Abstract
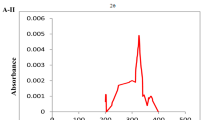
Copper (Cu2+) is an essential micronutrient for cyanobacteria, but it has a toxic effect above a certain threshold. The presence of Cu2+ in water is usually related to human activity due to it being used in pesticides, fertilizer, and algaecides. Previous studies observed that high Cu2+ concentrations stimulated toxin synthesis in cyanobacteria and microalgae. Furthermore, saxitoxins (STXs) can bind to Cu2+ transporters in microorganisms, decreasing the Cu2+ uptake and consequently reducing Cu toxicity. Therefore, considering the invasive capacity of the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii and its potential for STXs production, this study aimed to evaluate the effects of different Cu2+ concentrations in the production of STXs and growth of R. raciborskii. In acclimatized growth conditions, cultures of R. raciborskii strain (ITUC01) were exposed to four different copper concentrations for 20 days (0.8, 8, 80, and 800 × 10−3 μmol L−1 of CuCl2). Raphidiopsis raciborskii growth and physiological responses were evaluated measuring the cell concentration, cell volume, biovolume, chlorophyll a levels, and STXs concentration. Comparing the lowest and highest Cu2+ concentration (0.8 and 800 × 10−3 μmol L−1), it was observed that the increment of Cu2+ in the medium led to a reduced maximum growth rate (μmax), cell concentration, biovolume, and chlorophyll a levels, while the cell volume increased. Despite the low cell concentration and biovolume in the highest Cu2+ condition, it was observed that the STXs volumetric concentration was significantly high on day 5, which is indicative of the fact that increased Cu2+ concentration might induce STXs production in early growth. In addition, our results revealed that STXs production was uncoupled with growth and a reduction of R. raciborskii toxicity from day 5 to 20 was observed. Therefore, the present study identified some of the survival responses of R. raciborskii in Cu-stressed condition and suggested that Cu2+ might be one of the factors that can affect R. raciborskii bloom toxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalde J, Cid A, Reiriz S, Torres E, Herrero C (1995) Response of the marine microalga Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) to copper toxicity in short time experiments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 54:317–324
Aguilera A, Gómez EB, Kaštovský J, Echenique RO, Salerno GL (2018) The polyphasic analysis of two native Raphidiopsis isolates supports the unification of the genera Raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia. 57:130–146
Ahad RIA, Syiem MB (2018) Copper-induced morphological, physiological and biochemical responses in the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum Meg 1. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 17:1077–1086
Alexova R, Fujii M, Birch D, Cheng J, Waite TD, Ferrari BC, Neilan BA (2011) Iron uptake and toxin synthesis in the bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa under iron limitation. Environ Microbiol 13:1064–1077
Anderson DM (1994) Red tides. Sci Am 271:62–68
Baptista MS, Vasconcelos MT (2006) Cyanobacteria metal interactions: requirements, toxicity, and ecological implications. Crit Rev Microbiol 32:127–137
Baron M, Arellano JB, Gorge JL (1995) Copper and photosystem II: a controversial relationship. Physiol Plant 94:174–180
Bittencourt-Oliveira M d C, Molica R (2003) Cianobactéria Invasora - Aspectos moleculares e toxicológicos de Cylindropermopsis raciborskii no Brasil. Rev Biotecnol Ciência e Desenvolv 30:82–90
Boopathi T, Ki JS (2014) Impact of environmental factors on the regulation of cyanotoxin production. Toxins (Basel) 6:1951–1978
Briand JF, Leboulanger C, Humbert JF, Bernard C, Dufour P (2004) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) invasion at mid-latitudes: selection, wide physiological tolerance, or global warming? J Phycol 40:231–238
Burford MA, Davis TW (2011) Physical and chemical processes promoting dominance of the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 29:883–891
Burford MA, Beardall J, Willis A, Orr PT, Magalhaes VF, Rangel LM, Azevedo SMFO, Neilan BA (2016) Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 54:44–53
Carneiro RL, Dos Santos MEV, Pacheco ABF, Azevedo SMFO (2009) Effects of light intensity and light quality on growth and circadian rhythm of saxitoxins production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). J Plankton Res 31:481–488
Carneiro RL, Alípio ACN, Bisch PM, Azevedo SMFO, Pacheco ABF (2011) The inhibitory effect of calcium on Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) metabolism. Braz J Microbiol 42:1547–1559
Carneiro RL, Pacheco ABF, Azevedo SMFO (2013) Growth and saxitoxin production by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) correlate with water hardness. Mar Drugs 11:2949–2963
Casali SP, Dos Santos ACA, Falco PB, Calijuri MC (2017) Influence of environmental variables on saxitoxin yields by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in a mesotrophic subtropical reservoir. J Water Health 15:509–518
Castro D, Vera D, Lagos N, Garcı́a C, Vásquez M (2004) The effect of temperature on growth and production of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins by the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii C10. Toxicon 44:483–489
Chen Y, Yin J, Wei J, Zhang X (2020) FurA-dependent microcystin synthesis under copper stress in Microcystis aeruginosa. Microorganisms 8:832
Cid A, Herrero C, Torres E, Abalde J (1995) Copper toxicity on the marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum: effects on photosynthesis and related parameters. Aquat Toxicol 31:165–174
Cunha DGF, Bottino F, Do Carmo Calijuri M (2012) Can free-floating and emerged macrophytes influence the density and diversity of phytoplankton in subtropical reservoirs? Lake Reserv Manag 28:255–264
Cusick KD, Minkin SC, Dodani SC, Chang C, Wilhelm SW, Sayler GS (2012) Inhibition of copper uptake in yeast reveals the copper transporter Ctr1p as a potential molecular target of saxitoxin. Environ Sci Technol 46:2959–2966
Cusick KD, Wetzel RK, Minkin SC, Dodani SC, Wilhelm SW, Sayler GS (2013) Paralytic shellfish toxins inhibit copper uptake in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1388–1395
Davis TW, Orr PT, Boyer GL, Burford MA (2014) Investigating the production and release of cylindrospermopsin and deoxy-cylindrospermopsin by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii over a natural growth cycle. Harmful Algae 31:18–25
Everson S, Fabbro L, Kinnear S, Wright P (2011) Extreme differences in akinete, heterocyte and cylindrospermopsin concentrations with depth in a successive bloom involving Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Forti) and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenaya and Subba Raju. Harmful Algae 10:265–276
Facey JA, Apte SC, Mitrovic SM (2019) A review of the effect of trace metals on freshwater cyanobacterial growth and toxin production. Toxins 11:643
Fan J, Ho L, Hobson P, Brookes J (2013) Evaluating the effectiveness of copper sulphate, chlorine, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide and ozone on cyanobacterial cell integrity. Water Res 47:5153–5164
Ferrão-Filho A d S, da Silva DAC (2020) Saxitoxin-producing Raphidiopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) inhibits swimming and physiological parameters in Daphnia similis. Sci Total Environ 706:135751
Franklin NM, Stauber JL, Apte SC, Lim RP (2002) Effect of initial cell density on the bioavailability and toxicity of copper in microalgal bioassays. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:742–751
Franqueira D, Orosa M, Torres E, Herrero C, Cid A (2000) Potential use of flow cytometry in toxicity studies with microalgae. Sci Total Environ 247:119–126
García-Villada L, Rico M, Altamirano M, Sánchez-Martín L, López-Rodas V, Costas E (2004) Occurrence of copper resistant mutants in the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa: characterisation and future implications in the use of copper sulphate as algaecide. Water Res 38:2207–2213
Gorham PR, McLachlan J, Hammer UT, Kim WK (1964) Isolation and culture of toxic strains of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. SIL Proceedings, 1922-2010 15:796–804
Griffiths MJ, Garcin C, van Hille RP, Harrison STL (2011) Interference by pigment in the estimation of microalgal biomass concentration by optical density. J Microbiol Methods 85:119–123
Guillard RRL, Kilham P, Jackson TA (1973) Kinetics of silicon-limited growth in the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana Hasle and Heimdal (=Cyclotella nana Hustedt). J Phycol 9:233–237
Hackett JD, Wisecaver JH, Brosnahan ML, Kulis DM, Anderson DM, Bhattacharya D, Plumley FG, Erdner DL (2013) Evolution of saxitoxin synthesis in cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates. Mol Biol Evol 30:70–78
Hamed SM, Selim S, Klöck G, Elgawad H (2017) Sensitivity of two green microalgae to copper stress: growth, oxidative and antioxidants analyses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 144:19–25
Hawkins PR, Putt E, Falconer I, Humpage A (2001) Phenotypical variation in a toxic strain of the phytoplankter, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanophyceae) during batch culture. Environ Toxicol 16:460–467
Hillebrand H, Dürselen CD, Kirschtel D, Pollingher U, Zohary T (1999) Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424
Hrudey S, Burch M, Drikas M, Gregory R (1999) Remedial measures. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. E & FN Spon, London, pp 267–301
Huertas MJ, López-Maury L, Giner-Lamia J, Sánchez-Riego AM, Florencio FJ (2014) Metals in cyanobacteria: analysis of the copper, nickel, cobalt and arsenic homeostasis mechanisms. Life 4:865–886
Humble AV, Gadd GM, Codd GA (1997) Binding of copper and zinc to three cyanobacterial microcystins quantified by differential pulse polarography. Water Res 31:1679–1686
Iwinski KJ, Calomeni AJ, Geer TD, Rodgers JH (2016) Cellular and aqueous microcystin-LR following laboratory exposures of Microcystis aeruginosa to copper algaecides. Chemosphere 147:74–81
Jones GJ, Negri AP (1997) Persistence and degradation of cyanobacterial paralytic shellfish poisons (PSPs) in freshwaters. Water Res 31:525–533
Jones GJ, Orr PT (1994) Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Res 28:871–876
Kaebernick M, Neilan BA (2001) Ecological and molecular investigations of cyanotoxin production. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:1–9
Kumar D, Jha M, Kumar HD (1985) Copper toxicity in the fresh water cyanobacterium Nostoc linckia. J Gen Appl Microbiol 31:165–169
Küpper H, Küpper F, Spiller M (1998) In situ detection of heavy metal substituted chlorophylls in water plants. Photosynth Res 58:123–133
Long BM, Jones GJ, Orr PT (2001) Cellular microcystin content in N-limited Microcystis aeruginosa can be predicted from growth rate. Microbiology 67:278–283
Long M, Holland A, Planquette H, Santana DG, Whitby H, Soudant P, Sarthou G, Hégaret H, Jolley DF (2019) Effects of copper on the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum and its allelochemical potency. Aquat Toxicol 210:251–261
Machado MD, Soares EV (2014) Modification of cell volume and proliferative capacity of Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata cells exposed to metal stress. Aquat Toxicol 147:1–6
Maldonado MT, Hughes MP, Rue EL, Wells ML (2002) The effect of Fe and Cu on growth and domoic acid production by Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries and Pseudo-nitzschia australis. Limnol Oceanogr 47:515–526
Martínez-Ruiz EB, Martínez-Jerónimo F (2016) How do toxic metals affect harmful cyanobacteria? An integrative study with a toxigenic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to nickel stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:36–46
Mesquita MCB, Lürling M, Dorr F, Pinto E, Marinho MM (2019) Combined effect of light and temperature on the production of saxitoxins in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains. Toxins 11:38
Moeller PDR, Beauchesne KR, Huncik KM, Davis WC, Christopher SJ, Riggs-Gelasco P, Gelasco AK (2007) Metal complexes and free radical toxins produced by Pfiesteria piscicida. Environ Sci Technol 41:1166–1172
Murphy A, Taiz L (1997) Correlation between potassium efflux and copper sensitivity in 10 Arabidopsis ecotypes. New Phytol 136:211–222
Nogueira PFM, Lombardi AT, Nogueira MM (2012) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii exudate-Cu complexes: impact on copper dynamics and bioavailability in an aquatic food chain. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1245–1251
Nongrum NA, Syiem MB (2012) Effects of copper ion (Cu2+) on the physiological and biochemical activities of the cyanobacterium Nostoc ANTH. Environ Eng Res 17:63–67
Nusch EA (1980) Comparison of different methods for chlorophyll and pheopigment determination. Arch Hydrobiol Beih 14:14–36
Orr PT, Willis A, Burford MA (2018) Application of first order rate kinetics to explain changes in bloom toxicity—the importance of understanding cell toxin quotas. J Oceanol Limnol 36:1063–1074
Padisák J (1997) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Arch Hydrobiol Suppl Monogr Stud 107:563–593
Pierangelini M, Sinha R, Willis A, Burford MA, Orr PT, Beardall J, Neilan BA (2015) Constitutive cylindrospermopsin pool size in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii under different light and CO2 partial pressure conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:3069–3076
Polyak Y, Zaytseva T, Medvedeva N (2013) Response of toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to environmental pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1494
Pomati F, Rossetti C, Manarolla G, Burns BP, Neilan BA (2004) Interactions between intracellular Na+ levels and saxitoxin production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3. Microbiology 150:455–461
Qian H, Yu S, Sun Z, Xie X, Liu W, Fu Z (2010) Effects of copper sulfate, hydrogen peroxide and N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on oxidative stress and the expression of genes involved photosynthesis and microcystin disposition in Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 99:405–412
Rangel LM, Ger KA, Silva LHS, Soares MCS, Faassen EJ, Lürling M (2016) Toxicity overrides morphology on Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii grazing resistance to the calanoid copepod Eudiaptomus gracilis. Microb Ecol 71:835–844
Sabatini SE, Juárez ÁB, Eppis MR, Bianchi L, Luquet CM, Molina MCR (2009) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in two green microalgae exposed to copper. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1200–1206
Shavyrina OB, Gapochka LD, Azovskii AI (2001) Development of tolerance for copper in cyanobacteria repeatedly exposed to its toxic effect. Biol Bull 28:227–232
Sunda WG, Price NM, Morel FMM (2005) Trace metal ion buffers and their use in culture studies. In: Andersen RA (ed) Algal Culturing Techniques. Academic Press, Burlington, pp 35–63
Surosz W, Palinska KA (2004) Effects of heavy-metal stress on cyanobacterium Anabaena flos-aquae. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:40–48
Tonietto AE, Lombardi AT, Vieira AAH, Parrish CC, Choueri RB (2014) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) exudates: chemical characterization and complexation capacity for Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb. Water Res 49:381–390
Vargas SR, dos Santos PV, Bottino F, Calijuri MC (2019) Effect of nutrient concentration on growth and saxitoxin production of Raphidiopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyta) interacting with Monoraphidium contortum (Chlorophyceae). J Appl Phycol 32:421–430
Vico P, Bonilla S, Cremella B, Aubriot L, Iriarte A, Piccini C (2020) Biogeography of the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis (Cylindrospermopsis) raciborskii: integrating genomics, phylogenetic and toxicity data. Mol Phylogenet Evol 148:106824
Wang J, Salata JJ, Bennett PB (2003) Saxitoxin is a gating modifier of hERG K+ channels. J Gen Physiol 121:583–598
Wang T, Hu Y, Zhu M, Yin S (2020) Integrated transcriptome and physiology analysis of Microcystis aeruginosa after exposure to copper sulfate. J Oceanol Limnol 38:102–113
Wells ML, Maldonado MT, Hughes MP, Rue EL (2002) The effect of Fe and Cu on growth and domoic acid production by Pseudonitzschia multiseries and Pseudonitzschia australis. Limnol Oceanogr 47:515–526
Willis A, Adams MP, Chuang AW, Orr PT, O’Brien KR, Burford MA (2015) Constitutive toxin production under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes of three ecotypes of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju. Harmful Algae 47:27–34
Zhou S, Shao Y, Gao N, Deng Y, Qiao J, Ou H, Deng J (2013) Effects of different algaecides on the photosynthetic capacity, cell integrity and microcystin-LR release of Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Total Environ 463–464:111–119
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technicians and graduate students from the Department of Hydraulics and Sanitation for the technical support and discussions.
Funding
This work was supported by FAPESP (São Paulo Research Foundation) (grant 2008/55636-9) and CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development) (grant 131178/2012-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 37 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giraldi, L.A., Vargas, S.R., Santos, P.V. et al. Growth and saxitoxin production responses to copper (CuCl2) exposure by the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii. J Appl Phycol 33, 891–900 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02324-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02324-9