Abstract
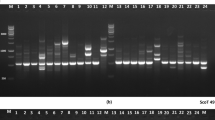
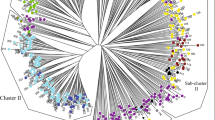
Tree peonies distributed in Baokang County (Hubei Province, China) (BKTPs) displayed extensive morphological variation, especially in flower color patterns and fruit setting rates. The genetic diversity of BKTPs and their relationships to nine wild species and 14 representative traditional cultivars were assessed using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in this study. All 19 analyzed loci were polymorphic, and 85 alleles were found. The number of alleles per locus varied from 3 to 7, with an average of 4.474. Cluster analysis with UPGMA method based on SSR markers partitioned 46 accessions of BKTPs into two major clusters and six subgroups, closing to P. ostii, P. qiui, P. rockii, P. jishanensis and different cultivars, respectively. Analysis of flavonoids with UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS revealed that Pn3G5G and Cy3G5G were the main anthocyanins of the pink and reddish-purple flowers of BKTPs, which were undetectable in white flowers. The fruit and seed setting rates of BKTPs ranged from 4.00 to 26.00 per plant, and 130.00 to 858.00 per plant, respectively. The content of unsaturated fatty acids was over 90% of the total fatty acids in the seed oils of BKTPs, with α-linolenic acid as the dominant compound (42.51–54.93%). Both phenotypic and molecular data suggested that the accessions of BKTPs were a hybrid complex resulted from introgression between the sympatrically distributed wild species and cultivars in Baokang, which provided novel genetic resources for tree peony breeding and germplasm innovation.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The reference transcriptome de novo assembled from the RNA-Seq of ‘Fengdan’ (P. ostii) were submitted to NCBI SRA database (SRA accession: PRJNA604317) and can be accessible with the following link after released: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA604317. Nineteen EST-SSR sequences generated for this study were deposited at GenBank with accession numbers MT012685-MT012703.
References
Han J, Liu Z, Li X, Li J, Hu Y (2016) Diversity in seed oil content and fatty acid composition in three tree peony species with potential as sources of omega-3 fatty acids. J Hort Sci B 91:175–179
Hong D, Pan K (2007) Paeonia cathayana D.Y.Hong & K.Y.Pan, a new tree peony, with revision of P.suffruticosa ssp.yinpingmudan. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica 45:285–288
Huang Y (2013) Population genetic structure and interspecific introgressive hybridization between Camellia meiocarpa and C. oleifera. Chin J Appl Ecol 24:2345–2352
Kimura M, Crow JF (1964) The number of alleles that can be maintained in finite population. Genetics 49:725–738
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2012) Fast R functions for robust correlations and hierarchical clustering. J Stat Softw 46:1–17
Li JJ (2011) Tree peony of China. Encyclopedia of China Publishing House, Beijing
Li SS, Yuan RY, Chen LG, Wang LS, Hao XH, Wang LJ, Zheng XC, Du H (2015) Systematic qualitative and quantitative assessment of fatty acids in the seeds of 60 tree peony (Paeonia section Moutan DC.) cultivars by GC-MS. Food Chem 173:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.017
Lin C, Lin HY, Chen JH, Tseng WP, Ko PY, Liu YS, Yeh WL, Lu DY (2015) Effects of paeonol on anti-neuroinflammatory responses in microglial cells. Int J Mol Sci 16:8844–8860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16048844
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research - an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Slatkin M, Barton NH (1989) A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution 43:1349–1368. https://doi.org/10.2307/2409452
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Zhang J, Wang L, Liu Z (2006) Recent advances in flower color research of tree peony. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 33:1383–1388
Zhang JJ, Wang LS, Shu QY, Liu ZA, Li CH, Zhang J, Wei XL, Tian D (2007) Comparison of anthocyanins in non-blotches and blotches of the petals of Xibei tree peony. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 114:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2007.05.009
Zhang Y, Han X, Niu L, Zhang J, He L (2015) Analysis of fatty acid in seed oil from nine wild peony species. J Chinese Cereals Oils Assoc 30:72–75
Zhao C, Chen W, Tian Z, Xie Z (2005) Altitudinal pattern of plant species diversity in Shennongjia Mountains, Central China. J Integr Plant Biol 47:1431–1449. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00164.x
Zhao D, Jiang Y, Ning C, Meng J, Lin S, Ding W, Tao J (2014) Transcriptome sequencing of a chimaera reveals coordinated expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes mediating yellow formation in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). BMC Genomics 15:689. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-689
Zhao D, Tang W, Hao Z, Tao J (2015) Identification of flavonoids and expression of flavonoid biosynthetic genes in two coloured tree peony flowers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 459:450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.126
Zhou SL, Zou XH, Zhou ZQ, Liu J, Xu C, Yu J, Wang Q, Zhang DM, Wang XQ, Ge S, Sang T, Pan KY, Hong DY (2014) Multiple species of wild tree peonies gave rise to the ‘king of flowers’, Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 281:20141687. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.168
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Ji Yang from Fudan University for his carefully reviewing this paper, Professor Jiajue Li from Shanghai Chenshan Botanical Garden for his valuable comments on this paper, and Mr. Hongxi Li from Baokang County Forestry Bureau for his assistance on sample collection. This research was supported by the Special Fund for Scientific Research of Shanghai Landscaping & City Appearance Administrative Bureau (Project No. G162403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JH: sample investigation and collection, writing of the manuscript, mentor, and the experiment initiator. JL: SSR analysis, writing of the manuscript, manuscript corrections. XL: fatty acid analysis. QL: flavonoids analysis. YH: mentor, results review and comment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Wook Oh.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Li, J., Li, X. et al. Genetic diversity generated by introgression between wild species and cultivars of tree peony in Baokang, China. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 62, 263–278 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00306-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00306-x