Abstract
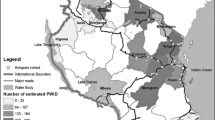
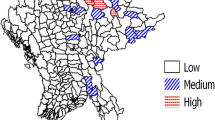
The aim of this cross-sectional study was investigation of geographical distribution and size estimation of people who inject drugs (PWIDs) in Dogonbadan, Iran, in 2018 using geographical mapping method. Data was obtained through interviewing primary and secondary key informants as well as field team observations. Population size was estimated by median in Stata software (version 14). GIS software (version 10.6.1) was used to prepare the density and distribution maps of the hotspots. We identified 52 hotspots of drug users; injection of drugs occurred in 31 of the hotspots. The prevalence of injecting drugs was 232.4 per 100,000 adults, while it was 21.9 and 441.8 among females and males, respectively. A large number of identified hotspots are not covered by harm reduction services. Increasing outreach teams, equipping of harm reduction centers, and moving them to the nearest location to hotspots are suggested.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azhdar, F., Esmaeilnasab, N., Moradi, G., Roshani, D., Ghaderi, E., & Nori, B. (2017). Estimation of intravenous drug users’ population in Kermanshah City, west of Iran in 2016 using capture-recapture method. Journal of Research in Health Sciences, 17(3). Retrieved from http://jrhs.umsha.ac.ir/index.php/JRHS/article/view/3418. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Chen, P., & Jacobson, K. C. (2012). Developmental trajectories of substance use from early adolescence to young adulthood: gender and racial/ethnic differences. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 50(2), 154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2011.05.013.
Emmanuel, F., Blanchard, J., Zaheer, H. A., Reza, T., & Holte-McKenzie, M. (2010). The HIV/AIDS surveillance project mapping approach: an innovative approach for mapping and size estimation for groups at a higher risk of HIV in Pakistan. AIDS, 24, S77–S84. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aids.0000386737.25296.c4.
Ferguson, C. J., & Meehan, D. J. E. P. (2011). With friends like these …: peer delinquency influences across age cohorts on smoking, alcohol and illegal substance use. European Psychiatry, 26(1), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.09.002.
Fizolahi, A., Danesh, P., Heidari, S., Sarokhani, M., & Sayehmiri, K. (2015). Estimation of number of addicts to drug abuse addicts by using capture-recapture method in Ilam City. Journal of Ilam University of Medical Sciences, 23(2), 120–124 Retrieved from http://sjimu.medilam.ac.ir/article-1-1671-en.html. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Ghasemian, R., Najafi, N., & Amirkhanloo, K. (2011). The study of infections due to injection drug abuse in the injecting drug users hospitalized at Imam Khomeini Hospital in Sari and Razi Hospital in Ghaemshahr in 2007-2009. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, 21(83), 9–15 Retrieved from http://jmums.mazums.ac.ir/article-1-684-fa.html. Accessed 22 May 2019.
JafariKhounigh, A., Haghdoost, A. A., SalariLak, S., Zeinalzadeh, A. H., Yousefi-Farkhad, R., Mohammadzadeh, M., & Holakouie-Naieni, K. (2014). Size estimation of most-at-risk groups of HIV/AIDS using network scale-up in Tabriz, Iran. Journal of Clinical Research & Governance, 3(1), 21–26. https://doi.org/10.13183/jcrg.v3i1.80.
Javadi, A., Ataei, B., Yaran, M., Nokhodian, Z., Kassaian, N., Tayeri, K., et al. (2013). Prevalence of HIV infection and related risk factors in Isfahan drop in centers. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences, 29(1), 346–350. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.291(Suppl).3531.
Khajehkazemi, R., Osooli, M., Sajadi, L., Karamouzian, M., Sedaghat, A., Fahimfar, N., Safaie, A., Mostafavi, E., & Haghdoost, A.-A. (2013). HIV prevalence and risk behaviours among people who inject drugs in Iran: the 2010 National Surveillance Survey. Sexually Transmitted Infections, 89(Suppl 3), 29–32. https://doi.org/10.1136/sextrans-2013-051204.
Khorshidi, A., Moradi, A., Shakiba, M., & Rahmani, K. (2015). Estimating the prevalence of drug abuse in Ilam using capture-recapture method. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, 25(124), 194–199.
Lotfi, Z., Gheirati, E., Tajik, F., Tavakoli, Z., Mahmoodi, M., & Holakouie Naieni, K. (2016). Estimation of the population of drug abusers using the network expansion method for assessment of the community in the Golhesar Village, Tehran. Journal of School of Public Health and Institute of Public Health Research, 14(3), 29–43 Retrieved from http://sjsph.tums.ac.ir/article-1-5407-en.html. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Modelling in Health Research Center, Regional Knowledge Hub and WHO Collaborating Center for HIV Surveillance, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University Of Medical Sciences, Kerman. Iran (2014). Estimating the size of drug and alcohol user populations and high-risk sexual groups in Iran. 2015,1–96 [Unpublished data].
Mohammad, K., Farahani, F. K. A., Mohammadi, M. R., Alikhani, S., Zare, M., Tehrani, F., & Ghanbari, H. (2007). Sexual risk-taking behaviors among boys aged 15–18 years in Tehran. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 41(4), 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.05.003.
Ministry of Health and Medical Education of Iran.(2014). Fourth Largest National Stratagem of HIV Infection in the Islamic Republic of Iran.4,1-379 Retrieved from http://port.health.gov.ir/mfdc/hiv/default.aspx. Accessed 22 May 2019.
The Ministry of Health and Medical Education of Iran.(2018). Reporting registered HIV infections in the Islamic Republic of Iran. 2018(4),1–7 Retrieved from Tehran: http://port.health.gov.ir/mfdc/hiv/default.aspx. Accessed 22 May 2019.
National Organization for Civil Registration of Iran .(2015). Population census and housing Islamic Republic Iran. 2016,1–53. Retrieved from Tehran: https://www.amar.org.ir/Portals/0/census/1395/results/ch_nsonvm_95.pdf. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Ndayongeje, J., Msami, A., Laurent, Y. I., Mwankemwa, S., Makumbuli, M., Ngonyani, A. M., et al. (2018). Illicit drug users in the Tanzanian hinterland: population size estimation through key informant-driven hot spot mapping. AIDS and Behavior, 22, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-018-2057-x.
Nguyen, T., Nguyen, L. T., Pham, M. D., Vu, H. H., & Mulvey, K. P. (2012). Methadone maintenance therapy in Vietnam: an overview and scaling-up plan. Advances in Preventive Medicine, 2012, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/732484.
Nikfarjam, A., Shokoohi, M., Shahesmaeili, A., Haghdoost, A. A., Baneshi, M. R., Haji-Maghsoudi, S., Rastegari, A., Nasehi, A. A., Memaryan, N., & Tarjoman, T. (2016). National population size estimation of illicit drug users through the network scale-up method in 2013 in Iran. The International Journal on Drug Policy, 31, 147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2016.01.013.
Pathack, A., Saumtally, A., Soobhany, S., Comins, C. A., Kinoo, S. A., & Emmanuel, F. (2018). Programmatic mapping to determine the size and dynamics of sex work and injecting drug use in Mauritius. African Journal of AIDS Research, 17(2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.2989/16085906.2018.1462216.
Razani, N., Mohraz, M., Kheirandish, P., Malekinejad, M., Malekafzali, H., Mokri, A., McFarland, W., & Rutherford, G. (2007). HIV risk behavior among injection drug users in Tehran, Iran. Addiction, 102(9), 1472–1482. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2007.01914.x.
Razzaghi, E., Rahimi Movaghar, A., Mohammad, K., & Hosseini, M. (2004). A qualitative study of risky sexual behavior in injecting drug users in Tehran. Journal of School of Public Health and Institute of Public Health Research, 2(2), 1–10 Retrieved from http://sjsph.tums.ac.ir/article-1-264-en.html. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Regional Knowledge Hub, and WHO Collaborating Center for HIV Surveillance, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University Of Medical Sciences, Kerman. Iran, Ministry of Health and Medical Education of Iran (2018). Executive protocol Mapping And Size Estimation of key Population In Iran 2(1)–86[In Persian].
Sarrami, H., Ghorbani, M., & Minooei, M. (2013). Survey of four decades of addiction prevalence researches in Iran. Research on Addiction, 7, 29–52 Retrieved from http://etiadpajohi.ir/article-1-286-en.html. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Shokoohi, M., Baneshi, M. R., & Haghdoost, A. A. (2010). Estimation of the active network size of Kermanian males. Addiction and Health, 2(3–4), 81–88.
Shokoohi, M., Baneshi, M. R., & Haghdoost, A.-A. (2012). Size estimation of groups at high risk of HIV/AIDS using network scale up in Kerman, Iran. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 3(7), 471–476.
Somi, M., Noorabadi, G., Ramazani, R., Azimian, F., & Shakib Far, F. (2017). Prevention, control and treatment of hepatitis in Iran. 2018,1–86. Retrieved from http://www.health.gov.ir/mfdc/hd/SitePages/Home.aspx [In Persian]. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) (2017). Ending AIDS progress towards the 90–90–90 targets. 2017,1-198. Retrieved from https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2017/20170720_Global_AIDS_update_2017. Accessed 22 May 2019.
United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (2018). Global overview of drug demand and supply. 2018,1–64. Retrieved from United Nations https://www.unodc.org/wdr2018. Accessed 22 May 2019.
Zamani, S., Vazirian, M., Nassirimanesh, B., Razzaghi, E. M., Ono-Kihara, M., Ravari, S. M., et al. (2010). Needle and syringe sharing practices among injecting drug users in Tehran: a comparison of two neighborhoods, one with and one without a needle and syringe program. AIDS and Behavior, 14(4), 885–890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-008-9404-2.
Funding
This research was supported by the Secretariat of the Counternarcotic Coordinating Council Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, Iran (Grant Number 15/2303162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Sayed Hassan Faghihi, Nima Ghalekhani, Parvin Afsar Kazerooni, and Maryam Nasirian. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sayed Hassan Faghihi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Research Deputy of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran (Ethical code.IR.MUI.REC.1396.3.886). Moreover, all procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faghihi, S.H., Ghalekhani, N., Kazerooni, P.A. et al. Size Estimation of People Who Inject Drugs and Their Geographical Distribution in Dogonbadan, Iran, During 2018: a Mapping Method. Int J Ment Health Addiction 20, 1246–1258 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00439-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00439-1