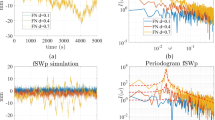
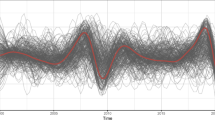
Abstract
A spatial curve dynamical model framework is adopted for functional prediction of counts in a spatiotemporal log-Gaussian Cox process model. Our spatial functional estimation approach handles both wavelet-based heterogeneity analysis in time, and spectral analysis in space. Specifically, model fitting is achieved by minimising the information divergence or relative entropy between the multiscale model underlying the data, and the corresponding candidates in the spatial spectral domain. A simulation study is carried out within the family of log-Gaussian Spatial Autoregressive \(\ell ^{2}\)-valued processes (SAR\(\ell ^{2}\) processes) to illustrate the asymptotic properties of the proposed spatial functional estimators. We apply our modelling strategy to spatiotemporal prediction of respiratory disease mortality.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alomari HM, Frías MP, Leonenko NN, Ruiz-Medina MD, Sakhno L, Torres A (2017) Asymptotic properties of parameter estimates for random fields with tapered data. Electron J Stat 11:3332–3367
Angulo JM, Ruiz-Medina MD (1997) On the orthogonal representation of generalized random fields. Stat Probab Lett 31:145–153
Baddeley A, Gregori P, Mateu J, Stoica R, Stoyan D (2006) Case Studies in Spatial Point Process Modeling. Springer, New York
Banks A, Vincent J, Anyakoha C (2007) A review of particle swarm optimization. Part I: background and development. Nat Comput 6:467–484
Bosq D, Ruiz-Medina MD (2014) Bayesian estimation in a high dimensional parameter framework. Electron J Stat 8:1604–1640
Choi KM, Serre ML, Christakos G (2003) Efficient mapping of California mortality fields at different spatial scales. J Expo Anal Environ Epidomol 13:120–133
Christakos G (1992) Random Field Models in Earth Sciences. Academic Press, San Diego
Christakos G (2000) Modern Spatiotemporal Geostatistics. Oxford University Press, New York
Chirstakos G (2017) Spatiotemporal Random Fields: Theory and Applications. Elsevier, New York
Christakos G, Bogaert P, Serre ML (2001) Temporal GIS. Springer, New York
Christakos G, Hristopulos DT (1998) Spatiotemporal Environmental Health Modelling: A Tractatus Stochasticus. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Boston
Christakos G, Olea RA (2005) New space-time perspectives on the propagation characteristics of the black death epidemic and its relation to bubonic plague. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 19:307–314
Congdon P (2017) Representing spatial dependence and spatial discontinuity in ecological epidemiology: a scale mixture approach. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 31:291–304
Cox DR (1955) Some statistical methods connected with series of events. J R Statist Soc B 17:129–164
Cronie O, Ghorbani M, Mateu J, Yu J (2020) Functional marked point processes: a natural structure to unify spatio-temporal frameworks and to analyse dependent functional data. Test. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-020-00730-2
Daley D, Vere-Jones D (2008) An Introduction to the Theory of Point Processes Vol II: General Theory and Structure 2nd Edition. Springer, New York
Daubechies I (1992) Ten Lectures on Wavelets. SIAM, Philadelphia
Diggle PJ (2013) Statistical Analysis of Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Point Patterns. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Diggle P, Guan Y, Hart A, Paize F, Stanton M (2010) Estimating individual-level risk in spatial epidemiology using spatially aggregated information on the population at risk. J Am Stat Assoc 105:1394–1402
Diggle PJ, Kaimi I, Abellana R (2010b) Partial-likelihood analysis of spatio-temporal point-process data. Biometrics 66:347–354
Diggle PJ, Moraga P, Rowlingson B, Taylor BM (2013) Spatial and spatio-temporal log-Gaussian Cox processes: Extending the Geostatistical paradigm. Stat Sci 28:542–563
Frías MP, Torres-Signes, A, Ruiz-Medina MD, Mateu, J (2020) Spatial Cox Processes in an infinite–dimensional framework. arXiv:1811.11139
Goia A, Vieu P (2016) An introduction to recent advances in high/infinite dimensional statistics. J Multivar Anal 146:1–6
Goicoa T, Ugarte MD, Etxeberria J, Militno AF (2012) Comparing CAR and P-spline models in spatial disease mapping. Environ Ecol Stat 19:573–599
Gonçalves FB, Gamerman D (2018) Exact bayesian inference in spatio-temporal Cox processes driven by multivariate Gaussian processes. J R Statist Soc B 80:157–175
González JA, Rodríguez-Cortés FJ, Cronie O, Mateu J (2016) Spatio-temporal point process statistics: A review. Spat Stat 18:505–544
Grandell J (1976) Doubly Stochastic Process. Springer, New York
Guan Y (2006) A composite likelihood approach in fitting spatial point process models. J Am Stat Assoc 101:1502–1512
He J, Chen G, Jiang Y, Jin R, Shortridge A, Agusti S, He M, Wu J, Duarte CM, Christakos G (2020) Comparative infection modeling and control of COVID-19 transmission patterns in China, South Korea, Italy and Iran. Sci Total Environ 747:141447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141447
Horváth L, Kokoszka P (2012) Inference for Functional Data with Applications. Springer, New York
Illian J, Penttinen A, Stoyan H, Stoyan D (2008) Statistical Analysis and Modelling of Spatial Point Patterns. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Jalilian A, Guan Y, Waagepetersen R (2019) Orthogonal series estimation of the pair correlation function of a spatial point process. Stat Sin 29:769–787
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks 4:1942–1948
Li Y, Brown P, Gesink DC, Rue H (2012) Log gaussian Cox processes and spatially aggregated disease incidence data. Stat Methods Med Res 21:479–507
Li L, Wang J, Cao Z, Zhong E (2008) An information-fusion method to identify pattern of spatial heterogeneity for improving the accuracy of estimation. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 22:689–704
Lindgren F, Rue H (2015) Bayesian spatial modelling with R-INLA. J Stat Softw 63:1–25
Maniglia S (2004) Gaussian measures on separable Hilbert spaces and applications. Quaderni di Matematica 1: ISBN 88-8305-010 e-ISBN 88-8305-011-8
Marinucci D, Peccati G (2011) Random fields on the sphere. Representation, limit theorems and cosmological applications. London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series 389. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Møller J, Syversveen AR, Waagepetersen R (1998) Log Gaussian Cox processes. Scand J Stat 25:451–482
Møller J, Toftaker H (2014) Geometric anisotropic spatial point pattern analysis and Cox processes. Scand J Stat 41:414–435
Møller J, Waagepetersen RP (2004) Statistical Inference and Simulation for Spatial Point Processes. Chapman & Hall, London, Boca Raton
Müller HG, Stadtmüller U (2005) Generalized functional linear models. Ann Statist 33:774–805
Ogata Y, Katsura K (1988) Likelihood analysis of spatial inhomogeneity for marked point patterns. Ann I Stat Math 40:29–39
Panaretos VM, Tavakoli S (2013a) Fourier analysis of stationary time series in function space. Ann Stat 41:568–603
Panaretos VM, Tavakoli S (2013) Cramér-Karhunen-Loéve representation and harmonic principal component analysis of functional time series. Stoch Proc Appl 123:2779–2807
Rathbun SL, Cressie N (1994) A space-time survival point process for a longleaf pine forest in Southern Georgia. J Am Stat Assoc 89:1164–1174
Rue H, Martino S, Chopin N (2009) Approximate bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J R Stat Soc Ser B 71:319–392
Ruiz-Medina MD (2011) Spatial autorregresive and moving average Hilbertian processes. J Multiv Anal 102:292–305
Ruiz-Medina MD (2012) Spatial functional prediction from Spatial Autoregressive Hilbertian Processes. Environmetrics 23:119–128
Ruiz-Medina MD, Angulo JM (2002) Spatio-temporal filtering using wavelets. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 16:241–266
Salap-Ayca S, Jankowski P (2018) Analysis of the influence of parameter and scale uncertainties on a local multi-criteria land use evaluation model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32:2699–2719
Serra L, Saez M, Mateu J, Varga D, Juan P, Díaz-Ávalos C, Rue H (2014) Spatio-temporal log-Gaussian Cox processes for modelling wildfire occurrence: the case of Catalonia 1994–2008. Environ Ecol Stat 21:531–563
Simpson D, Illian JB, Lindgren F, Sorbye SH, Rue H (2016) Going off grid: computationally efficient inference for log-Gaussian Cox processes. Biometrika 103:49–70
Taylor BM, Andrade-Pacheco R, Sturrock HJ (2018) Continuous inference for aggregated point process data. J R Stat Soc A 181:1125–1150
Torres A, Frías MP, Ruiz-Medina MD (2016) Log-Gaussian Cox processes in infinite-dimensional spaces. Theor Prob Math Stat 95:157–177
Vicente G, Goicoa T, Ugarte MD (2020) Bayesian inference in multivariate spatio-temporal areal models using INLA: analysis of gender-based violence in small areas. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 34:1421–1440
Waagepetersen R, Guan DY, Jalilian A, Mateu J (2016) Analysis of multispecies point patterns by using multivariate log-Gaussian Cox processes. J R Stat Soc C 65:77–96
Waller LA, Carlin BP, Xia H, Gelfand AE (1997) Hierarchical spatio-temporal mapping of disease rates. J Am Stat Assoc 92:607–617
Wu S, Müller HG, Zhang Z (2013) Functional data analysis for point processes with rare events. Stat Sin 23:1–23
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by MCIU/AEI/ERDF, UE grant PGC2018-099549-B-I00 (M.D. Ruiz–Medina, M.P. Frías, A. Torres-Signes), PID2019-107392RB-100 (J. Mateu), and by Grant A-FQM-345-UGR18 (M.D. Ruiz–Medina, M.P. Frías, A. Torres-Signes) cofinanced by ERDF Operational Programme 2014–2020 and the Economy and Knowledge Council of the Regional Government of Andalusia, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres-Signes, A., Frías, M.P., Mateu, J. et al. A spatial functional count model for heterogeneity analysis in time. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 35, 1825–1849 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01951-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01951-5