Abstract
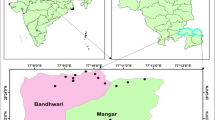
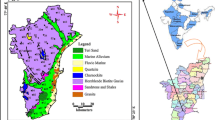
In this study, the impact of MSW landfill on the surface and groundwater resources pollution in Tehran Province was investigated using a multivariate statistical technique concerning multiple water quality indicators. To assess the role of the landfill on surface and groundwater pollution, a statistical approach was designed in a way that the distance from landfill was considered as the main factor while sub-factors were various physicochemical parameters of water samples collected from groundwater and surface water. Sampling took place for two years on a monthly basis. Results of groundwater samples indicated that SO42− (254 mg/l), PO43− (0.13 mg/l) and EC (1177.9 µs/cm) exceeded their acceptable limits of drinking water standard in near the landfill. For groundwater, all water quality parameters (except heavy metals, PO43−, SO42−, Na + , Mg2+, and pH) were higher adjacent to the landfill, than upstream and downstream locations (significance level P < 0.05). Concentrations of CU (0.32 mg/l), Fe (5.4 mg/l), NO3− (37 mg/l), BOD (244 mg/l), COD (340 mg/l), PO43− (8.5 mg/l), TDS (4345 mg/l) and the EC (8460 µs/cm) of the surface water at the near-landfill station exceeded their acceptable limits of the prescribed standard. Moreover, the statistical analysis carried out revealed that there is a direct relationship between the water quality parameters and the physicochemical characteristics of the leachate from the landfill. This study showed the usefulness of multivariate statistical techniques for the analysis and process of complex data sets and the identification of pollution sources. Based on the results obtained in this research, it is recommended to implement leachate collection and treatment facilities on-site as a high priority.
Highlights:
Impact of Robatkarim Landfill on Groundwater and Surface Water Quality
Studying A Wide Range of Important Parameters in Water Quality
Observing Higher Amount of Pollutants in Leachate Compared to Standards
Descending of Pollutants Concentration in Farther Areas from the Landfill

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelwaheb A, Moncef Z, Hamed BD (2012) Landfill leachate generation and its impact on water at an urban landfill (Jebel Chakir, Tunisia). Hydrol Curr Res 3:1–5
Ahani M, Arjmandi R, Hoveidi H, Ghodousi J, Lavasani MM (2019) A multi-objective optimization model for municipal waste management system in Tehran city, Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:5447–5462
Al-Sabahi E, Rahim SA, Wan Z, Al-Nozaily F, Alshaebi F (2009) The characteristics of leachate and groundwater pollution at municipal solid waste landfill of Ibb City,Yemen. Am J Environ Sci 5:256–266
Alemayehu T, Mebrahtu G, Hadera A, Bekele DN (2019) Assessment of the impact of landfill leachate on groundwater and surrounding surface water: a case study of Mekelle city, Northern Ethiopia. Sustain Water Resour Manag 5:1641–1649
APHA (2012) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. In: 22nd. edn. American Water Works Association (AWWA), American Public Health Association (APHA), Water Environment Federation: Washington DC
Ayers R, Westcott D (1985) Water quality for agriculture (No. 29): food and agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome, Italy
Aziz SQ, Aziz HA, Yusoff MS, Bashir MJ, Umar M (2010) Leachate characterization in semi-aerobic and anaerobic sanitary landfills: a comparative study. J Environ Manage 91:2608–2614
Bora M, Goswami DC (2017) Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index (WQI): case study of the Kolong River, Assam, India. Appl Water Sci 7:3125–3135
Chofqi A, Younsi A, Mania J, Mudry J, Veron A (2004) Environmental impact of an urban landfill on a coastal aquifer (El Jadida, Morocco). J Afr Earth Sci 39:509–516
de Medeiros EP et al (2017) Environmental monitoring of water resources around a municipal landfill of the Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21398–21411
DOE (2016) Iranian Standard of Wastewater Quality. https://doe.ir/portal/file/?944184/%D8%A7%D8%B3%D8%AA%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%AF-%D8%AE%D8%B1%D9%88%D8%AC%D9%8A-%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B6%D9%84%D8%A7%D8%A8.pdf
Eggen T, Moeder M, Arukwe A (2010) Municipal landfill leachates: a significant source for new and emerging pollutants. Sci Total Environ 408:5147–5157
El-Salam MMA, Abu-Zuid GI (2015) Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: a case study in Egypt. J Adv Res 6:579–586
Fatta D, Papadopoulos A, Loizidou M (1999) A study on the landfill leachate and its impact on the groundwater quality of the greater area. Environ Geochem Health 21:175–190
Han D, Tong X, Jin M, Hepburn E, Tong C, Song X (2013) Evaluation of organic contamination in urban groundwater surrounding a municipal landfill, Zhoukou, China. Environ Monit Assess 185:3413–3444
Hossain ML, Das SR, Hossain MK (2014) Impact of landfill leachate on surface and ground water quality. J Environ Sci Technol 7:337–346
Johari A, Alkali H, Hashim H, Ahmed SI, Mat R (2014) Municipal solid waste management and potential revenue from recycling in Malaysia. Modern Appl Sci 8:37
Kheradmand S, Karimi-Jashni A, Sartaj M (2010) Treatment of municipal landfill leachate using a combined anaerobic digester and activated sludge system. Waste Manage 30:1025–1031
Kjeldsen P, Barlaz MA, Rooker AP, Baun A, Ledin A, Christensen TH (2002) Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 32:297–336
Laner D, Crest M, Scharff H, Morris JW, Barlaz MA (2012) A review of approaches for the long-term management of municipal solid waste landfills. Waste Manage 32:498–512
Ling C, Zhang Q (2017) Evaluation of surface water and groundwater contamination in a MSW landfill area using hydrochemical analysis and electrical resistivity tomography: a case study in Sichuan province, Southwest China. Environ Monitor Assess 189:140
Longe E, Balogun M (2010) Groundwater quality assessment near a municipal landfill, Lagos, Nigeria. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 2:39–44
Lopez A, Pagano M, Volpe A, Di Pinto AC (2004) Fenton’s pre-treatment of mature landfill leachate. Chemosphere 54:1005–1010
Maqbool F, Bhatti Z, Malik A, Pervez A, Mahmood Q (2011) Effect of landfill leachate on the stream water quality. Int J Environ Res 5:491–500
Mor S, Ravindra K, Dahiya R, Chandra A (2006) Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Environ Monit Assess 118:435–456
Naveen B, Sumalatha J, Malik R (2018) A study on contamination of ground and surface water bodies by leachate leakage from a landfill in Bangalore, India. Int J Geo-Eng 9:27
Pazoki M, Abdoli MA, Karbassi A, Mehrdadi N, Yaghmaeian K (2014) Attenuation of municipal landfill leachate through land treatment. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:12
Przydatek G, Kanownik W (2019) Impact of small municipal solid waste landfill on groundwater quality. Environ Monit Assess 191:169
Renou S, Givaudan J, Poulain S, Dirassouyan F, Moulin P (2008) Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity. J Hazard Mater 150:468–493
Samadder S, Prabhakar R, Khan D, Kishan D, Chauhan M (2017) Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: a case study. Sci Total Environ 580:593–601
Schiopu AM, Gavrilescu M (2010) Options for the treatment and management of municipal landfill leachate: common and specific issues. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 38:1101–1110
Talalaj IA, Biedka P (2016) Use of the landfill water pollution index (LWPI) for groundwater quality assessment near the landfill sites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:24601–24613
USEPA (2018) Drinking Water Standards and Advisory Tables. Office of Water US Environmental protection Agency. Washington DC
Vahabian M, Hassanzadeh Y, Marofi S (2019) Assessment of landfill leachate in semi-arid climate and its impact on the groundwater quality case study: Hamedan, Iran. Environ Monitor Assess 191:109
Varol S, Davraz A (2015) Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: a case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 73:1725–1744
Vasanthi P, Kaliappan S, Srinivasaraghavan R (2008) Impact of poor solid waste management on ground water. Environ Monit Assess 143:227–238
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edition WHO chronicle, vol 38, pp 104–108
Xing W, Lu W, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Deng W, Christensen TH (2013) Environmental impact assessment of leachate recirculation in landfill of municipal solid waste by comparing with evaporation and discharge (EASEWASTE). Waste Manag 33:382–389
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farzaneh, G., Khorasani, N., Ghodousi, J. et al. Assessment of Surface and Groundwater Resources Quality Close to Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Using Multiple Indicators and Multivariate Statistical Methods. Int J Environ Res 15, 383–394 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00307-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00307-9