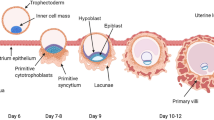
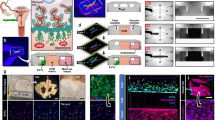
Abstract
Research into the human placenta’s complex functioning is complicated by a lack of suitable physiological in vivo models. Two complementary approaches have emerged recently to address these gaps in understanding, computational in silico techniques, including multi-scale modeling of placental blood flow and oxygen transport, and cellular in vitro approaches, including organoids, tissue engineering, and organ-on-a-chip models. Following a brief introduction to the placenta’s structure and function and its influence on the substantial clinical problem of preterm birth, these different bioengineering approaches are reviewed. The cellular techniques allow for investigation of early first-trimester implantation and placental development, including critical biological processes such as trophoblast invasion and trophoblast fusion, that are otherwise very difficult to study. Similarly, computational models of the placenta and the pregnant pelvis at later-term gestation allow for investigations relevant to complications that occur when the placenta has fully developed. To fully understand clinical conditions associated with the placenta, including those with roots in early processes but that only manifest clinically at full-term, a holistic approach to the study of this fascinating, temporary but critical organ is required.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, Y., A. Carnicer-Lombarte, L. Gardner, J. Thomas, J. J. Brosens, A. Moffett, A. M. Sharkey, K. Franze, G. J. Burton, and M. L. Oyen. Tissue stiffness at the human maternal-fetal interface. Hum. Reprod. 34:1999–2008, 2019.
Abbas, Y., C. M. Oefner, W. J. Polacheck, L. Gardner, L. Farrell, A. Sharkey, R. Kamm, A. Moffett, and M. L. Oyen. A microfluidic assay to study invasion of human placental trophoblast cells. J. R. Soc. Interface 14:20170131, 2017.
Abbas, Y., M. Y. Turco, G. J. Burton, and A. Moffett. Investigation of human trophoblast invasion in vitro. Hum. Reprod. Update. 26:501–513, 2020.
Abbas, Y., L. G. Brunel, M. S. Hollinshead, R. C. Fernando, L. Gardner, I. Duncan, A. Moffett, S. Best, M. Y. Turco, G. J. Burton, and R. E. Cameron. Generation of a three-dimensional collagen scaffold-based model of the human endometrium. Interface Focus. 10:20190079, 2020.
Acharya, G., J. Aplin, P. Brownbill, J. Bulmer, G. Burton, L. Chamley, I. Chernyavsky, A. Clark, S. Collins, E. Cottrell, M. Dilworth, D. Elad, M. Filoche, N. Hannan, A. E. P. Heazell, O. Jensen, E. D. Johnstone, L. Leach, R. Lewis, T. Morgan, J. Myers, G. Nye, M. Oyen, C. Salafia, H. Schneider, and P. O’Tierney-Ginn. IFPA meeting 2017 workshop report: Clinical placentology, 3D structure-based modeling of placental function, placental bed, and treating placental dysfunction. Placenta 64(Supp. 1):S4–S8, 2018.
Acar, B. S., M. Meric, and V. Esat. Hybrid foetus with an FE head for a pregnant occupant model for vehicle safety investigations. Int. J. Crashworthiness 23:540–548, 2018.
Alzamil, L., K. Nikolakopoulou, and M. Y. Turco. Organoid systems to study the human female reproductive tract and pregnancy. Cell Death Differ. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0565-5.
Arumugasaamy, N., K. D. Rock, C.-Y. Kuo, T. L. Bale, and J. P. Fisher. Microphysiological systems of the placental barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.08.010.
Auriault, F., L. Thollon, J. Peres, and M. Behr. Adverse fetal outcome in road accidents: Injury mechanism study and injury criteria development in a pregnant woman finite element model. Accid. Anal. Prev. 97:96–102, 2016.
Ban, Z., F. Knoespel, and M. R. Schneider. Shedding light into the black box: advances in in vitro systems for studying implantation. Dev. Biol. 463:1–10, 2020.
Bappoo, N., L. J. Kelsey, L. Parker, T. Crough, C. M. Moran, A. Thomson, M. C. Holmes, C. S. Wyrwoll, and B. J. Doyle. Viscosity and haemodynamics in a late gestation rat feta-placental arterial network. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 16:1361–1372, 2017.
Bartels, H.C., J. D. Postle, P. Downey, and D. J. Brennan. Placenta accrete spectrum: A review of pathology, molecular biology, and biomarkers. Disease Markers. 1507674, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1507674.
Belfort, M. A. Indicated preterm birth for placenta accrete. Semin. Perinatol. 35:252–256, 2011.
Berendsen, J. T. W., S. A. Kruit, N. Atak, E. Willink, and L. I. Segerink. Flow-free microfluidic device for quantifying chemotaxis in spermatozoa. Anal. Chem. 92:3302–3306, 2020.
Bell, AW, W. W. Hay, and R. A. Ehrhardt. Placental transport of nutrients and its implications for fetal growth. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 54:401-410, 1999.
Brosens, I., R. Pijnenborg, L. Vercruysse, and R. Romero. The “Great Obstetrical Syndromes” are associated with disorders of deep placentation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 204:193–201, 2011.
Bublitz, M. H., M. Carpenter, and G. Bourjeily. Preterm birth disparities between states in the United States: an opportunity for public health interventions. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 41:38–46, 2020.
Campagnolo, L., V. Lacconi, M. Massimiani, A. Magrini, and A. Pietroiusti. In vitro experimental models to study the efficiency of the placental barrier for environmental toxicants: tumor cell lines versus trophoblast primary cells. Biomed. Prev. Issues. 1:157, 2018.
Carter, A. M. Evolution of factors affecting placental oxygen transfer. Placenta 30:19–25, 2009.
Chernyavsky, I. L., O. E. Jensen, and L. Leach. A mathematical model of intervillous blood flow in the human placentome. Placenta 31:44–52, 2010.
Chua, W., and M. L. Oyen. Do we know the strength of the chorioamnion? A critical review and analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 144(Supp. 1):128–133, 2009.
Clark, A. R., M. Lin, M. Tawhai, R. Saghian, and J. L. James. Multi-scale modelling of the feto-placental vasculature. Interface Focus. 5:20140078, 2015.
Clark, A. R., T. C. Lee, and J. L. James. Computational modeling of the interactions between the maternal and fetal circulations in human pregnancy. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsbm.1502.
Claure, I., D. Anderson, C. M. Klapperich, W. Kuohung, and J. Y. Wong. Biomaterials and contraception: promises and pitfalls. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 48:2113–2131, 2020.
Connolly, A. M., V. L. Katz, K. L. Bash, M. J. McMahon, and W. F. Hansen. Trauma and pregnancy. Am. J. Perinatology. 14:331–336, 1997.
Convery, N., and N. Gadegaard. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2:76–91, 2019.
Cui, Y., H. Zhao, S. We, and X. Li. Human female reproductive system organoids: applications in developmental biology, disease modeling, and drug discovery. Stem Cell. Rev. Rep. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10039-0.
Culhane, J. F., and R. L. Goldenberg. Racial disparities in preterm birth. Semin. Perinatol. 35:234–239, 2011.
Delotte, J., M. Behr, L. Thollon, A. Bongain, and C. Brunet. Does placenta position modify the risk of placental abruption in car crashes? Comp. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 12:399–405, 2009.
DellSchaft, N. S., G. Hutchinson, S. Shah, N. W. Jones, C. Bradley, L. Leach, C. Platt, R. Bowtell, and P. A. Gowland. The haemodynamics of the human placenta in utero. PLoS Biol. 18:e3000676, 2020.
DiGregorio, S. Early: An intimate history of premature birth and what it teaches us about being human. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 2020.
Ding, H., N. P. Illsley, and R. C. Chang. 3D bioprinted GelMA based models for the study of trophoblast cell invasion. Sci. Rep. 9:18854, 2019.
Duncan, J. M. On a lower limit to the power exerted in the function of parturition, trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 24:639–651, 1867.
Dunn, P. M. Leonardo Da Vinci (1452–1519) and reproductive anatomy. Arch. Dis. Child. 77:F249–F251, 1997.
Dunn, P. M. John Whitridge Williams MD (1866-1931) of Baltimore: pioneer of academic obstetrics. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 92:F74–F77, 2007.
Erlich, A., P. Pearce, R. P. Mayo, O. E. Jensen, and I. L. Chernyavsky. Physical and geometric determinants of transport in fetoplacental microvascular networks. Sci. Adv. 5:eaav6326, 2019.
Erlich A, G.A. Nye, P. Brownbill, O.E. Jensen, I.L. Chernyavsky, Quantifying the impact of tissue metabolism on solute transport in feto-placental microvascular networks, Interface Focus 9: 20190021, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsfs.2019.0021
Frey, H. A., and M. A. Klebanoff. The epidemiology, etiology, and costs of preterm birth. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 21:68–73, 2016.
Gargus, E. S., H. B. Rogers, K. E. McKinnon, M. E. Edmonds, and T. K. Woodruff. Engineered reproductive tissues. Nature. Biomed. Eng. 4:381–393, 2020.
Guttmacher, A. E., Y. T. Maddox, and C. Y. Spong. The Human Placenta Project: Placental structure, development, and function in real time. Placenta 35:303–304, 2014.
Haider, S., G. Meinhardt, L. Saleh, V. Kunihs, M. Gamperl, U. Kaindl, A. Ellinger, T. R. Burkard, C. Fiala, J. Pollheimer, S. Mendjan, P. A. Latos, and M. Knöfler. Self-renewing trophoblast organoids recapitulate the developmental program of the Early Human Placenta. Stem Cell Rep. 11:537–551, 2018.
Han, Q., and Y. Du. Advances in the application of biomimetic endometrium interfaces for uterine bioengineering in female infertility. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:153, 2020.
Hill, C. C., and J. Pickinpaugh. Trauma and surgical emergencies in the obstetric patient. Surg. Clin. N Am. 88:421–440, 2008.
Holloway, E. M., M. M. Capeling, and J. R. Spence. Biologically inspired approaches to enhance human organoid complexity. Development 146:dev166173, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.166173.
Huang, Y., B. Agrawal, D. Sun, J. S. Kuo, and J. C. Williams. Microfluidics-based devices: New tools for studying cancer and cancer stem cell migration. Biomicrofluidics 5:13412, 2011.
Hughes, C. S., L. M. Postovit, and G. A. Lajoie. Matrigel: a complex protein mixture required for optimal growth of cell culture. Proteomics 10:1886–1890, 2010.
Jensen, O. E., and I. L. Chernyavsky. Blood flow and transport in the human placenta. Ann Rev Fluid Mech. 51:25–47, 2019.
Jiao, L., E. Ghorani, N. J. Sebire, and M. J. Seckl. Intraplacental choriocarcinoma: systematic review and management guidance. Gynecol. Oncol. 141:624–631, 2016.
Kato, Y., G. J. Burton, and M. L. Oyen. Villous tree model with active contractions for estimating blood flow conditions in the human placenta. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 11:36–48, 2017.
Kaufmann, P., S. Black, and B. Huppertz. Endovascular trophoblast invasion: implications for the pathogenesis of intrauterine growth retardation and pre-eclampsia. Biol. Reprod. 69:1–7, 2003.
Kreuder, A.-E., A. Bolanos-Rosales, C. Palmer, A. Thomas, M.-A. Geiger, T. Lam, A.-K. Amler, U. R. Markert, R. Lauster, and L. Kloke. Inspired by the human placenta: a novel 3D bioprinted membrane system to create barrier models. Scientific Reports. 10:15606, 2020.
Kuo, C.-Y., A. Eranki, J. K. Placone, K. R. Rhodes, H. Aranda-Espinoza, R. Fernandes, J. P. Fisher, and P. C. W. Kim. Development of a 3D printed, bioengineered placenta model to evaluate the role of trophoblast migration in pre-eclampsia. ACS Biomaterials Sci. Eng. 2:1817–1826, 2016.
Kuo, C.-Y., T. Guo, J. Cabrera-Luque, N. Aramugasaamy, L. Bracaglia, A. Garcia-Vivas, M. Santoro, H. Baker, J. Fisher, and P. Kim. Placental basement membrane proteins are required for effective cytotrophoblast invasion in a 3D bioprinted placenta model. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 106:1476–1487, 2018.
Lecarpentier, E., M. Bhatt, G. I. Bertin, B. Deloison, L. J. Salomon, P. Deloron, T. Fournier, A. I. Barakat, and V. Tsatsaris. Computational fluid dynamics simulations of maternal circulation: wall shear stress in the human placenta and its biological implications. PLoS ONE 11:e0147262, 2016.
Lee, J. S., R. Romero, Y. M. Han, H. C. Kim, C. J. Kim, J.-S. Hong, and D. Huh. Placenta-on-a-chip: a novel platform to study the biology of the human placenta. J. Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 29:1046–1054, 2016.
Lewis, R. M., J. K. Cleal, and B. G. Sengers. Placental Perfusion and mathematical modelling. Placenta 93:43–48, 2020.
Liu, J., B. Mosavati, A. V. Oleinikov, and E. Du. Biosensors for detection of human placental pathologies: a review of emerging technologies and current trends. Translat. Res. 213:23–49, 2019.
Ma, T., S.-T. Yang, and D. A. Kniss. Development of an in vitro human placenta model by the cultivation of human trophoblasts in a fiber-based bioreactor system. Tissue Eng. 5:91–102, 1999.
Ma, Z., L. Sagrillo-Fagundes, R. Tran, P. K. Parameshwar, N. Kalashnikov, C. Vaillancourt, and C. Moraes. Biomimetic micropatterned adhesive surfaces to mechanobiologically regulate placental trophoblast fusion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b.19906.
Malhotra, A., B. J. Allison, M. Castillo-Melendez, G. Jenkin, G. R. Polglase, and S. I. Miller. Neonatal morbidities of fetal growth restriction: pathophysiology and impact. Front. Endocrinol. 10:00055, 2019.
Mandt, D., P. Gruber, M. Markovic, M. Tromayer, M. Rothbauer, S. R. A. Krayz, F. Ali, J. V. Hoorick, W. Holnthoner, S. Mühleder, P. Dubruel, S. V. Vlierberghe, P. Ertl, R. Liska, and A. Ovsianikov. Fabrication of biomimetic placental barrier structures within a microfluidic device utilizing two-photon polymerization. Int. J. Bioprint. 4:144, 2018.
Marti-Figueroa, C. R., and R. S. Ashton. The case for applying tissue engineering methodologies to instruct human organoid morphogenesis. Acta Biomater. 54:35–44, 2017.
Mayhew, T. M. Estimating oxygen diffusive conductances of gas-exchange systems: a stereological approach illustrated with the human placenta. Ann. Anatomy 196:34–40, 2014.
Mirbod, P. Analytical model of the feta-placental vascular system: consideration of placental oxygen transport. R. Soc. Open Sci. 5:180219, 2018.
Moffett, A., and C. Loke. Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:584–594, 2006.
Nardozza, L. M., A. C. Caetano, A. C. Zamarian, J. B. Mazzola, C. P. Silva, V. M. Marcal, T. F. Lobo, A. B. Peixoto, and E. Araujo Junior. Fetal growth restriction: current knowledge. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 295:1061–1077, 2017.
Oefner, C. M., A. Sharkey, L. Gardner, H. Critchley, M. L. Oyen, and A. Moffett. Collagen type IV at the fetal-maternal interface. Placenta 36:59–68, 2015.
Parizi, M. I., M. T. Ahmadian, and H. Mohammadi. Rigid-bar loading on pregnant uterus and development of pregnant abdominal response corridor based on finite element biomechanical model. Int. J Num. Methods Biomed. Eng. 36:e3284, 2020.
Pemathilaka, R. L., D. E. Reynolds, and N. N. Hashemi. Drug transport across the human placenta: review of placenta-on-a-chip and previous approaches. Interface Focus. 9:20190031, 2019.
Pemathilaka, R. L., J. D. Caplin, S. S. Aykar, R. Montazami, and N. N. Hashemi. Placenta-on-a-chip: in vitro study of caffeine transport across placental barrier using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Glob. Chall. 3:1800112, 2019.
Plitman Mayo, R., D. S. Charnock-Jones, G. J. Burton, and M. L. Oyen. Three-dimensional modeling of human placental villi. Placenta. 43:54–60, 2016.
Plitman Mayo, R., J. Olsthoorn, D. S. Charnock-Jones, G. J. Burton, and M. L. Oyen. Computational modeling of the structure-function relationship in human placental terminal villi. J. Biomech. 49:3780–3787, 2016.
Plitman Mayo, R. Advances in human placental biomechanics. Comput. Struct. Biol. J. 16:298–306, 2018.
Plitman Mayo, R., Y. Abbas, D. S. Chanock-Jones, G. J. Burton, and G. Marom. Three-dimensional morphological analysis of placental terminal villi. Interface Focus. 9:20190037, 2019.
Quinn, J.-A., F. M. Munoz, B. Gonik, L. Frau, C. Cutland, T. Mallett-Moore, A. Kissou, F. Wittke, M. Das, T. Nunes, S. Pye, W. Watson, A.-M. A. Ramos, J. F. Cordero, W.-T. Huang, S. Kochhar, J. Buttery, Brighton Collaboration Preterm Birth Working Group. Preterm birth: case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunisation safety data. Vaccine. 34:6047–6056, 2016.
Rameshbabu, A. P., P. Ghosh, E. Subramani, K. Bankoti, K. Kapat, S. Datta, P. P. Maity, B. Subramanian, S. Roy, K. Chaudhury, and S. Dhara. Investigating the potential of human placenta-derived extracellular matrix sponges coupled with amniotic membrane-derived stem cells for osteochondral tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 4:613–625, 2016.
Rana, S., E. Lemoine, J. P. Granger, and S. A. Karumanchi. Pre-eclampsia: pathophysiology, challenges, and perspectives. Circ. Res. 124:1094–1112, 2019.
Richardson, L., S. Jeong, S. Kim, A. Han, and R. Menon. Amnion membrane organ-on-chip: an innovative approach to study cellular interactions. FASEB J. 33:8945–8960, 2019.
Richardson, L., S. Kim, R. Menon, and A. Han. Organ-on-chip technology: the future of feto-maternal interface research? Front. Physiol. 11:715, 2020.
Rossi, G., A. Manfrin, and M. P. Lutolf. Progress and potential in organoid research. Nat. Rev. Genet. 19:671–687, 2018.
Sackmann, E. K., A. L. Fulton, and D. J. Beebe. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 507:181–189, 2014.
Sakamoto, J., C. Michels, B. Eisfelder, and N. Joshi. Trauma in pregnancy. Emerg. Med. Clin. North Am. 37:317–338, 2019.
Serov, A. S., C. Salafia, P. Brownbill, D. S. Grebenkov, and M. Filoche. Optimal villi density for maximal oxygen uptake in the human placenta. J. Theor. Biol. 368:133–144, 2015.
Serov, A. S., C. Salafia, D. S. Grebenkov, and M. Filoche. The role of morphology in mathematical models of placental gas exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 120:17–28, 2016.
Shin, Y., S. Han, J. S. Jeon, K. Yamamoto, I. K. Zervantonakis, R. Sudo, R. D. Kamm, and S. Chung. Microfluidic assay for simultaneous culture of multiple cell types on surfaces or within hydrogels. Nat. Protoc. 7:1247–1259, 2012.
Sun, C., K. M. Groom, C. Oyston, L. W. Charley, A. R. Clark, and J. L. James. The placenta in fetal growth restriction: what is going wrong? Placenta 96:10–18, 2020.
Tikkanen, M. Placental abruption: epidemiology, risk factors, and consequences. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 90:140–149, 2011.
Truskey, G. A. Human microphysiological systems and organoids as in vitro models for toxicological studies. Front Public Health. 6:185, 2018.
Tun, W. M., C. H. Yap, S. N. Saw, J. L. James, and A. R. Clark. Differences in placental capillary shear stress in fetal growth restriction may affect endothelial cell function and vascular network formation. Sci. Rep. 9:9876, 2019.
Turco, M. Y., and A. Moffett. Development of the human placenta. Development 146:163428, 2019.
Turco, M. Y., L. Gardner, J. Hughes, T. Cindrova-Davies, M. J. Gomez, L. Farrell, M. Hollinshead, S. G. E. Marsh, J. J. Brosens, H. O. Critchley, B. D. Simons, M. Hemberger, B.-Y. Koo, A. Moffett, and G. J. Burton. Long-term, hormone-responsive organoid cultures of human endometrium in a chemically defined medium. Nat. Cell Biol. 19:568–577, 2017.
Turco, M. Y., L. Gardner, R. G. Kay, R. S. Hamilton, M. Prater, M. S. Hollinshead, A. McWhinnie, L. Esposito, R. Fernando, H. Skelton, F. Reimann, F. M. Gribble, A. Sharkey, S. G. E. Marsh, S. O’Rahilly, M. Hemberger, G. J. Burton, and A. Moffett. Trophoblast organoids as a model for maternal–fetal interactions during human placentation. Nature 564:263–267, 2018.
Vargesson, N. Thalidomide-induced teratogenesis: history and mechanisms. Birth Defects Res. Part C 105:140–156, 2015.
Villar, J., A. T. Papageorghiou, H. E. Knight, M. G. Gravett, J. Iams, S. A. Waller, M. Kramer, J. F. Culhane, F. C. Barros, A. Conde-Agudelo, Z. A. Bhutta, and R. L. Goldenberg. The preterm birth syndrome: a prototype phenotypic classification. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 206:119–123, 2012.
Walani, S. R. Global Burden of Preterm Birth. Int. J. Gynecol Obstet 150:31–33, 2020.
Wang, Z., X. He, H. Qiao, and P. Chen. Global trends of organoid and organ-on-a-chip in the past decade: a bibliometric and comparative study. Tissue Eng. Part A 26:656–671, 2020.
Westerveldt, A. R., and K. M. Myers. Computer modeling tools to understand the causes of preterm birth. Semin. Perinatol. 41:485–492, 2017.
Xiao, S., J. R. Coppeta, H. B. Rogers, B. C. Isenberg, J. Zhu, S. A. Olalekan, K. E. McKinnon, D. Dokic, A. S. Rashedi, D. J. Haisenleder, S. S. Malpani, C. A. Arnold-Murray, K. Chen, M. Jiang, L. Bai, C. T. Nguyen, J. Zhang, M. M. Laronda, T. J. Hope, K. P. Maniar, M. E. Pavone, M. J. Avram, E. C. Sefton, S. Getsios, J. E. Burdette, J. J. Kim, J. T, Borenstein, and T. K. Woodruff. A microfluidic culture model of the human reproductive tract and 28-day menstrual cycle. Nat. Commun. 8:14584, 2017.
Xu, H., X. Liu, and W. Le. Recent advances in microfluidic models for cancer metastasis research. Trends Anal. Chem. 105:1–6, 2018.
Zambuto, S. G., K. B. H. Clancy, and B. A. C. Harley. A gelatin hydrogel to study endometrial angiogenesis and trophoblast invasion. Interface Focus. 9:20190016, 2019.
Zhu, J.-Y., Z.-J. Pang, and Y.-H. Yu. Regulation of trophoblast invasion: the role of matrix metalloproteinases. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 5:e137–e143, 2012.
Zhu, Y., F. Yin, H. Wang, L. Wang, J. Yuan, and J. Qin. Placental barrier-on-a-chip: modeling placental inflammatory responses to bacterial infection. ACS Biomaterials Sci Eng. 4:3356–3363, 2018.
Funding
Funding was provided by the East Carolina University Division of Research, Economic Development and Engagement (REDE) via start-up funds to MLO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Associate Editor Stefan M. Duma oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wheeler, M.L., Oyen, M.L. Bioengineering Approaches for Placental Research. Ann Biomed Eng 49, 1805–1818 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02714-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-020-02714-7