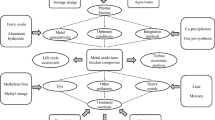
Abstract
As environmental regulations are becoming stricter, new techniques must be developed for the removal of trace concentrations of heavy metals from mineral processing effluents. Foam separation techniques are an interesting alternative to more conventional processes such as ion exchange because of their efficiency to treat dilute aqueous streams. In this paper, the simultaneous removal of Cd2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+ from dilute aqueous solutions was investigated by using sodium dodecyl sulfate as collector and triethylenetetramine as auxiliary ligand via a series of batch-mode flotation experiments. Experimental results showed that Cd2+, Mn2+, and Zn2+ can be completely removed in one step under the following conditions: pH 9.50, flotation time = 120 min, auxiliary concentration 0.1 mmol L−1, collector-to-metals molar ratio 2:1, ethanol concentration 0.5% (v/v), and a nitrogen gas flowrate set at 25 mL min−1. An excess in auxiliary ligand concentration yielded to low removal efficiency. The modeled speciation of the examined system suggested that the metals are separated from the bulk solution to the foam phase via a combination of ion flotation and precipitate flotation.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen T, Yan B, Lei C, Xiao X (2014) Pollution control and metal resource recovery for acid mine drainage. Hydrometallurgy 147–148:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2014.04.024
Azimi A, Azari A, Rezakazemi M, Ansarpour M (2017) Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: a review. ChemBioEng Rev 4:37–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201600010
Azevedo A, Oliveira HA, Rubio J (2018) Treatment and water reuse of lead-zinc sulphide ore mill wastewaters by high rate dissolved air flotation. Miner Eng 127:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.07.011
Somasundaran P (1975) Separation using foaming techniques. Sep Sci 10:93–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/00372367508057071
You-Cai Z, Zouboulis A, Matis K (1996) Flotation of molybdate oxyanions in dilute solutions. Part 1 Selective separation from arsenate. Hydrometallurgy 43:143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-386X(96)00018-7
Rubio J, Souza M, Smith R (2002) Overview of flotation as a wastewater treatment technique. Miner Eng 15:139–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(01)00216-3
Zamboulis D, Peleka EN, Lazaridis NK, Matis KA (2011) Metal ion separation and recovery from environmental sources using various flotation and sorption techniques. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2552
Pinfold T (1972) Ion flotation. In: Lemlich R (ed) Adsorptive bubble separation techniques. Academic Press, New York, pp 53–73
Grieves RB (1975) Foam separations: a review. Chem Eng J 9:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9467(75)80001-3
Sebba F (1959) Concentration by ion flotation. Nature 184:1062–1063. https://doi.org/10.1038/1841062a0
Matis KA, Mavros P (1991) Recovery of metals by ion flotation from dilute aqueous solutions. Sep Purif Rev 20:1–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602549108021407
Chang L, Cao Y, Fan G, Li C, Peng W (2019) A review of the applications of ion floatation: wastewater treatment, mineral beneficiation and hydrometallurgy. RSC Adv 9:20226–20239. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA02905B
Todd I, Distin P (1985) Precipitate flotation of nickel from acidic laterite leach solutions. Hydrometallurgy 14:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-386X(85)90041-6
Caballero M, Cela R, Perez-Bustamante J (1990) Analytical applications of some flotation techniques- a review. Talanta 37:275–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(90)80056-L
Lazaridis N, Peleka E, Karapantsios T, Matis K (2004) Copper removal from effluents by various separation techniques. Hydrometallurgy 74:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2004.03.003
Charewicz W, Walkowiak W (1972) Selective floatation of inorganic ions. Sep Sci 7:631–646. https://doi.org/10.1080/00372367208057972
Deliyanni EA, Kyzas GZ, Matis KA (2017) Various flotation techniques for metal ions removal. J Mol Liq 225:260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.11.069
Peng W, Chang L, Li P, Han G, Huang Y, Cao Y (2019) An overview on the surfactants used in ion flotation. J Mol Liq 286:110955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.110955
Doyle FM (2003) Ion flotation- its potential for hydrometallurgical operations. Int J Miner Process 72:387–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-7516(03)00113-3
Lu S, Pugh RJ, Forssberg E (2005) Interfacial separation of particles. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Eivazihollagh A, Bäckström J, Norgren M, Edlund H (2018) Electrochemical recovery of copper complexed by DTPA and C12-DTPA from aqueous solution using a membrane cell. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:1421–1431. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.55103
Doyle FM, Duyvesteyn S, Sreenivasarao K (1995) The use of ion flotation for detoxification of metal-contaminated waters and process effluents. In: Herbst JA (ed) Proceedings of the XIX International Mineral Congress, vol 4. Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, pp 176–179
Stalidis GA, Matis KA, Lazaridis NK (1989) Selective separation of Cu, Zn, and As from solution by flotation techniques. Sep Sci Technol 24:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496398908049754
Scorzelli I, Fragomeni A, Torem M (1999) Removal of cadmium from a liquid effluent by ion flotation. Miner Eng 12:905–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(99)00077-1
Ulewicz M, Walkowiak W, Jang Y, Kim JS, Bartsch RA (2003) Ion flotation of Cadmium(II) and Zinc(II) in the presence of proton-ionizable lariat ethers. Anal Chem 75:2276–2279. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac026322y
Polat H, Erdogan D (2007) Heavy metal removal from waste waters by ion flotation. J Hazard Mater 148:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.013
Yenial Ü, Bulut G (2017) Examination of flotation behavior of metal ions for process water remediation. J Mol Liq 241:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.06.011
Yenidünya MD (2006) Recovery of Zn(II), Mn(II) and Cu(II) in aqueous solutions by foam fractionation with sodium dodecyl sulphate in combination with chelating agents. Sep Sci Technol 41:1741–1756. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390600636959
Eivazihollagh A, Tejera J, Svanedal I, Edlund H, Blanco A, Norgren M (2017) Removal of Cd2+, Zn2+, and Sr2+ by ion flotation, using a surface- active derivative of DTPA (C12-DTPA). Ind Eng Chem Res 56:10605–10614. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b03100
Liu Z, Doyle FM (2001) A thermodynamic approach to ion flotation. I. Kinetics of cupric ion flotation with alkylsulfates. Colloids Surf A 178:79–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00555-0
Liu Z, Doyle FM (2001) A thermodynamic approach to ion flotation. II. Metal ion selectivity in the SDS- Cu-Ca and SDS- Cu- Pb systems. Colloids Surf A 178:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(00)00554-9
Liu Z, Doyle FM (2009) Ion flotation of Co2+, Ni2+, and Cu2+ using dodecyldiethylenetriamine (Ddien). Langmuir 25:8927–8934. https://doi.org/10.1021/la900098g
Schaider LA, Senn DB, Estes ER, Brabander DJ, Shine JP (2014) Sources and fates of heavy metals in a mining-impacted stream: temporal variability and the role of iron oxides. Sci Total Environ 490:456–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.126
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg DA (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J Occup Med Toxicol 1:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-1-22
Plum LM, Rink L, Hajo H (2010) The essential toxin: impact of zinc on human health. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7:1342–1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7041342
O’Neal SL, Zheng W (2015) Manganese toxicity upon overexposure: a decade in review. Curr Environ Health Rep 2:315–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-015-0056-x.Manganese
Doyle FM, Liu Z (2003) The effect of triethylenetetraamine (Trien) on the ion flotation of Cu2+ and Ni2+. J Colloid Interface Sci 258:396–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(02)00092-9
Dean JA (1999) Lange’s handbook of chemistry, 15th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Cho Y, Laskowski J (2002) Effect of flotation frothers on bubble size and foam stability. Int J Miner Process 64:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-7516(01)00064-3
World Health Organization (2018) A global overview of national regulations and standards for drinking- water quality. WHO CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO, Geneva.
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community’s Horizon 2020 Programme under Grant Agreement No. 812580 (MSCA- ETN SULTAN). This publication reflects only the authors’ view, exempting the Community from any liability.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was D. Panias.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xanthopoulos, P., Binnemans, K. Removal of Cadmium, Zinc, and Manganese from Dilute Aqueous Solutions by Foam Separation. J. Sustain. Metall. 7, 78–86 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00322-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00322-2