Abstract
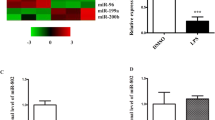
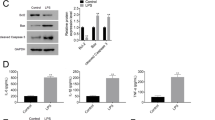
Inflammatory responses play significant role in infectious etiology-induced acute lung injury (ALI). Histone deacetylase 2 is found to be essential and stimulated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI by regulating proinflammatory cytokines. miR-23b has been demonstrated to be downregulated in LPS-induced inflammatory injury. In this study, we aimed to explore the interaction between miR-23b and HDAC2 and their function in LPS-induced ALI. LPS treatment was induced on murine alveolar macrophage cell line MH-S. Level of miR-23b and HDAC2 were determined by real-time PCR or Western blot. Proinflammatory cytokines expression and secretion were detected by real-time PCR and ELISA assay. The levels of miR-23b and HDAC2 were manipulated by transient transfection of miRNA mimics, shRNA or overexpression vector. The interaction between miR-23b and HDAC2 were tested by Luciferase reporter assay. LPS treatment inhibited miR-23b expression, while increased HDAC2 level in MH-S cells. Proinflammatory cytokines were stimulated by LPS treatment. Knockdown of HDAC2 or overexpression of miR-23b significantly repressed the expression of proinflammatory cytokines induced by LPS. miR-23b could suppress HDAC2 expression by directly targeting to its mRNA. LPS treatment stimulated the inflammatory responses in macrophages through inhibition of miR-23b, enhanced HDAC2 expression and inducing the expression of its downstream targets TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Overexpression of miR-23b was sufficient to suppress inflammatory responses by targeting HDAC2, making it a promising therapeutic target to ALI treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.015
Altemeier WA et al (2005) Modulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced gene transcription and promotion of lung injury by mechanical ventilation. J Immunol 175:3369–3376
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:175–205. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123406
Cao J et al (2017) microRNA-23b suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting Pyk2. Biomed Pharmacother 89:642–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.030
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303:83–86. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1091903
Choudhary C et al (2009) Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 325:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1175371
Deng W, Wang DX, Zhang W, Li CY (2011) Regulation of epithelial sodium channel alpha-subunit expression by adenosine receptor A(2)a in alveolar epithelial cells. Chin Med J 124:1551–1555
Deng W, Li CY, Tong J, Zhang W, Wang DX (2012) Regulation of ENaC-mediated alveolar fluid clearance by insulin via PI3K/Akt pathway in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Respir Res 13:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1465-9921-13-29
Fukumoto I et al (2016) The tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster regulates the MET oncogene in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 49:1119–1129. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3602
Goss CH, Brower RG, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD, Network A (2003) Incidence of acute lung injury in the United States. Crit Care Med 31:1607–1611. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000063475.65751.1D
Ishii M et al (2009) Epigenetic regulation of the alternatively activated macrophage phenotype. Blood 114:3244–3254. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-04-217620
Ito K et al (2005) Effect of Ulinastatin, a human urinary trypsin inhibitor, on the oleic acid-induced acute lung injury in rats via the inhibition of activated leukocytes. Injury 36:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2004.06.018
Ivashkiv LB (2013) Epigenetic regulation of macrophage polarization and function. Trends Immunol 34:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2012.11.001
Liu G et al (2009) miR-147, a microRNA that is induced upon Toll-like receptor stimulation, regulates murine macrophage inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:15819–15824. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901216106
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Margueron R, Reinberg D (2010) Chromatin structure and the inheritance of epigenetic information. Nat Rev Genet 11:285–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2752
Matute-Bello G, Winn RK, Martin TR, Liles WC (2004) Sustained lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation in mice is attenuated by functional deficiency of the Fas/Fas ligand system. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:358–361
Mullican SE et al (2011) Histone deacetylase 3 is an epigenomic brake in macrophage alternative activation. Genes Dev 25:2480–2488. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.175950.111
Papamichos-Chronakis M, Peterson CL (2013) Chromatin and the genome integrity network. Nat Rev Genet 14:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3345
Rojas M, Woods CR, Mora AL, Xu J, Brigham KL (2005) Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: structural, functional, and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol 288:L333–341. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00334.2004
Rubenfeld GD et al (2005) Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med 353:1685–1693. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa050333
De Santa F et al (2009) Jmjd3 contributes to the control of gene expression in LPS-activated macrophages. The EMBO journal 28:3341–3352. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.271
Stender JD et al (2012) Control of proinflammatory gene programs by regulated trimethylation and demethylation of histone H4K20. Mol Cell 48:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.07.020
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Baltimore D (2007) MicroRNAs and immunity: tiny players in a big field. Immunity 26:133–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2007.02.005
Ware LB (2006) Pathophysiology of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 27:337–349. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-948288
Ware LB, Matthay MA (2000) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342:1334–1349. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200005043421806
Wu C, Li A, Leng Y, Li Y, Kang J (2012) Histone deacetylase inhibition by sodium valproate regulates polarization of macrophage subsets. DNA Cell Biol 31:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2011.1401
Wu C, Li A, Hu J, Kang J (2018) Histone deacetylase 2 is essential for LPS-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages. Immunol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/imcb.12203
Xiao C, Rajewsky K (2009) MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell 136:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.027
Yang Z, Tang Y, Zhao Q, Lu H, Xu G (2018) Down-regulation of microRNA-23b aggravates LPS-induced inflammatory injury in chondrogenic ATDC5 cells by targeting PDCD4. Iran J Basic Med Sci 21:529–535. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2018.25856.6364
Zhang H et al (2011) Genome-wide functional screening of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer metastasis. Nat Commun 2:554. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1555
Zhou VW, Goren A, Bernstein BE (2011) Charting histone modifications and the functional organization of mammalian genomes. Nat Rev Genet 12:7–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2905
Zhu S et al (2012) The microRNA miR-23b suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-alpha. Nat Med 18:1077–1086. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2815
Zhu T et al (2013) Andrographolide protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inactivation of NF-kappaB. PLoS ONE 8:e56407. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056407
Funding
This work was supported by The Hunan Provincial Natural Science Fund of China (No. 2015JJ2131), The Scientific Research Projects of Hunan Provincial Educational Department (No. 13C890), The Medical Research Plan Projects Foundation of Hunan Provincial Health Department (No. B2014-070), The Scientific Research Fund of Xiangnan University (No. 2011YY47), The Chenzhou Municipal Key Research and Development and Technology Innovation Guiding Funds (No. Zdyf201811), The Research Learning and Innovative Experiment Plan for College Students of Xiangnan University in 2013 (No. 87) and The Research Learning and Innovative Experiment Plan for College Students of Xiangnan University in 2018 (No. 56).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, ZF., Jiang, XH., Liu, H. et al. miR-23b Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Acute Lung Injury via Inhibition of HDAC2. Biochem Genet 59, 604–616 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-10018-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-10018-7