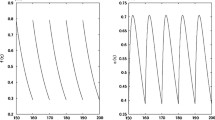
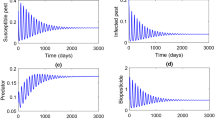
Abstract
In this paper, we assume that the pest population is divided into susceptible pests and infected pests, and only susceptible pests do harm to crops. Considering the two methods of spraying pesticides and releasing infected pests and natural enemies to control susceptible pests (the former is applied more frequently), and assuming that only susceptible pests develop resistance to pesticides, a pest control model with resistance development is established. By using the basic theory of impulsive differential systems and analytical methods, the sufficient condition for the global attractiveness of the susceptible pest eradication periodic solution is given. Combined with numerical simulations, the effects of spraying frequency of pesticides on critical threshold conditions for eradicating susceptible pests are discussed. The results confirm that it is not that the more frequently the pesticides are sprayed, the better the result of the pest control is. Two control strategies for eradicating susceptible pests are proposed: switching pesticides and releasing natural enemies elastically. Finally, the parameters in the critical threshold are analyzed from the following two aspects: (1) The key factors affecting pest control are determined by parameter sensitivity analyses. The results indicate that the correlation of the critical threshold concerning the killing efficiency rate and the decay rate of pesticides to susceptible pests varies due to the resistance development of susceptible pests. (2) Three-dimensional graphs and contours of susceptible pest eradication critical threshold with two parameters are simulated, and the effects of the main parameters on the critical threshold are analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blower, S.M., Dowlatabadi, H. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of complex models of disease transmission: an HIV model, as an example. Int. Stat. Rev., 62: 229–243 (1994)
Fu, J. B., Chen, L. S. Modelling and qualitative analysis of water hyacinth ecological system with two state-dependent impulse controls. Complexity, 2018: 4543976 (2018)
Gao, S. J., Luo, L., Yan, S. X., Meng, X.Z. Dynamical behavior of a novel impulsive switching model for HLB with seasonal fluctuations. Complexity, 2018: 2953623 (2018)
Jakel, T., Promkerd, P., Sitthirath, R., Guedant, P., Khoprasert, Y. Biocontrol of rats in an urban environment in Southeast Asia using Sarcocystis singaporensis. Pest Manag. Sci., 75: 2148–2157 (2019)
Jiao, J.J., Chen, L.S. A pest management SI model with periodic biological and chemical control concern. Appl. Math. Comput., 18: 1018–1026 (2006)
Jiao, J.J., Chen, L.S. Global attractivity of a stage-structure variable coefficients predator-prey system with time delay and impulsive perturbations on predators. Int. J. Biomath., 1: 197–208 (2008)
Joop, C.V.L., Herman, J.W.V.R., Susanne, S. Biological control of greenhouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum) with the parasitoid Encarsia formosa: how does it work? Biol. Control., 6: 1–10 (1996)
Kang, B.L., Liu, B., Tao, F.M. An integrated pest management model with dose-response effect of pesticides. J. Biol. Syst., 26: 59–86 (2018)
Lan, G.J., Fu, Y. J., Wei, C.J., Zhang, S.W. A research of pest management SI stochastic model concerning spraying pesticide and releasing natural enemies. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci., 2018: 3648 (2018)
Li, C.T., Tang, S.Y. The effects of timing of pulse spraying and releasing periods on dynamics of generalized predator-prey model. Int. J. Biomath., 5: 1250012 (2012)
Li, Y.K., Teng, Z.D., Wang, K. Dynamic analysis of general integrated pest management model with double impulsive control. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc., 2015: 839097 (2015)
Liang, J.H., Tang, S.Y., Cheke, R.A. An integrated pest management model with delayed responses to pesticide applications and its threshold dynamics. Nonlinear Anal. Real. World Appl., 13: 2352–2374 (2012)
Liang, J.H., Tang, S.Y., Nieto, J.J., Cheke, R.A. Analytical methods for detecting pesticide switches with evolution of pesticide resistance. Math. Biosci., 245: 249–257 (2013)
Liang, J.H., Tang, S.Y., Cheke, R.A., Wu, J.H. Adaptive release of natural enemies in a pest-natural enemy system with pesticide resistance. Bull. Math. Biol., 75: 2167–2195 (2013)
Liang, J.H., Tang, S.Y., Cheke, R.A. Beverton-Holt discrete pest management models with pulsed chemical control and evolution of pesticide resistance. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 36: 327–341 (2016)
Liang, J.H., Zhu, Y.H., Xiang, C.C., Tang, S.Y. Travelling waves and paradoxical effects in a discrete-time growth-dispersal model. Appl. Math. Model, 59: 132–146 (2018)
Liang, J.H., Yan, Q., Xiang, C.C., Tang, S.Y. A reaction-diffusion population growth equation with multiple pulse perturbations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 74: 122–137 (2019)
Liu, B., Tian, Y., Kang. B.L. Dynamics on a Holling II predator-prey model with state-dependent impulsive control. Int. J. Biomath., 5: 1260006 (2012)
Liu, B., Zhi, Y., Chen, L.S. The dynamics of a predator-prey model with Ivlevs functional response concerning integrated pest management. Acta. Math. Appl. Sin-E., 20: 133–146 (2004)
Liu, B., Wang, Y., Kang, B.L. Dynamics on a pest management SI model with control strategies of different frequencies. Nonlinear Anal. Hybri., 12: 66–78 (2014)
Marino, S., Hogue, LB., Ray, C.J., Kirschner, D. A methodology for performing global uncertainty and sensitivity analysis in systems biology. J. Theoret. Biol., 254: 178–196 (2008)
Gervassio, N.S., Luna, M.G., Minardi, G., Sanchez, N.E. Assessing inoculative releases of Pseudapanteles dignus (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) for the biological control of Tuta absoluta. Crop. Prot., 124: 104830 (2019)
Nie, L.F., Teng, Z.D., Nieto, J.J. State impulsive control strategies for a two-languages competitive model with bilingualism and interlinguistic similarity. Physica A, 430: 136–147 (2015)
Pang, G.P., Chen, L.S., Xu, W.J. A stage structure pest management model with impulsive state feedback control. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat., 23: 78–88 (2015)
Panetta, J.C. A Logistic Model of Periodic Chemotherapy. Appl. Math. Lett., 8: 83–86 (1995)
Rajasingh, J., Murugesupest, R. Pest interaction on sexual reproductive system of forest seed dynamics. Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci., 2017: 3343 (2017)
Shi, R.Q., Chen, L.S. An impulsive predator-prey model with disease in the prey for integrated pest management. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul., 15: 421–429 (2010)
Suandi, D., Wijaya, K.P., Apri, M., et al. A one-locus model describing the evolutionary dynamics of resistance against insecticide in Anopheles mosquitoe. Appl. Math. Comput., 359: 90–106 (2019)
Tan, Y.S., Chen, L.S. Modelling approach for biological control of insect pest by releasing infect pest. Chaos Soliton Fract., 39: 304–315 (2009)
Tang, S.Y., Tang, G.Y., Cheke, R.A. Optimum timing for integrated pest management: Modelling rates of pesticide application and natural enemy releases. J. Theoret. Biol., 264: 623–638 (2010)
Tang, S.Y., Tan, X.W., Yang, J., Liang, J.H. Periodic solution bifurcation and spiking dynamics of impacting predator-prey dynamical model. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos, 28: 1850147 (2018)
Tang, S.Y., Liang, J.H., Xiang, C.C., Xiao, Y.N. A general model of hormesis in biological systems and its application to pest management. J. R. Soc. Interface, 16: 0468 (2019)
Tian, Y., Tang, S.Y., Cheke, R.A. Dynamic complexity of a predator-prey model for IPM with nonlinear impulsive control incorporating a regulatory factor for predator releases. Math. Model. Anal., 24: 134–154 (2019)
Wang, L.M., Chen, L.S., Nieto, J.J. The dynamics of an epidemic model for pest control with impulsive effect. Nonlinear Anal-Real, 11: 1374–1386 (2010)
Wang, S., Huang, Q.D. Bifurcation of nontrivial periodic solutions for a Beddington-DeAngelis interference model with impulsive biological control. Appl. Math. Model, 39: 1470–1479 (2015)
Zhang, Y.J., Chen, L.S. The periodic model with mutual interference and impulsive effect. Int. J. Biomath., 5: 12600054 (2012)
Zhao, Z., Pang, L.Y., Song, X.Y. Optimal control of phytoplankton-fish model with the impulsive feedback control. Nonlinear Dynam., 88: 2003–2011 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11371030), the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 20170540001) and Liaoning Bai Qian Wan Talents Program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Kang, Bl., Tao, Fm. et al. Modelling the Effects of Pest Control with Development of Pesticide Resistance. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. Engl. Ser. 37, 109–125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10255-021-0988-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10255-021-0988-x