Abstract
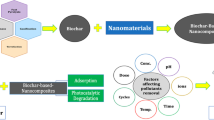
This paper highlights the efficient adsorption of Cr (VI) from wastewater using polyacrylonitrile (PAN)/montmorillonite (Mt) and polyacrylonitrile/zinc oxide nanoparticle-modified montmorillonite (ZnO-Mt) nanofibrous nanocomposites as adsorbents. Mt was modified using zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO) by an adsorption process. The particle size of ZnO-Mt was found to be 18 ± 2 nm. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images showed the presence of ZnO on and within the layers of Mt. Mt and ZnO-Mt were used to prepare PAN/clay nanofibrous nanocomposites which were further used as adsorbents for Cr (VI) ions. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis showed that Mt and ZnO-Mt were exfoliated in the PAN nanofibrous matrix. Mt, ZnO-Mt, PAN/Mt and PAN/ZnO-Mt nanofibrous nanocomposites were analyzed as adsorbents for the adsorption of Cr (VI) ions. The effect of pH, concentration, time and amount of adsorbent on the removal of Cr (VI) ions from water were investigated. Adsorption of Cr (VI) ions over the adsorbents follows pseudo-second-order kinetics, and Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. PAN/ZnO-Mt and PAN/Mt nanofibrous nanocomposites were found to be more effective adsorbents for Cr (VI) ions compared to ZnO-Mt and Mt.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang G, Hua Y, Su X et al (2016) Cr(VI) adsorption by montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl Clay Sci 124–125:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.02.008
Upadhyay RK, Soin N, Roy SS (2013) Role of graphene/metal oxide composites as photocatalysts, adsorbents and disinfectants in water treatment: a review. RSC Advances 4:3823–3851. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA45013A
Ngwenya N, Ncube EJ, Parsons J (2013) Recent Advances in Drinking Water Disinfection: Successes and Challenges. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 222:111–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4717-7_4
Ahmad M, Zhang B, Wang J et al (2019) New method for hydrogel synthesis from diphenylcarbazide chitosan for selective copper removal. Int J Biol Macromol 136:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.084
Yi J, Li Y, Yang L, Zhang LM (2019) Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of Cu2+ and methylene blue to casein hydrogels. J Polym Res 26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1870-x
Li L, Wang Z, Ma P et al (2015) Preparation of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan hydrogel compounded with graphene oxide to enhance the adsorption properties for Cu(II) in aqueous solution. J Polym Res 22:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0794-3
Li T, Liu X, Li L, et al (2019) Polydopamine-functionalized graphene oxide compounded with polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan hydrogels on the recyclable adsorption of cu(II), Pb(II) and cd(II) from aqueous solution. J Polym Res 26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1971-6
Manzoor K, Ahmad M, Ahmad S, Ikram S (2019a) Synthesis, Characterization, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics of EDTA-Modified Chitosan-Carboxymethyl Cellulose as Cu(II) Ion Adsorbent. ACS Omega 4:17425–17437. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02214
Manzoor K, Ahmad M, Ahmad S, Ikram S (2019b) Removal of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii) from wastewater using arginine cross-linked chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose beads as green adsorbent. RSC Advances 9:7890–7902. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00356H
Cheng R, Ou S, Xiang B et al (2009) Adsorption behavior of hexavalent chromium on synthesized ethylenediamine modified starch. J Polym Res 16:703–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-009-9276-9
Li P, Dai X, Yan Q, et al (2020) A novel modification method for polystyrene microspheres with dithizone and the adsorption properties for Pb2+. J Polym Res 27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02180-8
Haddad MY, Alharbi HF (2019) Enhancement of heavy metal ion adsorption using electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers loaded with ZnO nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 136. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47209
Cai J, Lei M, Zhang Q et al (2017) Composites: Part A Electrospun composite nanofiber mats of Cellulose@Organically modified montmorillonite for heavy metal ion removal: Design, characterization, evaluation of absorption performance. Compos A 92:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.10.034
sen Gupta S, Bhattacharyya KG, (2012) Adsorption of heavy metals on kaolinite and montmorillonite: a review. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:6698. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp40093f
Uddin MK (2017) A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem Eng J 308:438–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.029
Wang Y, Zhao X, Duan L et al (2015) Structure, luminescence and photocatalytic activity of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by auto combustion method. Mater Sci Semicond Process 29:372–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.07.034
Deng Z, Chen M, Gu A, Wu L (2008) A facile method to fabricate ZnO hollow spheres and their photocatalytic property. J Phys Chem B 112:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp077662w
Rezapour M, Talebian N (2011) Comparison of structural, optical properties and photocatalytic activity of ZnO with different morphologies: Effect of synthesis methods and reaction media. Mater Chem Phys 129:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.04.012
Akkari M, Aranda P, ben Rhaiem H, et al (2016) ZnO/clay nanoarchitectures: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation as photocatalysts. Appl Clay Sci 131:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.12.013
Yang SJ, Park CR (2008) Facile preparation of monodisperse ZnO quantum dots with high quality photoluminescence characteristics. Nanotechnol 19. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/03/035609
Talebian N, Amininezhad SM, Doudi M (2013) Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their morphology-dependent antibacterial and optical properties. J Photochem Photobiol, B 120:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.01.004
Yamamoto O (2001) Influence of particle size on the antibacterial activity of zinc oxide. Int J Inorg Mater 3:643–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1466-6049(01)00197-0
Raghupathi KR, Koodali RT, Manna AC (2011) Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:4020–4028. https://doi.org/10.1021/la104825u
Zarrindokht Emami-Karvani (2012) Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Afr J Microbiol Res 5. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR10.159
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A et al (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett 7:219–242
Upadhyaya L, Singh J, Agarwal V, et al (2014) In situ grafted nanostructured ZnO/carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposites for efficient delivery of curcumin to cancer. J Polym Res 21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0550-0
Upadhyaya L, Singh J, Agarwal V et al (2015) Efficient water soluble nanostructured ZnO grafted O-carboxymethyl chitosan/curcumin-nanocomposite for cancer therapy. Process Biochem 50:678–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.12.029
Dimapilis EAS, Hsu C-S, Mendoza RMO, Lu M-C (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for water disinfection. Sustain Environ Res 28:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SERJ.2017.10.001
Ong CB, Ng LY, Mohammad AW (2018) A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:536–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2017.08.020
Kumar JP, Ramacharyulu PVRK, Prasad GK, Singh B (2015) Montmorillonites supported with metal oxide nanoparticles for decontamination of sulfur mustard. Appl Clay Sci 116–117:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.04.007
Sani HA, Ahmad MB, Hussein MZ et al (2017) Nanocomposite of ZnO with montmorillonite for removal of lead and copper ions from aqueous solutions. Process Saf Environ Prot 109:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.03.024
Bel Hadjltaief H, ben Ameur S, da Costa P, et al (2018) Photocatalytic decolorization of cationic and anionic dyes over ZnO nanoparticle immobilized on natural Tunisian clay. Appl Clay Sci 152:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.008
Akkari M, Aranda P, Belver C et al (2018) ZnO/sepiolite heterostructured materials for solar photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals in wastewater. Appl Clay Sci 156:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.01.021
Unuabonah EI, Taubert A (2014) Clay–polymer nanocomposites (CPNs): Adsorbents of the future for water treatment. Appl Clay Sci 99:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2014.06.016
Patel S, Hota G (2016) Iron oxide nanoparticle-immobilized PAN nanofibers: synthesis and adsorption studies. RSC Advances 6:15402–15414. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA20345G
Hallaji H, Keshtkar AR, Moosavian MA (2015) A novel electrospun PVA/ZnO nanofiber adsorbent for U(VI), Cu(II) and Ni(II) removal from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 46:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.09.007
Kampalanonwat P, Supaphol P (2010) Preparation and adsorption behavior of aminated electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats for heavy metal ion removal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:3619–3627. https://doi.org/10.1021/am1008024
Makaremi M, Lim CX, Pasbakhsh P et al (2016) Electrospun functionalized polyacrylonitrile-chitosan Bi-layer membranes for water filtration applications. RSC Advances 6:53882–53893. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra05942b
Bode-Aluko CA, Pereao O, Ndayambaje G, Petrik L (2017) Adsorption of Toxic Metals on Modified Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibres: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3222-3
Purwar R, Goutham KS, Srivastava CM (2016) Electrospun Sericin/PVA/Clay Nanofibrous Mats for Antimicrobial Air Filtration Mask. Fibers Polym 17:1206–1216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6345-7
Kumar A, Prasad B, Mishra IM (2008) Adsorptive removal of acrylonitrile by commercial grade activated carbon: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 152:589–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.048
Kahraman HT, Yar A, Avcı A, Pehlivan E (2018) Preparation of nanoclay incorporated PAN fibers by electrospinning technique and its application for oil and organic solvent absorption. Sep Sci Technol (Philadelphia) 53:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2017.1384018
Li L, Li Y, Cao L, Yang C (2015) Enhanced chromium (VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohyd Polym 125:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.02.037
Parlayıcı Ş, Yar A, Pehlivan E, Avcı A (2019) ZnO-TiO2 doped polyacrylonitrile nano fiber-Mat for elimination of Cr (VI) from polluted water. J Anal Sci Technol 10:0–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-019-0183-3
Pradhan D, Sukla LB, Mishra BB, Devi N (2019) Biosorption for removal of hexavalent chromium using microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J Clean Prod 209:617–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.288jornal
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M et al (2003) Adsorption of heavy metals on Na-montmorillonite. Effect of pH and organic substances. Water Res 37:1619–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00524-9
El-Bayaa AA, Badawy NA, AlKhalik EA (2009) Effect of ionic strength on the adsorption of copper and chromium ions by vermiculite pure clay mineral. J Hazard Mater 170:1204–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2009.05.100
Anirudhan TS, Ramachandran M (2008) Synthesis and Characterization of Amidoximated Polyacrylonitrile/Organobentonite Composite for Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions and Industry Wastewaters. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:6175–6184. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie070735d
Şölener M, Tunali S, Özcan AS et al (2008) Adsorption characteristics of lead(II) ions onto the clay/poly(methoxyethyl)acrylamide (PMEA) composite from aqueous solutions. Desalination 223:308–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2007.01.221
Dinari M, Haghighi A (2018) Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of nanocomposites based on aromatic polyamide and modified ZnO nanoparticle for removal of toxic Cr(VI) from water. Ultrason Sonochem 41:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.09.023
Tangaromsuk J, Pokethitiyook P, Kruatrachue M, Upatham ES (2002) Cadmium biosorption by Sphingomonas paucimobilis biomass. Biores Technol 85:103–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00066-4
Bhattacharyya KG, Gupta S, sen, (2006) Adsorption of chromium(VI) from water by clays. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:7232–7240. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060586j
Khan TA, Nazir M, Ali I, Kumar A (2017) Removal of Chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using guar gum–nano zinc oxide biocomposite adsorbent. Arabian J Chem 10:S2388–S2398. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ARABJC.2013.08.019
Singh S, Barick KC, Bahadur D (2013) Functional oxide nanomaterials and nanocomposites for the removal of heavy metals and dyes. Nanomater Nanotechnol 3:1–19. https://doi.org/10.5772/57237
Zhao Y, Qi W, Chen G et al (2015) Behavior of Cr(VI) removal from wastewater by adsorption onto HCl activated Akadama clay. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 50:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.12.016
Akar ST, Yetimoglu Y, Gedikbey T (2009) Removal of chromium (VI) ions from aqueous solutions by using Turkish montmorillonite clay: effect of activation and modification. Desalination 244:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.04.040
Recillas S, Colón J, Casals E et al (2010) Chromium VI adsorption on cerium oxide nanoparticles and morphology changes during the process. J Hazard Mater 184:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.052
Kummer G, Schonhart C, Fernandes MG et al (2018) Development of Nanofibers Composed of Chitosan/Nylon 6 and Tannin/Nylon 6 for Effective Adsorption of Cr(VI). J Polym Environ 26:4073–4084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1281-9
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge the financial support received from the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India (EMR/2017/002833).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, P., Purwar, R. Polyacrylonitrile/clay nanofibrous nanocomposites for efficient adsorption of Cr (VI) ions. J Polym Res 28, 7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02362-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02362-4