Abstract
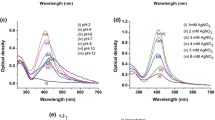
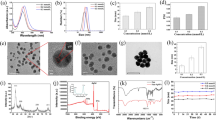
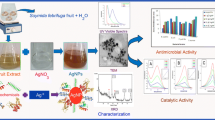
The emergence of multidrug-resistant microbes and newly outbreaking diseases are one of the major threats before mankind. This paves the way for researchers to explore new antimicrobial agents that possess common day-to-day applications. In this concern, we have fabricated the antimicrobial Ag-kaolin functional nanostructures by simple and sustainable protocol employing Murraya koenigii fruit extract. UV-visible spectra (UV-Vis) of the Ag-kaolin exhibit absorption peak at 430 nm which corresponds to the characteristic surface plasmon resonance of Ag nanoparticles. X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD) shows the diffraction peak at 37.6° confirms their face-centred cubic nature with (111) plane. Furthermore, the formation of Ag-kaolin functional nanostructures was confirmed through a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrum (EDX) analysis. The transmission electron microscopic (TEM) studies reveal the effective formation of quasi-spherical monodispersed Ag nanoparticles having 20–30-nm diameters on the kaolin clay. The bio-synthesized Ag-kaolin nanostructures showed excellent antimicrobial activity against pathogenic gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis) and gram-negative (Escherichia coli) bacteria respectively with the inhibition zones of 26 mm, 25 mm and 30 mm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G.: General introduction: clays, clay minerals, and clay science. In: Bergaya, F., Theng, B.K.G., Lagaly, G. (eds.) Handbook of clay science, pp. 1–18. Elsevier, Oxford (2006)
Murray, H.H.: Traditional and new applications for kaolin, smectite, and palygorskite: a general overview. Appl Clay Sci. 17, 207–221 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(00)00016-8
Murray, H.H.: Overview—clay mineral applications. Appl Clay Sci. 5, 379–395 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-1317(91)90014-Z
Carretero, M.I.: Clay minerals and their beneficial effects upon human health. A review. Appl Clay Sci. 21, 155–163 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(01)00085-0
Martynková, G.S., Valášková, M.: Antimicrobial nanocomposites based on natural modified materials: a review of carbons and clays. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 14, 673–693 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.8903
Gaskell, E.E., Hamilton, A.R.: Antimicrobial clay-based materials for wound care. Future Med Chem. 6, 641–655 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.14.17
Bergaya, F., Theng, B., Lagaly, G.: Modified clays and clay minerals. In: Bergaya, F., Theng, B.K.G., Lagaly, G. (eds.) Handbook of clay science, pp. 261–422. Elsevier, Oxford (2006)
Hong, S.I., Rhim, J.W.: Antimicrobial activity of organically modified nano-clays. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 8, 5818–5824 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2008.248
Ummartyotin, S., Bunnak, N., Manuspiya, H.: A comprehensive review on modified clay based composite for energy based materials. Renew Sust Energ Rev. 61, 466–472 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.022
Uddin, M.K.: A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem Eng J. 308, 438–462 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.029
Liz-Marzán, L.M.: Nanometals: formation and color. Mater Today. 7, 26–31 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-7021(04)00080-X
Girase, B., Depan, D., Shah, J., Xu, W., Misra, R.: Silver–clay nanohybrid structure for effective and diffusion-controlled antimicrobial activity. Mater Sci Eng. 31, 1759–1766 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2011.08.007
Yakub, I., Soboyejo, W.: Adhesion of E. coli to silver-or copper-coated porous clay ceramic surfaces. J Appl Phys. 111, 124324 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4722326
Pillai, S.K., Ray, S.S., Scriba, M., Bandyopadhyay, J., Roux-van der Merwe, M.P., Badenhorst, J.: Microwave assisted green synthesis and characterization of silver/montmorillonite heterostructures with improved antimicrobial properties. Appl Clay Sci. 83, 315–321 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.08.014
Hariram, M., Vivekanandhan, S.: Phytochemical process for the functionalization of materials with metal nanoparticles: current trends and future perspectives. ChemistrySelect. 3, 13561–13585 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201802748
Vishnukumar, P., Vivekanandhan, S., Misra, M., Mohanty, A.: Recent advances and emerging opportunities in phytochemical synthesis of ZnO nanostructures. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 80, 143–161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.01.026
Saikia, I., Sonowal, S., Pal, M., Boruah, P.K., Das, M.R., Tamuly, C.: Biosynthesis of gold decorated reduced graphene oxide and its biological activities. Mater Lett. 178, 239–242 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.05.011
Sadanand, V., Rajini, N., Rajulu, A.V., Satyanarayana, B.: Preparation of cellulose composites with in situ generated copper nanoparticles using leaf extract and their properties. Carbohydr Polym. 150, 32–39 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.121
Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, S.M.: Green synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of the Pd/TiO2 nanoparticles for the ligand-free Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. J Colloid Interface Sci. 465, 121–127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.038
Hatamifard, A., Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, S.M.: Biosynthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of an Ag/zeolite nanocomposite for base-and ligand-free oxidative hydroxylation of phenylboronic acid and reduction of a variety of dyes at room temperature. New J Chem. 40, 2501–2513 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ02909K
Rostami-Vartooni, A., Nasrollahzadeh, M., Alizadeh, M.: Green synthesis of seashell supported silver nanoparticles using Bunium persicum seeds extract: application of the particles for catalytic reduction of organic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci. 470, 268–275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.02.060
Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, S.M., Hatamifard, A.: Waste chicken eggshell as a natural valuable resource and environmentally benign support for biosynthesis of catalytically active Cu/eggshell, Fe3O4/eggshell and Cu/Fe3O4/eggshell nanocomposites. Appl Catal B. 191, 209–227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.042
Hariram, M., Vivekanandhan, S., Ganesan, V., Muthuramkumar, S., Rodriguez-uribe, A., Mohanty, A.K., Misra, M.: Tecoma stans flower extract assisted biogenic synthesis of functional Ag-Talc nanostructures for antimicrobial applications. Bioresour Technol Rep. 7, 100298 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100298
Sohrabnezhad, S., Rassa, M., Seifi, A.: Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles in montmorillonite. Mater Lett. 168, 28–30 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.01.025
Sohrabnezhad, S., Seifi, A.: The green synthesis of Ag/ZnO in montmorillonite with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci. 386, 33–40 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.102
Issaabadi, Z., Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, S.M.: Green synthesis of the copper nanoparticles supported on bentonite and investigation of its catalytic activity. J Clean Prod. 142, 3584–3591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.109
Saikia, P.K., Bhattacharjee, R.P., Sarmah, P.P., Saikia, L., Dutta, D.K.: A green synthesis of Pd nanoparticles supported on modified montmorillonite using aqueous Ocimum sanctum leaf extract: a sustainable catalyst for hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol. RSC Adv. 6, 110011–110018 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA22788K
Christensen, L., Vivekanandhan, S., Misra, M., Mohanty, A.K.: Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using murraya koenigii (curry leaf): an investigation on the effect of broth concentration in reduction mechanism and particle size. Adv Mat Lett. 2, 429–434 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2011.4256
Vivekanandhan, S., Christensen, L., Misra, M., Mohanty, A.K.: Green process for impregnation of silver nanoparticles into microcrystalline cellulose and their antimicrobial bionanocomposite films. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol. 3, 371 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4236/jbnb.2012.33035
Vivekanandhan, S., Tang, D., Misra, M., Mohanty, A.K.: Novel glycine max (soybean) leaf extract based biological process for the functionalization of carbon nanotubes with silver nanoparticles. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett. 2, 240–243 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1166/nnl.2010.1087
Marambio-Jones, C., Hoek, E.M.: A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J Nanopart Res. 12, 1531–1551 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9900-y
Ahmed, S., Ahmad, M., Swami, B.L., Ikram, S.: A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res. 7, 17–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
Rai, M., Yadav, A., Gade, A.: Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 27, 76–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002
Acknowledgements
S.V. acknowledges the University Grants Commission (UGC), Delhi, India, for the financial support for this research activity through the Minor Research Project (MRP/UGC-SERO-Proposal No.: 1593). The authors express sincere thanks to Sophisticated Test and Instrumentation Centre (STIC), Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, Kerala, India, for providing their valuable support through various analytical services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hariram, M., Ganesan, V., Muthuramkumar, S. et al. Functionalization of kaolin clay with silver nanoparticles by Murraya koenigii fruit extract-mediated bioreduction process for antimicrobial applications. J Aust Ceram Soc 57, 505–513 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00545-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00545-2