Abstract
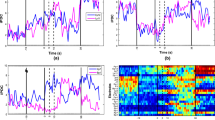
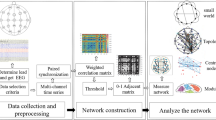
In this paper, phase space reconstruction from stereo-electroencephalography data of ten patients with focal epilepsy forms a series of graphs. Those obtained graphs reflect the transition characteristics of brain dynamical system from pre-seizure to seizure of epilepsy. Interestingly, it is found that the rank of Laplacian matrix of these graphs has a sharp decrease when a seizure is close to happen, which thus might be viewed as a new potential biomarker in epilepsy. In addition, the reliability of this method is numerically verified with a coupled mass neural model. In particular, our simulation suggests that this potential biomarker can play the roles of predictive effect or delayed awareness, depending on the bias current of the Gaussian noise. These results may give new insights into the seizure detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Matlab code and data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ayoubian L, Lacoma H, Gotman J (2013) Automatic seizure detection in seeg using high frequency activities in wavelet domain. Med Eng Phys 35(3):319–328
Behnam M, Pourghassem H (2016) Real-time seizure prediction using RLS? ltering and interpolated histogram feature based on hybrid optimization algorithm of Bayesian classi?er and Hunting search. Comput Method Progr Biomed 132:115–136
Bian C, Ning X (2004) Determining the minimum embedding dimension of nonlinear time series based on prediction method. Chin Phys 13(5):633–635
Chisci L, Mavino A, Perferi G, Sciandrone M, Anile C, Colicchio G, Fuggetta F (2010) Real-time epileptic seizure prediction using AR models and support vector machines. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(5):1124–1132
Cho D, Min B, Kim J, Lee B (2017) EEG-based prediction of epileptic seizures using phase synchronization elicited from noise-assisted multivariate empirical mode decomposition. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 25(8):1309–1318
Da Silva FL, Blanes W, Kalitzin SN, Parra J, Suffczynski P, Velis DN (2003) Epilepsies as dynamical diseases of brain systems: basic models of the transition between normal and epileptic activity. Epilepsia 44(s12):73–83
Dologlou I, Carayannis G (1991) Physical interpretation of signal reconstruction from reduced rank matrices. IEEE Trans Signal Process 39(7):1681–1682
Dong X, Thanou D, Frossard P, Vandergheynst P (2016) Learning laplacian matrix in smooth graph signal representations. IEEE Trans Signal Process 64(23):6160–6173
Fan M, Chou C (2019) Detecting abnormal pattern of epileptic seizures via temporal synchronization of EEG signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 66(3):601–608
Gandhi T, Gandhi T, Panigrahi BK, Bhatia M, Anand S (2010) Expert model for detection of epileptic activity in EEG signature. Expert Syst Appl 37(4):3513–3520
Gao Z, Jin N (2009) Complex network from time series based on phase space reconstruction. Chaos: An Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 19(3):033137
Gomez-Alonso J, Giraldez BG (2007) Epilepsy: a new definition for an old disease. Revista de neurologia 45(5):126–127
Hejazi M, Nasrabadi AM (2019) Prediction of epilepsy seizure from multi-channel electroencephalogram by effective connectivity analysis using Granger causality and directed transfer function methods. Cognit Neurodynamics 13:461–473
He K, Sun J, Tang X (2010) Fast matting using large kernel matting Laplacian matrices. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2165–2172
Hussain L (2018) Detecting epileptic seizure with different feature extracting strategies using robust machine learning classification techniques by applying advance parameter optimization approach. Cognit Neurodynamics 12:271–294
Jansen BH et al (1995) Electroencephalogram and visual evoked potential generation in a mathematical model of coupled cortial columns. Biol Cybern 73:357–366
Jansen BH (1996) Nonlinear dynamics and quantitative EEG analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol [Suppl] 45:39–56
Jansen BH, Zouridakis G, Brandt ME (1993) A neurophysiologically-based mathematical model of flash visual evoked potentials. Biol Cybern 68:275–283
Kennel MB, Brown R, Abarvanel HDI (1992) Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction. Phys Rev A 45(6):3403–3411
Kiymik MK, Subasi A, Ozcalik HR (2004) Neural networks with periodogram and autoregressive spectral analysis methods in detection of epileptic seizure. J Med Syst 28:511–522
Lekscha J, Donner RV (2018) Phase space reconstruction for non-uniformly sampled noisy time series. Chaos: An Interdiscip J Nonlinear Sci 28(8):085702
Lopes Da Silva FH, van Rotterdam A, Barts P, van Heusden E, Burr W (1976) Model of neuronal population: the basic mechanisms of rhythmicity. Progress Brain Res 45:281–308
Luckkett P, Pavelescu E, McDonald T, Hively L, Ochoa J (2019) Predicting state transitions in brain dynamics through spectral difference of phase-space graphs. J Comput Neurosci 380:91–106
Lurie J (1999) Review of spectral graph theory: by Fan R. K. Chung. ACM SIGACT News 30(2):14–16
Ma H, Han C (2006) Selection of embedding dimension and delay time in phase space reconstruction. Front Electr Electron Eng Chin 1:111–114
Maass B, Stobart R, Deng J (2009) Diesel engine emissions prediction using parallel neural networks. Am Control Conf 9:1122–1127
Mormann F, Lehnertz K, David P, Elger CE (2000) Mean phase coherence as a measure for phase synchronization and its application to the EEG of epilepsy patients. Phys D: Nonlinear Phenom 144(3–4):358–369
Ngamga EJ, Bialonski S, Marwan N, Kurths J, Geier C, Lehnertz K (2016) Evaluation of selected recurrence measures in discriminating pre-ictal and inter-ictal periods from epileptic EEG data. Phys Lett A 380(16):1419–1425
Ozcan AR, Erturk S (2019) Seizure prediction in scalp EEG using 3D convolutional neural networks with an image-based approach. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(11):2284–2293
Ozcan AR, Erturk S (2019) Seizure prediction in scalp eeg using 3d convolutional neural networks with an image-based approach. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(11):2284–2293
Park Y, Luo L, Parhi KK, Netoff T (2011) Seizure prediction with spectral power of EEG using cost-sensitive support vector machines. Epilepsia 52(10):1761–1770
Park YS, Hochberg LR, Eskandar EN, Cash SS, Truccolo W (2020) Early detection of human epileptic seizures based on intracortical microelectrode array signals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 67(3):817–831
Povinelli RJ, Johnson MT, Lindgren AC, Roberts FM, Ye J (2006) Statistical models of reconstructed phase spaces for signal classification. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(6):2178–2186
Raghu S, Sriraam N, Kumar GP, Hegde AS (2018) A novel approach for real-time recognition of epileptic seizures using minimum variance modified fuzzy entropy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(11):2612–2621
Sakiyama A, Tanaka Y (2014) Oversampled graph laplacian matrix for graph filter banks. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62(24):6425–6437
Shukla A, Majumdar A (2015) Exploiting inter-channel correlation in EEG signal reconstruction. Biomed Signal Process Control 18:49–55
Subasi A (2007) EEG signal classification using wavelet feature extraction and a mixture of expert model. Expert Syst Appl 32(4):1084–1093
Trinajstic N, Babic D, Nikolic S, Plavsic D, Amic D, Mihalic Z (1994) The Laplacian matrix in chemistry. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 34(2):368–376
Tsiouris KM, Konitsiotis S, Markoula S, Rigas G, Koutsouris DD, Fotiadis DI (2018) Unsupervised detection of epileptic seizures from EEG signals: A channel-specific analysis of long-term recordings. IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI) 92–95
Tsiouris KM, Markoula S, Konitsiotis S, Koutsouris DD, Fotiadis DI (2018) A robust unsupervised epileptic seizure detection methodology to accelerate large EEG database evaluation. Biomed Signal Process Control 40:275–285
Wang N, Lyu MR (2014) Extracting and selecting distinctive EEG features for efficient epileptic seizure prediction. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 19(5):1648–1659
Wendling F, Bellanger JJ, Bartolomei F, Chauvel P (2000) Relevance of nonlinear lumped-parameter models in the analysis of depth-EEG epileptic signals. Biol Cybern 83:367–378
Wendling F, Bartolomei F, Bellanger JJ, Chauvel P (2002) Epileptic fast activity can be explained by a model of impaired GABAergic dendritic inhibition. Eur J Neurosci 15(9):1499–1508
Williamson JR, Bliss DW, Browne DW, Narayanan JT (2012) Seizure prediction using EEG spatiotemporal correlation structure. Epilepsy Behav 25(2):230–238
Winawer MR (2006) Phenotype definition in epilepsy. Epilepsy & behavior 8(3):462–476
Yang C, Luan G, Wang Q, Liu Z, Zhai F, Wang Q (2018) Localization of epileptogenic zone with the correction of pathological networks. Front Neurol 9:143
Yang CZ, Luan G, Liu Z, Wang Q (2019) Dynamical analysis of epileptic characteristics based on recurrence quantification of SEEG recordings. Phys A: Stat Mech Appl 523:507–515
Youngerman BE, Khan FA, Mckhann GM (2019) Stereoelectroencephalography in epilepsy, cognitive neurophysiology, and psychiatric disease: safety, efficacy, and place in therapy. Neuropsychiatric Dis Treat 15:1701–1716
Zhang Y, Guo Y, Yang P, Chen W, Lo B (2020) Epilepsy seizure prediction on eeg using common spatial pattern and convolutional neural network. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 24(2):465–474
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Chuanzuo Yang for the pre-processing of data and constructive discussion. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12072021, 11772019 and 11932003), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-20-013A3), the Capital Health Research and Development of Special (2016-1-8012), Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission, China (Z161100000516230, Z161100002616016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors designed, performed the research and analyzed the data as well as wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Sanbo Brain Hospital of Capital Medical University and all subjects were written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Fan, D., Wang, Q. et al. Sharp decrease in the Laplacian matrix rank of phase-space graphs: a potential biomarker in epilepsy. Cogn Neurodyn 15, 649–659 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09662-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09662-x