materials industry. Chem Soc Rev 38(8):2434–2446
Liu F, Li J, Zhang X (2019) Bioplastic production from wastewater sludge and application. IOP Conf Series Earth Environ Sci 344(1):012071
Koller M, Bona R, Braunegg G, Hermann C, Horvat P, Kroutil M, Martinz J, Neto J, Pereira L, Varila P (2005) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from agricultural waste and surplus materials. Biomacromolecules 6(2):561–565
Amelia TSM, Govindasamy S, Tamothran AM, Vigneswari S, Bhubalan K (2019) Applications of PHA in agriculture. In: Kalia VC (ed) Biotechnological applications of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Springer, Singapore, pp 347–361
Kasirajan S, Ngouajio M (2012) Polyethylene and biodegradable mulches for agricultural applications: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 32(2):501–529
Solaiman DK, Ashby RD, Foglia TA, Marmer WN (2006) Conversion of agricultural feedstock and coproducts into poly (hydroxyalkanoates). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71(6):783–789
Cinelli P, Coltelli MB, Signori F, Morganti P, Lazzeri A (2019) Cosmetic packaging to save the environment: future perspectives. Cosmetics 6(2):26
Sudesh K, Loo CY, Goh LK, Iwata T, Maeda M (2007) The oil-absorbing property of polyhydroxyalkanoate films and its practical application: a refreshing new outlook for an old degrading material. Macromol Biosci 7(11):1199–1205
Gao X, Chen J-C, Wu Q, Chen G-Q (2011) Polyhydroxyalkanoates as a source of chemicals, polymers, and biofuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22(6):768–774
Snell KD, Peoples OP (2009) PHA bioplastic: a value-added coproduct for biomass biorefineries. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining Innov Sustain Econ 3(4):456–467
Wei D-X, Chen C-B, Fang G, Li S-Y, Chen G-Q (2011) Application of polyhydroxyalkanoate binding protein PhaP as a bio-surfactant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(4):1037–1047
Ong SY, Chee JY, Sudesh K (2017) Degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): a review
Aditi S, D’Souza Shalet NM, Pranesh R, Katyayini T (2015) Microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from novel sources: a review. Int J Res Biosci 4:16–28
Poltronieri P (2018) Polyhydroxyalkanoate production in biofermentor monitored through biosensor application. Int J Biosen Bioelectron 4(5):235–240
Chen G-Q, Wu Q (2005) Microbial production and applications of chiral hydroxyalkanoates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(5):592–599
Chee J-Y, Yoga S-S, Lau N-S, Ling S-C, Abed RM, Sudesh K (2010) Bacterially produced polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): converting renewable resources into bioplastics. Curr Res Technol Educ Topics Appl Microbiol Microbial Biotechnol 2:1395–1404
Arora A, Padua GW (2010) Nanocomposites in food packaging. J Food Sci 75(1):R43–R49
Dhingra HK, Priya K (2013) Physiological and molecular identification of polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB) producing microorganisms isolated from root nodules of leguminous plants. Afr J Microbiol Res 7(30):3961–3967
Mascarenhas J, Aruna K (2017) Screening of polyhydroxyalkonates (PHA) accumulating bacteria from diverse habitats. J Global Biosci 6:4835–4848
Lasemi Z, Darzi GN, Baei MS (2013) Media optimization for poly (β-hydroxybutyrate) production using Azotobacter Beijerinckii. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 62(5):265–269
Singh G, Kumari A, Mittal A, Yadav A, Aggarwal NK (2013) Poly β-hydroxybutyrate production by Bacillus subtilis NG220 using sugar industry waste water. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–10
Mercan N, Beyatli Y (2005) Production of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by rhizobium meliloti, R-viciae and Bradyrhizobium japonicum with different carbon and nitrogen sources, and inexpensive substrates. Zuckerindustrie 130(5):410–415
Keenan TM, Tanenbaum SW, Stipanovic AJ, Nakas JP (2004) Production and characterization of poly-β-hydroxyalkanoate copolymers from Burkholderiacepacia utilizing xylose and Levulinic acid. Biotechnol Prog 20(6):1697–1704
Qi Q, Rehm BH (2001) Polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Caulobacter crescentus: molecular characterization of the polyhydroxybutyrate synthase. Microbiology 147(12):3353–3358
Shahid S, Mosrati R, Ledauphin J, Amiel C, Fontaine P, Gaillard J-L, Corroler D (2013) Impact of carbon source and variable nitrogen conditions on bacterial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates: evidence of an atypical metabolism in Bacillus megaterium DSM 509. J Biosci Bioeng 116(3):302–308
Gomaa EZ (2014) Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) by Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli grown on cane molasses fortified with ethanol. Braz Arch Biol Technol 57(1):145–154
Bhattacharyya A, Pramanik A, Maji SK, Haldar S, Mukhopadhyay UK, Mukherjee J (2012) Utilization of vinasse for production of poly-3-(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) by Haloferax mediterranei. AMB Express 2(1):34
Quillaguaman J, Hashim S, Bento F, Mattiasson B, Hatti-Kaul R (2005) Poly (β-hydroxybutyrate) production by a moderate halophile, Halomonas boliviensis LC1 using starch hydrolysate as substrate. J Appl Microbiol 99(1):151–157
Kulkarni S, Kanekar P, Nilegaonkar S, Sarnaik S, Jog J (2010) Production and characterization of a biodegradable poly (hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)(PHB-co-PHV) copolymer by moderately haloalkalitolerant Halomonas campisalis MCM B-1027 isolated from Lonar Lake, India. Bioresour Technol 101(24):9765–9771
Biswas A, Patra A, Paul A (2009) Production of poly-3-hydroxyalkanoic acids by a moderately halophilic bacterium, Halomonas marina HMA 103 isolated from solar saltern of Orissa, India. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 56(2):125–143
Koller M, Hesse P, Bona R, Kutschera C, Atlic A, Braunegg G (2007) Potential of various archae-and eubacterial strains as industrial polyhydroxyalkanoate producers from whey. Macromol Biosci 7(2):218–226
Bourque D, Pomerleau Y, Groleau D (1995) High-cell-density production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) from methanol by Methylobacterium extorquens: production of high-molecular-mass PHB. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44(3–4):367–376
Smit A-M, Strabala TJ, Peng L, Rawson P, Lloyd-Jones G, Jordan TW (2012) Proteomic phenotyping of Novosphingobium nitrogenifigens reveals a robust capacity for simultaneous nitrogen fixation, polyhydroxyalkanoate production, and resistance to reactive oxygen species. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(14):4802–4815
Yamane T, Chen X, Ueda S (1996) Growth-associated production of poly (3-Hydroxyvalerate) from n-Pentanol by a methylotrophic bacterium, Paracoccus denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(2):380–384
Jau M-H, Yew S-P, Toh PS, Chong AS, Chu W-L, Phang S-M, Najimudin N, Sudesh K (2005) Biosynthesis and mobilization of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)[P (3HB)] by Spirulina platensis. Int J Biol Macromol 36(3):144–151
Abdel-Rahman MA, Desouky SE-S, Azab MS, Esmael ME (2017) Fermentative production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from glycerol by Zobellella taiwanensis Azu-IN1. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 5(05):16–25
Kunasundari B, Sudesh K (2011) Isolation and recovery of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Express Polym Lett 5(7):620–634
Wei L, McDonald AG, Stark NM (2015) Grafting of bacterial polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) onto cellulose via in situ reactive extrusion with dicumyl peroxide. Biomacromolecules 16(3):1040–1049
Verhoogt H, Ramsay B, Favis B (1994) Polymer blends containing poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) s. Polymer 35(24):5155–5169
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the teaching and non-teaching staff of the Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology (Gujarat University) for the preparation of this manuscript. The authors would also like to appreciate the assistance provided by Mr. Rohit Patel at revision stage.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KP and RN have written the manuscript. AS and DG suggested changes and rearrangement of the manuscript. PP contributed in Figure designing whereas MS reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prajapati, K., Nayak, R., Shukla, A. et al. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: An Exotic Gleam in the Gloomy Tale of Plastics. J Polym Environ 29, 2013–2032 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-02025-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-02025-x