Abstract
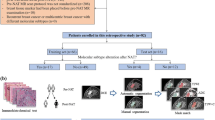
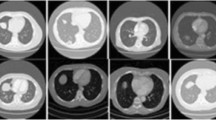
Adenocarcinoma (AC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) are frequent reported cases of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), responsible for a large fraction of cancer deaths worldwide. In this study, we aim to investigate the potential of NSCLC histology classification into AC and SCC by applying different feature extraction and classification techniques on pre-treatment CT images. The employed image dataset (102 patients) was taken from the publicly available cancer imaging archive collection (TCIA). We investigated four different families of techniques: (a) radiomics with two classifiers (kNN and SVM), (b) four state-of-the-art convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with transfer learning and fine tuning (Alexnet, ResNet101, Inceptionv3 and InceptionResnetv2), (c) a CNN combined with a long short-term memory (LSTM) network to fuse information about the spatial coherency of tumor’s CT slices, and (d) combinatorial models (LSTM + CNN + radiomics). In addition, the CT images were independently evaluated by two expert radiologists. Our results showed that the best CNN was Inception (accuracy = 0.67, auc = 0.74). LSTM + Inception yielded superior performance than all other methods (accuracy = 0.74, auc = 0.78). Moreover, LSTM + Inception outperformed experts by 7–25% (p < 0.05). The proposed methodology does not require detailed segmentation of the tumor region and it may be used in conjunction with radiological findings to improve clinical decision-making.
Graphical abstract

Lung cancer histology classification from CT images based on CNN + LSTM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E, Flieder DB, Geisinger K, Hirsch FR, Ishikawa Y, Kerr KM, Noguchi M, Pelosi G, Powell CA, Tsao MS, Wistuba I, WHO Panel (2015) The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J Thorac Oncol 10:1243–1260. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630
Zhang L, Wang L, Du B, Wang T, Tian P, Tian S (2016) Classification of non-small cell lung cancer using significance analysis of microarray-gene set reduction algorithm. Biomed Res Int 2016:2491671. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2491671
Kawase A, Yoshida J, Ishii G, Nakao M, Aokage K, Hishida T, Nishimura M, Nagai K (2012) Differences between squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the lung: are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma prognostically equal? Jpn J Clin Oncol 42:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyr188
Pankratz VS, Sun Z, Aakre J, Li Y, Johnson C, Garces YI, Aubry MC, Molina JR, Wigle DA, Yang P (2011) Systematic evaluation of genetic variants in three biological pathways on patient survival in low-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6:1488–1495. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0B013E318223BF05
Wiener RS, Schwartz LM, Woloshin S, Welch HG (2011) Population-based risk for complications after transthoracic needle lung biopsy of a pulmonary nodule: an analysis of discharge records. Ann Intern Med 155:137. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-3-201108020-00003
Aerts HJWL, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RTH, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, Bussink J, Monshouwer R, Haibe-Kains B, Rietveld D, Hoebers F, Rietbergen MM, Leemans CR, Dekker A, Quackenbush J, Gillies RJ, Lambin P (2014) Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 5:4006. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006
Yip SSF, Aerts HJWL (2016) Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys Med Biol 61:R150–R166. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/61/13/R150
Keek SA, Leijenaar RT, Jochems A, Woodruff HC (2018) A review on radiomics and the future of theranostics for patient selection in precision medicine. Br J Radiol 91:20170926. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20170926
Thawani R, McLane M, Beig N, Ghose S, Prasanna P, Velcheti V, Madabhushi A (2018) Radiomics and radiogenomics in lung cancer: a review for the clinician. Lung Cancer 115:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.10.015
Lee G, Park H, Sohn I, Lee S-H, Song SH, Kim H, Lee KS, Shim YM, Lee HY (2018) Comprehensive computed tomography radiomics analysis of lung adenocarcinoma for prognostication. Oncologist 23:806–813. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0538
Mattonen SA, Palma DA, Haasbeek CJA, Senan S, Ward AD (2014) Early prediction of tumor recurrence based on CT texture changes after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for lung cancer. Med Phys 41:033502. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4866219
Wei G, Cao H, Ma H, Qi S, Qian W, Ma Z (2018) Content-based image retrieval for lung nodule classification using texture features and learned distance metric. J Med Syst 42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-017-0874-5
Patil R, Mahadevaiah G, Dekker A (2016) An approach toward automatic classification of tumor histopathology of non-small cell lung cancer based on radiomic features. Tomogr (Ann Arbor, Mich) 2:374–377. https://doi.org/10.18383/j.tom.2016.00244
Haga A, Takahashi W, Aoki S, Nawa K, Yamashita H, Abe O, Nakagawa K (2018) Classification of early stage non-small cell lung cancers on computed tomographic images into histological types using radiomic features: interobserver delineation variability analysis. Radiol Phys Technol 11:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-017-0433-2
Wu W, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Quackenbush J, Lambin P, Bussink J, Mak R, Aerts HJWL (2016) Exploratory study to identify radiomics classifiers for lung cancer histology. Front Oncol 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2016.00071
Tajbakhsh N, Shin JY, Gurudu SR, Hurst RT, Kendall CB, Gotway MB, Liang J (2016) Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning? IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:1299–1312. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2535302
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, van der Laak JAWM, van Ginneken B, Sánchez CI (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEDIA.2017.07.005
Meyer P, Noblet V, Mazzara C, Lallement A (2018) Survey on deep learning for radiotherapy. Comput Biol Med 98:126–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.05.018
Kumar D, Wong A, Clausi DA. Lung nodule classification using deep features in CT images. 2015 12th Conf Comput Robot Vis IEEE; 2015, p. 133–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/CRV.2015.25
Zhang G, Jiang S, Yang Z, Gong L, Ma X, Zhou Z, Bao C, Liu Q (2018) Automatic nodule detection for lung cancer in CT images: A review. Comput Biol Med 103:287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPBIOMED.2018.10.033
Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Litjens G, Gerke P, Jacobs C, van Riel SJ, Wille MMW, Naqibullah M, Sanchez CI, van Ginneken B (2016) Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:1160–1169. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2536809
Liu K, Kang G (2017) Multiview convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 27:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22206
Gao M, Bagci U, Lu L, Wu A, Buty M, Shin H-C, Roth H, Papadakis GZ, Depeursinge A, Summers RM, Xu Z, Mollura DJ (2018) Holistic classification of CT attenuation patterns for interstitial lung diseases via deep convolutional neural networks. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng Imaging Vis 6:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681163.2015.1124249
Chaunzwa TL, Christiani DC, Lanuti M, Shafer A, Diao N, Mak RH, Aerts H (2018) Using deep-learning radiomics to predict lung cancer histology. J Clin Oncol 36:8545–8545. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.8545
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Proces Syst:1097–1105
Ravishankar H, Sudhakar P, Venkataramani R, Thiruvenkadam S, Annangi P, Babu N et al (2016) Understanding the mechanisms of deep transfer learning for medical images. Springer, Cham, pp 188–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46976-8_20
Vallières M, Freeman CR, Skamene SR, El Naqa I (2015) A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Phys Med Biol 60:5471–5496
Shafiq-ul-Hassan M, Latifi K, Zhang G, Ullah G, Gillies R, Moros E (2018) Voxel size and gray level normalization of CT radiomic features in lung cancer. Sci Rep 8:10545. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28895-9
Bar Y, Diamant I, Wolf L, Lieberman S, Konen E, Greenspan H (2018) Chest pathology identification using deep feature selection with non-medical training. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng Imaging Vis 6:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681163.2016.1138324
Huynh BQ, Li H, Giger ML (2016) Digital mammographic tumor classification using transfer learning from deep convolutional neural networks. J Med Imaging 3:034501. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.3.3.034501
Loukas C (2019) Surgical phase recognition of short video shots based on temporal modeling of deep features. Proc. 12th Int. Jt. Conf. Biomed. Eng. Syst. Technol. - Vol. 2 Bioimaging, Prague, Czech Republic, p. 21–9. https://doi.org/10.5220/0007352000210029
Margeta J, Criminisi A, Cabrera Lozoya R, Lee DC, Ayache N (2017) Fine-tuned convolutional neural nets for cardiac MRI acquisition plane recognition. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng Imaging Vis 5:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681163.2015.1061448
Li Y, Charalampaki P, Liu Y, Yang G-Z, Giannarou S (2018) Context aware decision support in neurosurgical oncology based on an efficient classification of endomicroscopic data. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 13:1187–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-018-1806-7
Ben-Hamo R, Boue S, Martin F, Talikka M, Efroni S (2013) Classification of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma samples based on their gene expression profile in the sbv IMPROVER Diagnostic Signature Challenge. Syst Biomed 1:268–277. https://doi.org/10.4161/sysb.25983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The CT data employed in this study were anonymized and are publicly available from ‘The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA)’ website.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marentakis, P., Karaiskos, P., Kouloulias, V. et al. Lung cancer histology classification from CT images based on radiomics and deep learning models. Med Biol Eng Comput 59, 215–226 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02302-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02302-w