Abstract
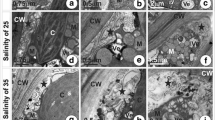
Although the thin-blade strain (HR-5) of Pyropia haitanensis could be cultivated in the south coast of China, the effect of low-salt tolerance on it is not clear. In this study, the conchospores and blades of the wild cultivated strain (WT-10) of P. haitanensis and HR-5 strain were cultured in media with salinity of 26‰, 10‰, and 3‰, respectively. The results illustrated that: After being cultured for 7 days, the survival percentages of conchospores were not significantly different between WT-10 and HR-5 at the salinity of 26‰ and 10‰ (P > 0.05), but the survival percentage was 60.8% higher in the latter than in the former at the salinity of 3‰ (P < 0.01). When the 25-day-old blades of WT-10 and HR-5 were cultured at the salinity of 26‰, 10‰, and 3‰ for another 20 days, the specific growth rates of the blades length in HR-5 were similar to WT-10, respectively. The contents of total phycobiliprotein of the HR-5 were 127.9, 88.7, and 83.0 mg/g, respectively, which were 1.8, 1.7, and 2.1 times those of the WT-10, showing highly significant differences (P < 0.01). In addition, with the decrease of culture salinity, the Fv/Fm values of WT-10 and HR-5 gradually decreased, but the reduction rate between the two strains was not significantly different (P > 0.05). The above results indicated that the low-salt tolerance of conchospores and blades of HR-5 was not weaker than that of WT-10, which provided a theoretical basis for the management mode when continuous precipitation was encountered in the cultivation process of HR-5 strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao YZ, Ding HC, Zhao S, Yang XW, Yan XH (2019) Cytological studies on Pyropia suborbiculata. J Appl Phycol 31:4049–4060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01835-4
Chen CS et al (2009) Selective breeding and comparison of economic traits of the new thin-thallus strain Porphyra haitanensis. Prog Fish Sci 30:100–105. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2009.02.017
Chen SS, Ding HC, Yan XH (2016) Isolation and characterization of an improved strain of Porphyra chauhanii (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) with high-temperature resistance. J Appl Phycol 28:3031–3041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0803-x
Ding HC, Yan XH (2019) Advances in Pyropia (formerly Porphyra) genetics and breeding. J Fish Sci China 26:592–603. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.19024
Ding HC, Lv F, Wu HX, Yan XH (2018) Selection and characterization of an improved strain produced by interspecies hybridization between Pyropia sp. from India and Pyropia haitanensis from China. Aquaculture 491:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.03.015
Ding HC, Wang TG, Zhang P, Lu YD, Yan XH (2020) High-temperature resistance of the thin-blade strain of Pyropia haitanensis and its pilot cultivation in mariculture farm. J Appl Phycol 32:2261–2270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01885-8
Fisheries and Fisheries Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture (2017) China fishery statistical yearbook in 2017. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, China, p 46
Hill DR, Keenan TW, Helm RF, Potts M, Crowe LM, Crowe JH (1997) Extracellular polysaccharide of Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria) inhibits fusion of membrane vesicles during desiccation. J Appl Phycol 9:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007965229567
Huang LB, Huang W, Yan XH (2020) Low-salinity tolerance of two high-temperature resistant strains in Pyropia yezoensis. J Fish China 44:222–233. https://doi.org/10.11964/jfc.20190311687
Jahnke LS, White AL (2003) Long-term hyposaline and hypersaline stresses produce distinct antioxidant responses in the marine alga Dunaliella tertiolecta. J Plant Physiol 160:1193–1202. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-01068
Kim EY, Choi YH, Nam TJ (2018) Identification and antioxidant activity of synthetic peptides from phycobiliproteins of Pyropia yezoensis. Int J Mol Med 42:789–798. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3650
Kitade Y, Miyabe Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeda H, Shimizu T, Yasui H, Kishimura H (2017) Structural characteristics of phycobiliproteins from red alga Mazzaella japonica. J Food Biochem e12436. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12436
Li B, Xu Y, Ji DH, Zhang Y, Xie CT (2013) Effects of high temperature and non-aeration stress on the quality of Porphyra haitanensis. Prog Fish Sci 34:104–110. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2013.03.014
Liang Y et al (2009) Research on the main economic traits of the new strain of high quality Porphyra haitanensis. Prog Fish Sci 30:108–116. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2009.04.017
Liu QM, Xu SS, Li L, Pan TM, Shi CL, Liu H, Cao MJ, Su WJ, Liu GM (2017) In vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory activity of sulfated polysaccharide from Porphyra haitanensis. Carbohyd Polym 165:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.032
Morant-Manceau A, Pradier E, Tremblin G (2004) Osmotic adjustment, gas exchanges and chlorophyll fluorescence of a hexaploid triticale and its parental species under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 161:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-00963
Stein JR (1973) Handbook of phycological methods: culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 289–311
Tamaru Y, Takani Y, Yoshida T, Sakamoto T. (2005) Crucial role of extracellular polysaccharides in desiccation and freezing tolerance in the terrestrial Cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7327–7333. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.7327-7333.2005
Tan YH, Huang LB, Yan XH (2014) Selection and characterization of a low-salinity tolerant strain in Pyropia haitanensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Oceanol Limnol Sinica 45:504–512. https://doi.org/10.11693/hyhz20130400022
Venkatraman KL, Mehta A (2019) Health benefits and pharmacological effects of Porphyra species. Plant Food Hum Nutr 74:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-018-0707-9
Wang QX (2005) Development of the processing industry of Porphyra haitanensis in Fujian Province. J Fujian Fish 105:71–74. https://doi.org/10.14012/j.cnki.fjsc.2005.02.017
Wang S, Liang Y (2015) Effects of salt stress on the growth and chlorophyll fluorescence of Dunaliella salina. Period Ocean Univ China 45:33–38
Wang SJ, Zhang XP, Xu ZD, Sun YL (1986) A study on the cultivation of the vegetative cells and protoplasts of Pyropia haitanensis I. Oceanol Limnol Sinica 17:217–221
Wu HL, Kim JK, Huo YZ, Zhang JH, He PM (2017) Nutrient removal ability of seaweeds on Pyropia yezoensis aquaculture rafts in China’s radial sandbanks. Aquat Bot 137:72–79. 10. 1016/j.aquabot.2016.11.011
Xu Y, Wang WL, Xu K, Xu Y, Ji DH, Chen CS, Xie CT (2018) Effect of different saline stress on physiological indexes of Pyropia haitanensis. J Appl Oceanog 37:380–386. 10. 3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.03.010
Yan XH, Jiang HB (1993) Effects of salinity on the growth and development of somatic cells and preliminary observation of lower salinity resistant in Porphyra yezoensis. J Shanghai Fish Univ 2:34–40
Funding
This study was supported by the Open Project Fund for the Key Laboratory of Healthy Mariculture for the East China Sea, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (2020ESHML05), the Startup Foundation for Young Teachers of Shanghai Ocean University (A2-2006-20-200301), the Major Science and Technology Specific Program of Zhejiang Province (2016C02055-6), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0900606).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that the manuscript submitted is their own original work and all authors have approved the submission. The manuscript has not been published elsewhere. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Huang, L. & Yan, X. Low-salt tolerance of the thin-blade strain in Pyropia haitanensis. Aquacult Int 29, 387–397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00637-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00637-7