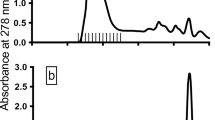
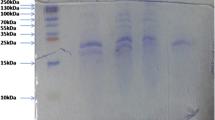
Abstract
Microalgae like Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) are protein rich and can be alternative protein sources to fishmeal and soybean meal in fish feed formulation. The present study aims to improve the protein bioavailability of Spirulina by cost-effective protein extraction followed by protease supplementation in fish feed, using in vitro studies. Different extraction procedures such as microwave-assisted, high pressure, and temperature-mediated extraction, boiling and an isoelectric precipitation were employed to study the protein yield from Spirulina powder, and this was compared with the conventional soybean meal and fishmeal conditioning during feed manufacture. Bromelain is a potent protease that has not been widely used as a feed additive with Spirulina. To study the comparative efficiency of bromelain and other proteases like papain and trypsin on Spirulina and conventional feed substrates, a protease assay was performed at different temperatures and enzyme concentrations. The digestibility of these substrates was also studied in vitro, using gut extracts from the fingerlings of Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Unlike an in vivo feeding trial, a novel method was used to study the effect of protease supplementation on the inherent digestibility of the gut with an in vitro method. Bromelain showed the highest activity on all the substrates at both the temperatures. Bromelain supplementation improved the in vitro digestibility of the Spirulina that were subjected to protein extraction, more than the un-extracted one. The results of the present in vitro study suggest that Spirulina could serve as an alternative protein source, and bromelain-based supplementation could improve the digestibility of Spirulina-based fish diets.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Warith AA, Younis EM, Al-Asgah NA, Mahboob S (2020) Effect of replacing fish meal by full fat soybean meal on growth performance, feed utilization and gastrointestinal enzymes in diets for African catfish Clarias gariepinus. Braz J Biol 80:535–543
Amri E, Mamboya F (2012) Papain, a plant enzyme of biological importance: a review. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 8:99–104
Anukoolprasert T, Srinuansom K, Rukdontri T, Nonkhukhetkhong S, Petkam R (2019) Postprandial in vitro protease-specific activity of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) digestive organs. Pak J Nutr 18:125–133
Bai M, Qin G, Sun Z, Long G (2016) Relationship between molecular structure characteristics of feed proteins and protein in vitro digestibility and solubility. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 29:1159–1165
Bais B (2018) Fish scenario in India with emphasis on Indian major carps. Int J Avian Wildl Biol 3:409–411
Baldwin J, Hochachka PW (1970) Functional significance of isoenzymes in thermal acclimatization. Acetylcholinesterase from trout brain. Biochem J 116:883–887
Barba FJ, Grimi N, Vorobiev E (2015) New approaches for the use of non-conventional cell disruption technologies to extract potential food additives and nutraceuticals from microalgae. Food Eng Rev 7:45–62
Becker EW (2007) Micro-algae as a source of protein. Biotechnol Adv 25:207–210
Bleakley S, Hayes M (2017) Algal proteins: extraction, application, and challenges concerning production. Foods 6:33
Borowitzka MA (1997) Microalgae for aquaculture: opportunities and constraints. J Appl Phycol 9:393–401
Carter CG, Bransden MP, van Barneveld RJ, Clarke SM (1999) Alternative methods for nutrition research on the southern bluefin tuna, Thunnus maccoyii: in vitro digestibility. Aquaculture 179:57–70
Castillo S, Gatlin DM (2015) Dietary supplementation of exogenous carbohydrase enzymes in fish nutrition: a review. Aquaculture 435:286–292
Choi WM, Lam CL, Mo WY, Wong MH (2016) Upgrading food wastes by means of bromelain and papain to enhance growth and immunity of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:7186–7194
Chong ACS, Hashim R, Ali AB (2002) Assessment of dry matter and protein digestibilities of selected raw ingredients by discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciata) using in vivo and in vitro methods. Aquac Nutr 8:229–238
Cupp-Enyard C (2008) Sigma’s non-specific protease activity assay - casein as a substrate. JOVE- J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/899
Diken G, Demir O, Naz M (2016) The potential inhibitory effects of microalgae and macroalgae on protease activities of Argyrosomus regius (Pisces, Scanidae) larvae using in vitro assays. J Int Sci Publ 4:473–483
Encarnação P (2016) Functional feed additives in aquaculture feeds. In: Nates S (ed) Aquafeed formulation. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 217–237
Ezquerra JM, García-Carreño FL, Carrillo O (1998) In vitro digestibility of dietary protein sources for white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 163:123–136
Fan X, Cui Y, Zhang R, Zhang X (2018) Purification and identification of anti-obesity peptides derived from Spirulina platensis. J Funct Foods 47:350–360
Fernandes IM, Bastos YF, Barreto DS et al (2017) The efficacy of clove oil as an anaesthetic and in euthanasia procedure for small-sized tropical fishes. Braz J Biol 77:444–450
Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 199:197–227
Grabner M (1985) An in vitro method for measuring protein digestibility of fish feed components. Aquaculture 48:97–110
Hardy RW, Barrows FT (2003) Diet Formulation and manufacture. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish nutrition, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 505–600
Jun-sheng L, Jian-lin L, Ting-ting W (2006) Ontogeny of protease, amylase and lipase in the alimentary tract of hybrid Juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus). Fish Physiol Biochem 32:295–303
Kim K-D, Lim SG, Kang YJ, Kim KW, Son MH (2012) Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth and body composition of juvenile far eastern catfish Silurus asotus. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 25:369–374
Kolkovski S (2001) Digestive enzymes in fish larvae and juveniles—implications and applications to formulated diets. Aquaculture 200:181–201
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Montoya-Martínez C, Nolasco-Soria H, Vega-Villasante F, Carrillo-Farnés O, Álvarez-González A, Civera-Cerecedo R (2018) In vitro protein digestibility of animal, vegetal and microbial feed ingredients for Macrobrachium tenellum. Lat Am J Aquat Res 46:495–501
Muzyaka O, Musienko V, Osmak A, Plischenko A, Semiletko Y (2020) GraphPad Prism. Version 8.4.2. San Diego, California, USA. www.graphpad.com. Accessed 27 Apr 2020
Nandeesha MC, Gangadhar B, Varghese TJ, Keshavanath P (1998) Effect of feeding Spirulina platensis on the growth, proximate composition and organoleptic quality of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Aquac Res 29:305–312
Olsen JV, Ong S-E, Mann M (2004) Trypsin cleaves exclusively C-terminal to arginine and lysine residues. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:608–614
Parimi NS, Singh M, Kastner J, Das KC, Forsberg LS, Azadi P (2015) Optimization of protein extraction from Spirulina platensis to generate a potential co-product and a biofuel feedstock with reduced nitrogen content. Front Energy Res 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2015.00030
Patil DW, Singh H (2014) Effect of papain supplemented diet on growth and survival of post -larvae of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 1:176–179
Pavan R, Jain S, Shraddha KA (2012) Properties and therapeutic application of bromelain: a review. Biotechnol Res Int 2012:976203
Rachmawati D, Samidjan I (2018) the effects of papain enzyme supplement in feed on protein digestibility, growth and survival rate in Sangkuriang catfish (Clarias sp). Omni-Akuatika 14:91–99
Rick W (1974) Trypsin. Methods Enzym Anal 2:1013–1024
Rostika R, Nurhayati A, Buwono I, Rizal A, Dewanti LP, Maulana T (2018) Papain and bromelain crude enzyme extract in commercial feed, effectiveness toward pisciculture production of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) in aquaculture facility. AACL Bioflux 11:1598–1604
Rungruangsak-Torrissen K, Rustad A, Sunde J, Eiane SA, Jensen HB, Opstvedt J, Nygård E, Samuelsen TA, Mundheim H, Luzzana U, Venturini G (2002) In vitro digestibility based on fish crude enzyme extract for prediction of feed quality in growth trials. J Sci Food Agric 82:644–654
Scott M, Johnsen C, Phillips KA (1987) The pH optima for papain and bromelain treatment of red cells. Vox Sang 52:223–227
Sharma SA, Krishnakumar V, Arulraj J (2019) Impact of Ananas comosus extract supplementation on the growth and biochemical profile of Cyprinus carpio fingerlings. Trends Fish Res 8:69–77
Sheikhzadeh N, Mousavi S, Oushani AK, Firouzamandi M, Mardani K (2019) Spirulina platensis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) feed: effects on growth, fillet composition, and tissue antioxidant mechanisms. Aquac Int 27:1613–1623
Sigma-Aldrich (2020a) Bromelain. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/life-science/biochemicals/biochemical-products.html?TablePage=16410479. Accessed 8 Jul 2020
Sigma-Aldrich (2020b) Papain. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/life-science/metabolomics/enzyme-explorer/analytical-enzymes/papain.html. Accessed 8 Jul 2020
Subandiyono, Hastuti S, Nugroho RA (2018) Feed utilization efficiency and growth of Java barb (Puntius javanicus) fed on dietary pineapple extract. AACL Bioflux 11:309–318
Sun Y, Chang R, Li Q, Li B (2016) Isolation and characterization of an antibacterial peptide from protein hydrolysates of Spirulina platensis. Eur Food Res Technol 242:685–692
Tacon A (1997) Feeding tomorrow’s fish: keys for sustainability. In: Tacon A, Bascuro B (eds) Feeding tomorrow’s fish. Cahiers Options Méditerranéennes, No. 22. CIHEAM, Zaragosa, pp 11–33
Tewari G, Ram R, Singh A (2018) Effect of plant base digestive enzyme ‘Papain’on growth, survival and behavioural response of Cyprinus carpio. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 6:210–214
Valverde-Chavarría S, Álvarez-González CA, Brais-Medina M, Calvo-Elizondo E, Ulloa-Rojas JB (2016) In vitro digestibility and proteases inhibitory effect of several feedstuffs for Parachromis dovii juveniles and P. dovii hybrid larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1767–1776
Velasquez SF, Chan MA, Abisado RG, Traifalgar RFM, Tayamen MM, Maliwat GCF, Ragaza JA (2016) Dietary Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) replacement enhances performance of juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Appl Phycol 28:1023–1030
Yigit N, Koca S, Didinen BI, Diler I (2016) Effect of protease and phytase supplementation on growth performance and nutrient digestibility of rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss , Walbaum) fed soybean meal-based diets. J Appl Anim Res 46:29–32
Yuangsoi B, Klahan R, Charoenwattanasak S, Shi-Mei L (2018) Effects of supplementation of pineapple waste extract in diet of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on growth, feed utilization and nitrogen excretion. J Appl Aquac 30:227–237
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Mr. C Mugundhan of SpikingTM products (2M Biotech), Ramanathapuram, Tamilnadu, India, for providing the Spirulina powder. We thank all the staff of the Department of Life Sciences, CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bangalore Central Campus, Bengaluru, Karnataka, for their help and all the facilities to carry out this research. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAS and SS conceived the project. SAS designed and performed the experiments, and analyzed the data. SS, JA, and KV helped with experimental design and troubleshooting. SAS and KV performed the statistical analysis. SAS wrote the paper, and all authors commented and contributed to the previous versions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 652 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S.A., Surveswaran, S., Arulraj, J. et al. Bromelain enhances digestibility of Spirulina-based fish feed. J Appl Phycol 33, 967–977 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02337-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02337-4