Abstract
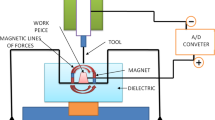
The present paper presents an experimental study on the performance evaluation of different electrode materials and dielectric fluids on high carbon high chromium (HcHcr) tool steel in electric discharge machining (EDM). Dielectric fluids (kerosene, distilled water, and EDM oil), electrode materials (copper, brass, and graphite) with current and pulse-on time are considered as input parameters while material removal rate (MRR), and surface roughness (Ra) as output parameters. HcHcr tool steel is used as work material due to its extensive use in aerospace, automotive, and tooling industries. Experiments are performed using Taguchi (L29) orthogonal array. Additionally, ANOVA analysis is performed to determine the most influencing parameters on the output. The results show that the electrode material is most influential for MRR, while dielectric fluid for Ra. Optimal setting obtained for MRR is electrode material (graphite), peak current (9 A), pulse-on time (50 µs), and dielectric (kerosene) and for Ra is electrode material (copper), peak current (3 A), pulse-on time (50 µs) and dielectric (kerosene). Similarly, the overall optimization is done via multi-objective optimization on the basis of ratio analysis method and optimal parameter setting obtained with graphite electrode, peak current (10 A), pulse-on-time (50 µs), and distilled led water as dielectric fluid. The microstructure of the machined surface is taken by scanning electron microscope to study the surface integrity and results revealed that smooth and uniform distribution of surface during the machining of HcHcr tool steel in EDM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luis C, Puertas I, Villa G (2005) Material removal rate and electrode wear study on the EDM of silicon carbide. J Mater Process Tech 164:889–896
Xiaohui L, Dongbo W, Qi L, Xiaodong Y (2020) Study on effects of electrode material and dielectric medium on arc plasma in electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107:4403–4413
Sahu AK (2020) Mahapatra, SS (2020) Performance analysis of tool electrode prepared through laser sintering process during electrical discharge machining of titanium. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106:1017–1041
Chakraborty S, Dey V, Ghosh SK (2015) A reviews on the use of dielectric fluids and their effects in electrical discharge machining characteristics. Precis Eng 40:1–6
Bai CY, Koo CH (2006) Effects of kerosene or distilled water as dielectric on electrical discharge alloying of super alloy Haynes 230 with Al-Mo composite electrode. Surf Co Technol 200:4127–4135
Chen SL, Yan BH, Huang FY (1999) Influence of kerosene and distilled water as dielectrics on the Electric Discharge Machining characteristics of Ti-6A1-4V. J Mater Proces Tech 87:107–111
Misbah N, Shoaib S, Haris A, Mirza J, Essam S, Wasim A, Salman H (2017) Effect of different dielectrics on material removal rate, electrode wear rate and microstructures in EDM. Procedia CIRP 60:2–7
Sadagopan P, Mouliprasanth B (2017) Investigation on the influence of different types of dielectrics in electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 92:277–291
Ankit KS, Rahul M, Anmol T, Dhruva Ghadai RK (2018) Effect of dielectric on electrical discharge machining: a review. IOP Conf Series Mat Sci Eng 377:1–9
Kumar A, Mandal A, Dixit AR, Deepak KM (2020) Quantitative analysis of bubble size and electrodes gap at different dielectric conditions in powder mixed EDM process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107:3065–3075
Singh S, Maheshwari S, Pandey PC (2004) Some investigations into the electric discharge machining of hardened tool steel using different electrode materials. J Mater Proces Tech 149(1–3):272–277
Chattopadhyay KD, Verma S, Satsangi PS, Sharma PC (2009) Development of empirical model for different process parameters during rotary electrical discharge machining of copper-steel (EN-8) system. J Mater Proces Tech 209(3):1454–1465
Muttamara A, Fukuzawa Y, Mohri N, Tani T (2009) Effect of electrode material on electric discharge machining of alumina. J Mater Proces Tech 115(3):344–358
Singh H, Singh A (2012) Effect of pulse-on/pulse-off time on machining of AISI D3 Die steel using copper and brass electrode in EDM. Int J Eng Sci 1(9):19–22
Hascalık A, Caydas U (2007) Electrical discharge machining of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V). App Surfa Sci 253(22):9007–9016
Haronb CH, Ghani JA, Burhanuddin Y, Swee CY (2008) Copper and graphite electrodes performance in electrical-discharge machining of XW42 tool steel. J Mater Proces Tech 201:570–573
Bhaumik M, Maity K (2019) Effect of electrode materials on different EDM aspects of titanium alloy. Silicon 11:187–196
Ugrasen G, Ravindra HV, Prakash GVN, Prasad YNT (2015) Optimization of process parameters in wire EDM of HcHcr Material using Taguchi technique. Mater Today Proc 2:2443–2452
Pushyanth VRS, Bhaskar A (2017) Experimental investigation and improvement of surface finish analysis on HCHCR AISI-D7 using EDM. Mater Today Proc 5:12115–12123
Chaubey SK, Singh S, Singh A (2018) some investigations into machining of AISI D2 tool steel using wire electro discharge machining (WEDM) process. Mater Today Proc 5:24347–24357
Anand G, Satyanarayana S, Hussain MM (2017) Optimization process parameters in EDM with magnetic field using gray relational analysis with Taguchi technique. Mater Today Proc 4:7723–7730
Tripathy S, Tripathy DK (2016) Multi-attribute optimization of machining process parameters in powder mixed electro-discharge machining using TOPSIS and gray relational analysis. Int J Eng Sci Tech 19:62–70
Gaitonde VN, Manjaiah M, Maradi S, Karnik SR, Petkar MP, Davim JP (2017) Multi response optimization in WEDM of HcHcr steel by integrating response surface methodology (RSM) with differential evolution (DE). In: Davim JP (ed) Computational methods and production engineering: research and development, 1st edn. Woodhead Portugal, Portugal, pp 199–221
Dastagiri M, Rao PS, Valli PM (2018) Optimization of EDM process parameters by using heuristic approach. Mater Today Proc 5:27036–27042
Das S, Chakraborty S (2011) Selection of non-traditional machining process using analytic network process. J Manuf Syst 30:41–53
Jagadish, Bhowmik B, Ray A (2015) Prediction and optimization of process parameters of green composites in AWJM process using Response Surface Methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(5):1359–1370
Jagadish, Ray A (2014) Optimization of process parameters of green electrical discharge machining using principle component analysis (PCA). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87(5):1299–1311
Garg A, Jasmine SLL (2016) Modeling multiple-response environmental manufacturing characteristics of EDM process. J Cleaner Prod 137:1588–1601
Karande P, Chakraborty C (2012) Application of multi-objective optimization on the basis of ratio analysis (MOORA) method for materials selection. Mater Des 37:317–324
Brauers WK (2004) Optimization methods for a stakeholder society. Springer, US
Brauers WKM (2008) Multi-objective contractor’s ranking by applying the MOORA method. J Bus Econ Mgt 4:245–255
Sahu AK, Mahapatra SS, Chatterjee S, Thomas J (2018) Optimization of surface roughness by MOORA in EDM by electrode prepared via selective laser sintering process. Mater Today Proc 5:19019–19026
Muthuramalingam T, Mohan B (2013) Influence of discharge current pulse-on machinability in electrical discharge machining. Mat Manuf Proc 28(4):375–380
Sen I (2012) A study on machinability of B-modified Ti-6Al-4V alloys by EDM. Mat Manuf Proc 27(3):348–354
Kiyak M, Cakir O (2007) Examination of machining parameters on surface roughness in EDM of tool steel. J Mater Proces Tech 191(1–3):141–144
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge to Dr.S.K.Jain, Head of Mechanical Engineering Department, Ambala College of Engg and Applied Research, Mithapur, Harayana, India, for providing the necessary resources and other facilities during the research work and Also, thanks to Prof.Ishwar Chander Ramola and Prof.Narendra Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Ambala College of Engg and Applied Research, Mithapur, Ambala, Haryana, India, for his valuable guidance during experimentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagadish, Kumar, S. & Soni, D.L. Performance Analysis and Optimization of Different Electrode Materials and Dielectric Fluids on Machining of High Carbon High Chromium Steel in Electrical Discharge Machining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. A Phys. Sci. 92, 273–284 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-020-00727-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-020-00727-4